
24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_fig2_270427958
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Leucoloma zeyheri (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger

Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B_fig9_331675612
. Belonging to the Dicranaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Leucoloma. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this remarkable plant and explore its intricate world.
Background
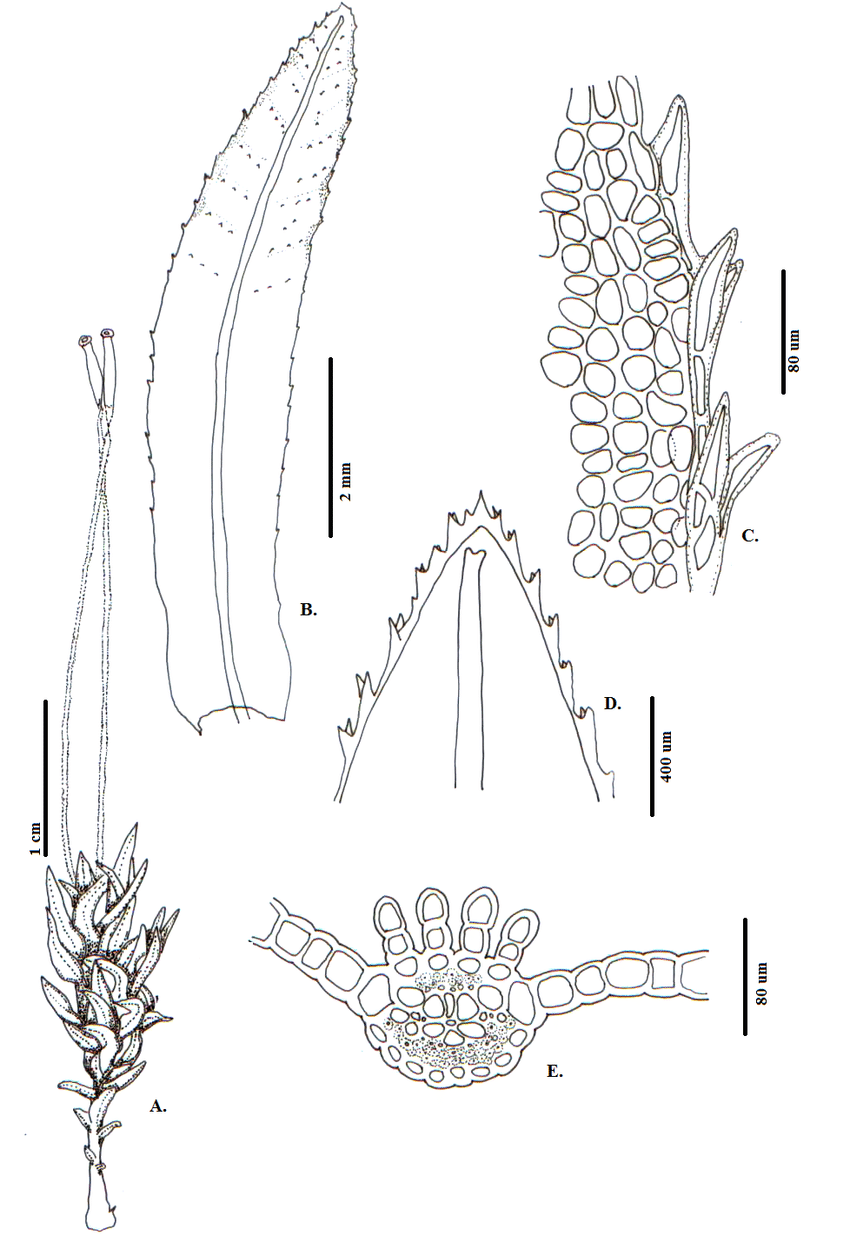
Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_fig1_318217800
Before delving into the specifics of Leucoloma zeyheri, it’s essential to understand the broader context of
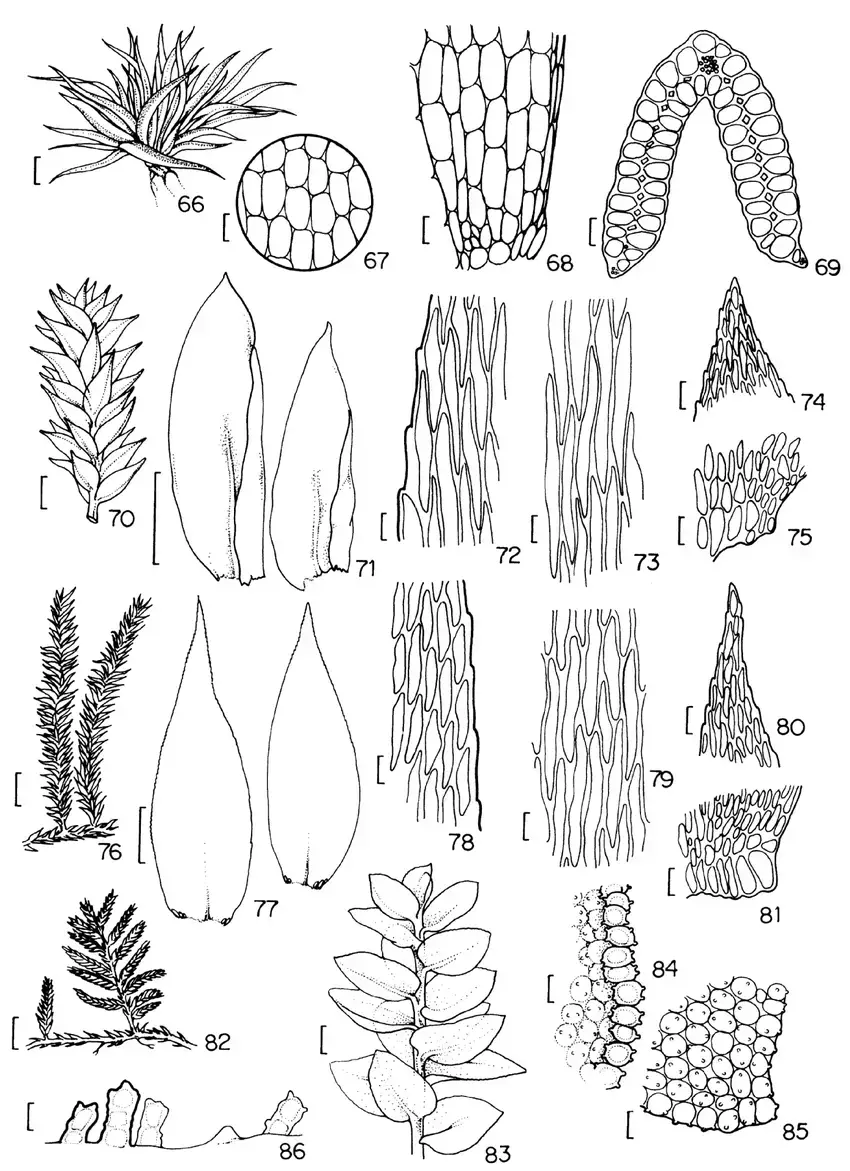
Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-66-69-Leucophanes-molleri-Muell-Hal-66-Aspecto-geral-do-gametofito-67_fig5_240765931
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Leucoloma zeyheri is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like structure. This characteristic feature, known as the hair-point, is a key identifier for this species.
The sporophytes of Leucoloma zeyheri are also quite distinctive. The seta (the stalk that supports the capsule) is reddish-brown in color, and the capsule itself is erect and cylindrical. When mature, the capsule opens via a terminal lid, releasing the spores that will eventually give rise to new moss plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Leucoloma zeyheri is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Africa, Asia, Australia, and South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from tropical rainforests to temperate woodlands, and can be found growing on tree trunks, rocks, and

a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914
soil.
This moss species is particularly well-adapted to humid and shaded environments, where it can take advantage of the moisture and protection provided by the canopy. However, it also exhibits remarkable resilience and can survive in drier conditions by entering a state of

bryologie2022v43a10-visuel.jpg from: https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/en/periodiques/bryologie/43/10
dormancy until favorable conditions return.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Leucoloma zeyheri plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps to stabilize and enrich the soil, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Leucoloma zeyheri is its ability to desiccate and rehydrate rapidly. During dry periods, the moss can lose up to 97% of its water content without suffering permanent damage. When moisture returns, it can quickly rehydrate and resume its metabolic activities, a remarkable feat of resilience.
