cca100004-od-BOT_B003064-008-i.jpg from: https://tcmb.culture.tw/zh-tw/detail?indexCode=online_metadata&id=22504
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the
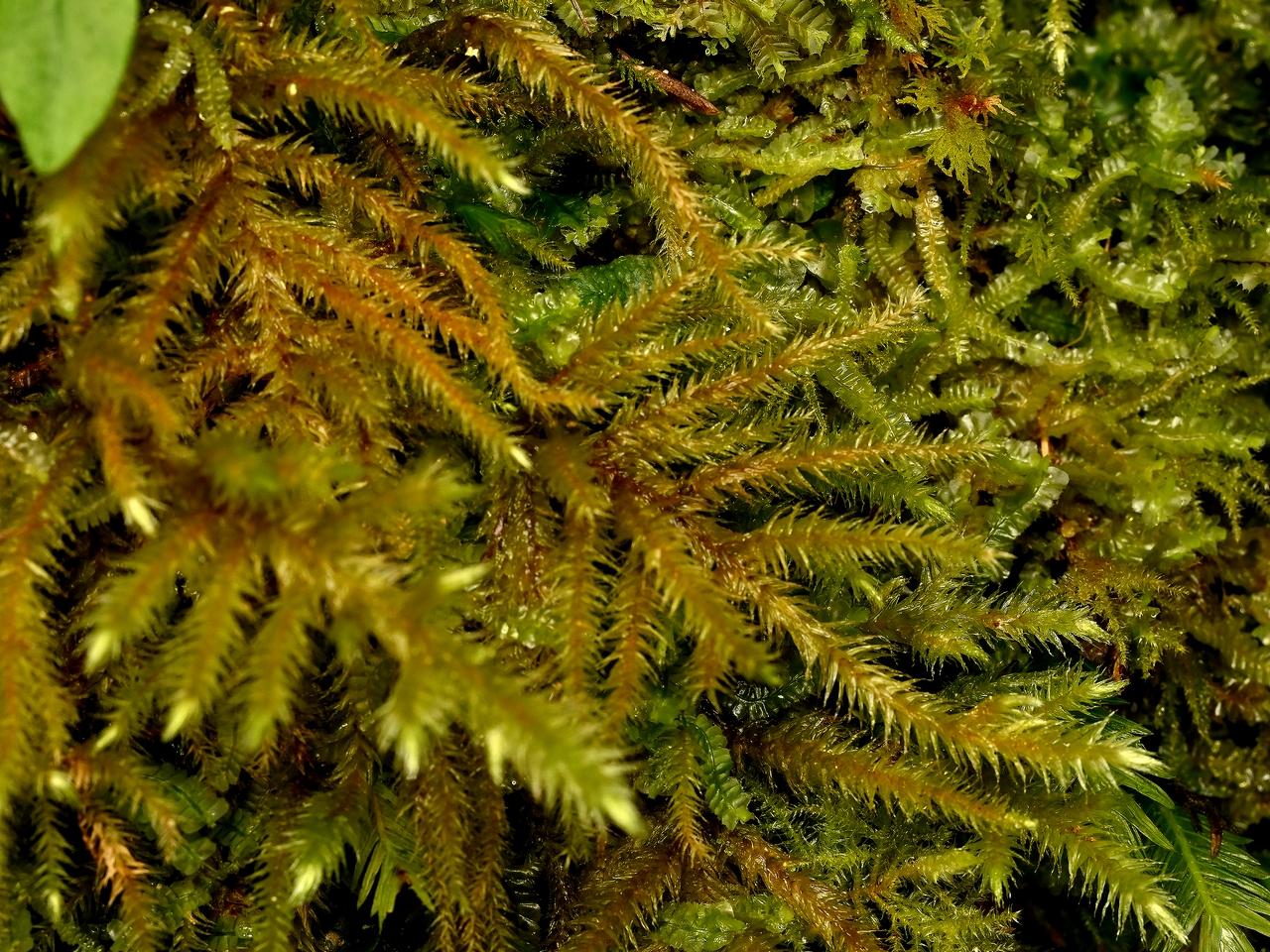

matsumuragoke221206_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2022/

b9d6992aea77281018dc335e7b426753.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/1088
Duthiella rigida Broth. moss, commonly known as Duthiella. This unassuming yet remarkable plant belongs to the Meteoriaceae family and has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Duthiella rigida Broth., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.

Duthiella-speciosissima07L.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Duthiella speciosissima/Duthiella_speciosissima.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
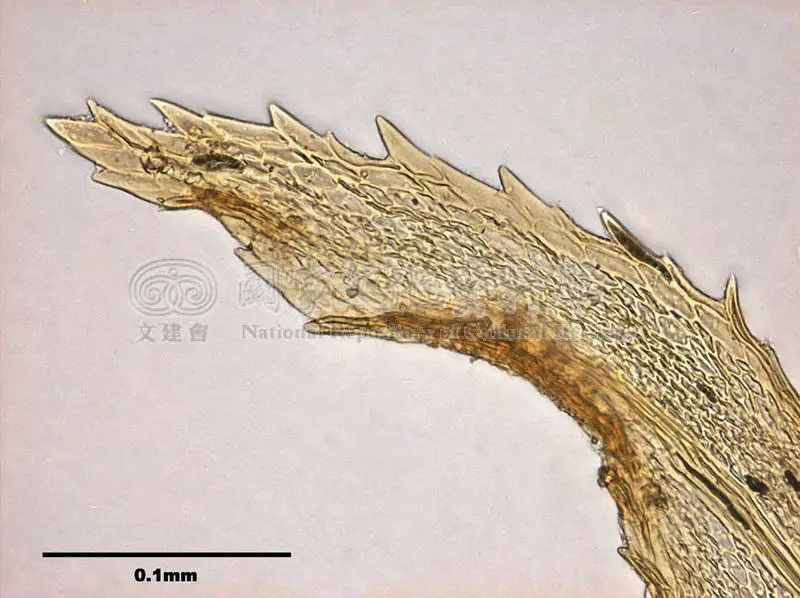
Duthiella rigida Broth. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are erect, and the leaves are rigid, lanceolate, and keeled, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. The leaf margins are entire, and the leaf cells are elongated and smooth. When mature, the moss produces capsules on short setae, which are the spore-bearing structures.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Duthiella is widely distributed across various regions, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded rock surfaces to tree bark and soil. This moss is particularly well-adapted to humid, tropical, and subtropical environments, where it can often be found growing on tree trunks, branches, and even on rocks in forested areas.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Duthiella rigida Broth. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps in the colonization of bare surfaces, contributing to soil formation and providing a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss acts as a natural sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps regulate the local microclimate and prevent soil erosion.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Duthiella is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture becomes available, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a tropical rainforest in Costa Rica, researchers discovered that Duthiella rigida Broth. played a crucial role in the epiphytic community (plants growing on other plants). The moss provided a suitable substrate for other epiphytic species, such as orchids and ferns, to establish themselves, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Meteoriaceae |
| Genus | Duthiella |
| Species | Duthiella rigida Broth. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, keeled, with a midrib |
| Leaf Margin | Entire |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Capsules | Produced on short setae |
Conclusion
Duthiella rigida Broth., a remarkable moss species, exemplifies the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, Duthiella serves as a reminder of the importance of preserving and protecting these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems. Perhaps the next time you encounter a cushion-like mat of moss, you’ll pause and wonder if it’s the remarkable Duthiella rigida Broth., a true marvel of nature’s engineering.