
image from: https://www.bunnings.com.au/diy-advice/garden/planting-and-growing/planting-growing-and-pruning-grevilleas
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the world of Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt., a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Pilotrichaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lepidopilum, this unassuming plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered by enthusiasts and nature lovers alike.
Background

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280989042_Taxonomic_Revision_of_the_Moss_Genus_Lepidopilidium_Pilotrichaceae
Before we delve into the intricacies of Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt., it’s essential to understand its place within the grand scheme of things. This moss is a member of the Bryophyta division, which encompasses a diverse array of non-vascular plants commonly known as bryophytes. Within this division, Lepidopilum falls under the class Bryopsida, a group that includes the true mosses.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt.

image from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/myuriumhebridarumlepidopilumfontanum–312578030356897895/
is a true masterpiece of nature, with its delicate fronds and intricate structures. This moss boasts a
image from: https://www.europeana.eu/de/item/841/NHMUKXBOTXBM000722897
pleurocarpous growth habit, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its leaves are
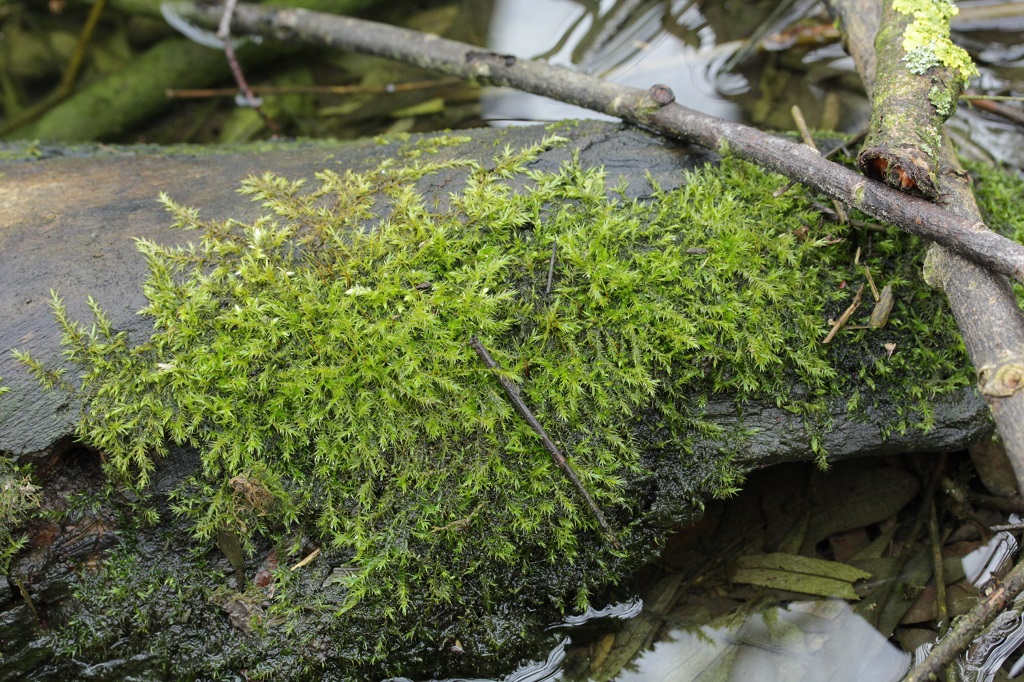

image from: https://natl.ifas.ufl.edu/biota/moss.php
ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive acuminate apex and a costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf tip.
One of the most striking features of Lepidopilum is its alar cells
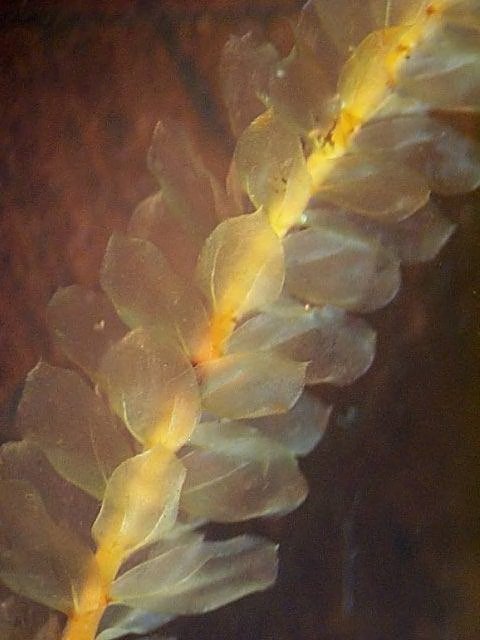

image from: https://popmicrosoftnueva.blogspot.com/2020/01/musgos-pleurocarpicos-hypnales.html
, which are specialized cells located at the base of the leaves. These cells are inflated

image from: http://plantspedia.wikia.com/wiki/IUCN_Red_List_critically_endangered_species
and often colored

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Some-mosses-in-Mt-Kalatungan-Range-Natural-Park-A-Pogonatum-macrophyllum-Dozy-Molk_fig6_326770986
, adding a touch of vibrancy to the overall appearance of the moss.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt. is a widely distributed species, found across various regions of the world. It thrives in tropical and subtropical areas, often inhabiting moist and shaded environments such as rainforests, cloud forests, and montane forests. This moss is particularly fond of growing on tree trunks, logs, and rocks, where it can access the necessary moisture and nutrients.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt. plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a bryophyte, it contributes to the overall biodiversity and serves as a vital component of the forest floor community. Additionally, this moss acts as a pioneer species, colonizing disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lepidopilum is its ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive in harsh environments and quickly resume its metabolic activities when conditions improve.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Ecuadorian Andes, researchers discovered that Lepidopilum grevilleanum Mitt. played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture balance and nutrient cycling within the cloud forest ecosystem. The moss’s ability to absorb and retain water contributed to the overall health and resilience of the forest.
Technical Table

image from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/1578979
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Division
 image from: https://moonmoths.blogspot.com/2011/04/melin-mynach-epiphytes.html |
Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Pilotrichaceae |
| Genus | Lepidopilum |
| Species | grevilleanum Mitt. |
| Growth Habit | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Acuminate |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf tip |
| Alar Cells | Inflated, often colored |