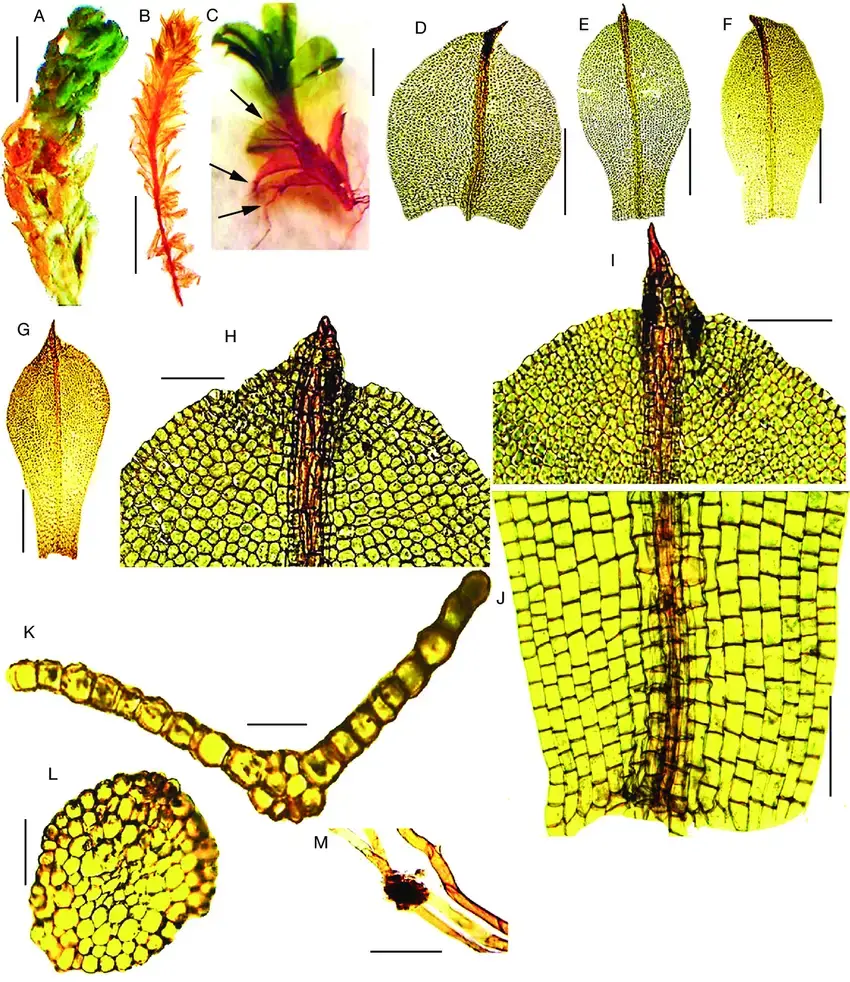
Leptophascum-leptophyllum-MuellHal-JGuerra-MJCano-A-dry-plant-B-wet-plant.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Leptophascum-leptophyllum-MuellHal-JGuerra-MJCano-A-dry-plant-B-wet-plant_fig2_339071342
Case Study: Leucoloma zeyheri in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest
A recent study conducted in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest highlighted the importance of Leucoloma zeyheri in this biodiversity hotspot. Researchers found that this moss species played a crucial role in nutrient cycling and water retention, contributing to the overall health and productivity of the forest ecosystem.
Furthermore, the study revealed that Leucoloma zeyheri served as a habitat for a diverse array of microorganisms, including fungi and bacteria. This symbiotic relationship not only benefits the moss but also contributes to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Technical Table

native.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/8175540
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Genus | Leucoloma |
| Species | zeyheri |
Growth Form
 24-Acrocarpic-mosses-of-Chapada-das-Mesas-National-Park-15-Leucoloma-tortellum-Mitt.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-Acrocarpic-mosses-of-Chapada-das-Mesas-National-Park-15-Leucoloma-tortellum-Mitt_fig6_328697430 |
Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with a hair-point |
Seta Color
 ea618f0f725517b65e1c9ace47ea3f44.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8574 |
Reddish-brown |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical |
| Spore Release | Terminal lid |
| Habitat | Tree trunks, rocks, soil (humid, shaded) |
| Distribution | Africa, Asia, Australia, South America |
Conclusion
The Leucoloma zeyheri (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss, or simply Leucoloma, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this tiny bryophyte plays a vital role in various ecosystems, contributing to soil stabilization, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us not overlook the importance of these often-overlooked organisms. Who knows what other secrets and marvels await discovery in the intricate world of mosses?
Thought-provoking question: Can the study of bryophytes like Leucoloma zeyheri provide insights into developing more sustainable and resilient agricultural practices?