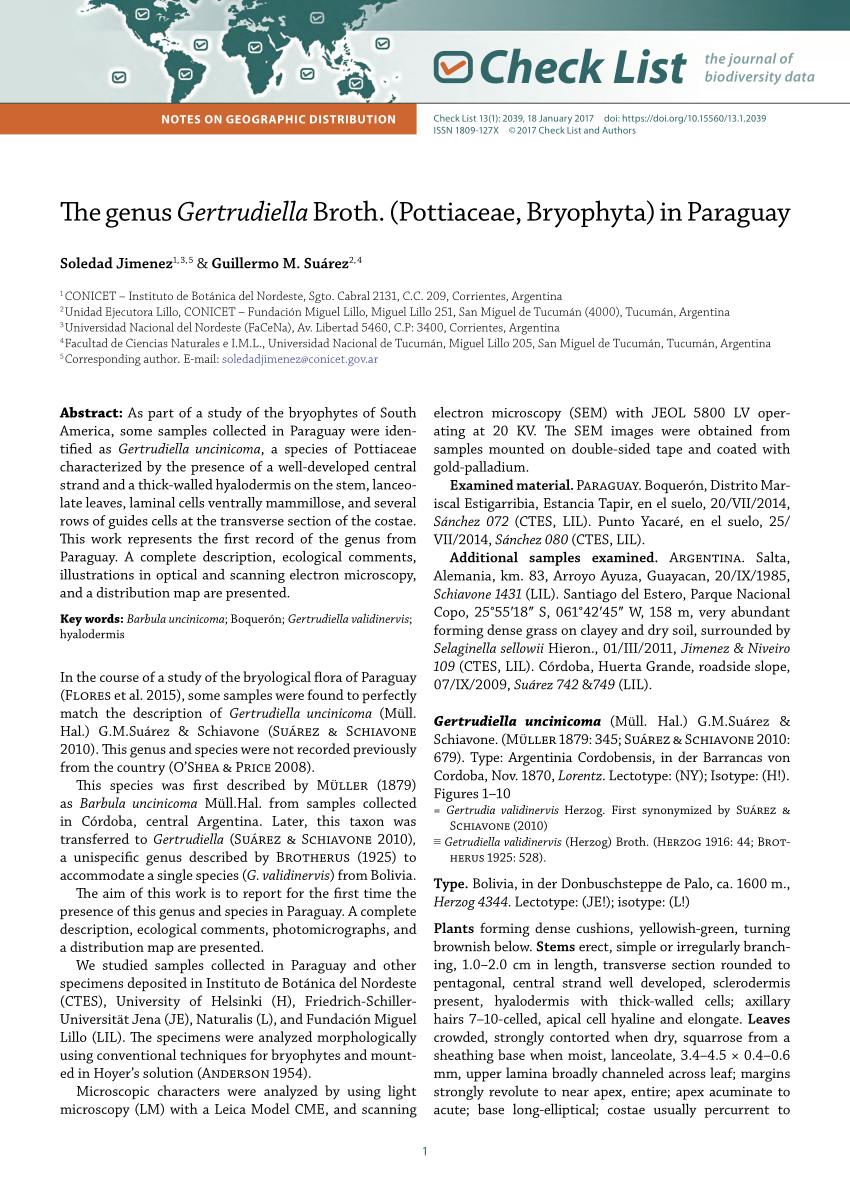
largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264086914_Gertrudiella_validinervis_Herz_Broth_Pottiaceae_Musci_un_nuevo_registro_para_la_flora_briologica_de_Argentina
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of Gertrudiella validinervis (Herzog) Broth., a captivating moss species from the Pottiaceae family. Also known simply as Gertrudiella, this tiny plant has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Gertrudiella validinervis, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide. Despite their diminutive size, they contribute significantly to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Gertrudiella validinervis

d7ed39c024675bbf3fd0017ade44b87f.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/50ac8e12d5d165847a5efd2c2ebc025c
is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate

UCSB047057.jpg from: https://macroalgae.org/portal/collections/individual/index.php?occid=990237
, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-point. The leaf margins are entire (smooth), and the cells are elongate and smooth-walled. When mature, the moss produces capsules on short setae (stalks), which are erect and

Slide431.jpg from: https://bobklips.com/goblet-moss/
cylindrical.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This fascinating moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including North America, South America, Europe, Asia

Brothera_leana02_031018L.jpg from: https://www.digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Brothera leana/Brothera_leana1.html
, and Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from disturbed areas and roadsides to rock outcrops and soil banks. Gertrudiella validinervis is particularly well-adapted to dry, exposed, and nutrient-poor environments, making it a true survivor in harsh conditions.

9ba13f0e2f7c85270bd4a461f07e9870.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/066f8adbf1dc27f5f7041c6008ed3bb8
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small stature, Gertrudiella validinervis plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, acting as a pioneer species in disturbed areas. Additionally, its dense tufts provide microhabitats for various invertebrates and serve as a moisture reservoir in arid environments.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Gertrudiella validinervis is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in areas where other plants might struggle.
Case Studies/Examples
img from: https://checklist.pensoft.net/article/19641/
In a recent study conducted in the Mojave Desert, researchers found that Gertrudiella validinervis played a crucial role in stabilizing soil and facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas. Its presence helped create favorable conditions for seedling germination and growth, contributing to the overall ecosystem recovery.

GH0002493_lg.jpg from: https://macroalgae.org/portal/collections/individual/index.php?occid=660442
Technical Table

000000001169_CnhAMJU.jpg from: https://www.zeroplants.com/shopdetail/000000001169/

JL-Moss-1000.jpg from: https://blog.garnetcommunity.org.uk/category/summary-for-non-specialists/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Gertrudiella |
| Species | validinervis |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire (smooth) |
| Leaf Cells | Elongate, smooth-walled |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf apex as a hair-point |
| Capsules | Erect, cylindrical |
Conclusion
Gertrudiella validinervis (Herzog) Broth., a remarkable moss species, has proven its resilience and ecological significance time and again. From its ability to thrive in harsh environments to its role in soil stabilization and ecosystem recovery, this tiny plant deserves our admiration and respect. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, Gertrudiella validinervis serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and adaptability found in nature’s smallest wonders.
Ponder this: How can our understanding of species like Gertrudiella validinervis inspire us to appreciate and protect the often-overlooked members of our ecosystems?