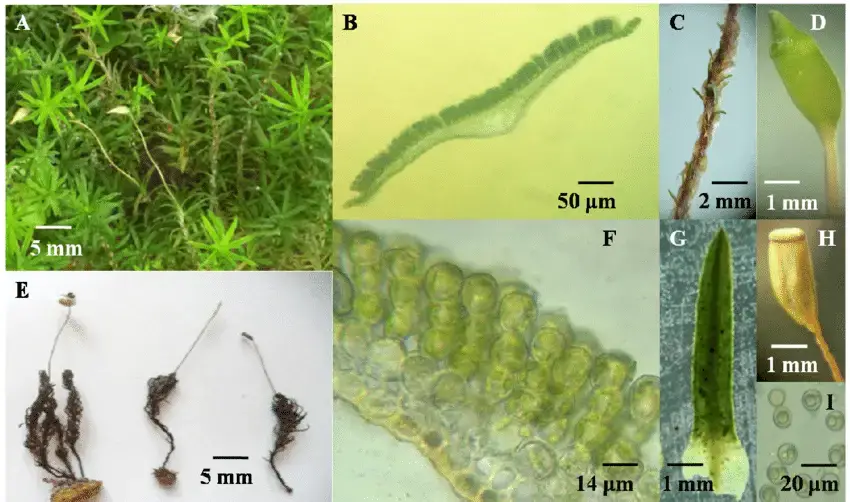

Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-subtortile-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-A-female-gametophytes-with-sporophytes-B_fig9_331675612
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Leucoloma dichelymoides (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger. Belonging to the Dicranaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Leucoloma. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this remarkable plant and explore its intricate world.
Background

Hypnodontopsis-pilifer-J-P-Frahm-from-SIZK-K-5943-habit_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/24-Isopterygium-minutirameum-Muell-Hal-A-Jaeger-from-SIZK-K-3178-stems-with_fig2_270427958
Before delving into the specifics of Leucoloma dichelymoides, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Leucoloma dichelymoides is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are erect, and the leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. The leaves themselves are narrow, lanceolate, and often curved or falcate, with a distinctive midrib running along their length.
One of the most striking features of Leucoloma dichelymoides is its sporophyte, which consists of a slender seta (stalk) topped by a curved, cylindrical capsule. This capsule is often referred to as the “urn,” and it houses the spores that are essential for the moss’s reproduction and dispersal.
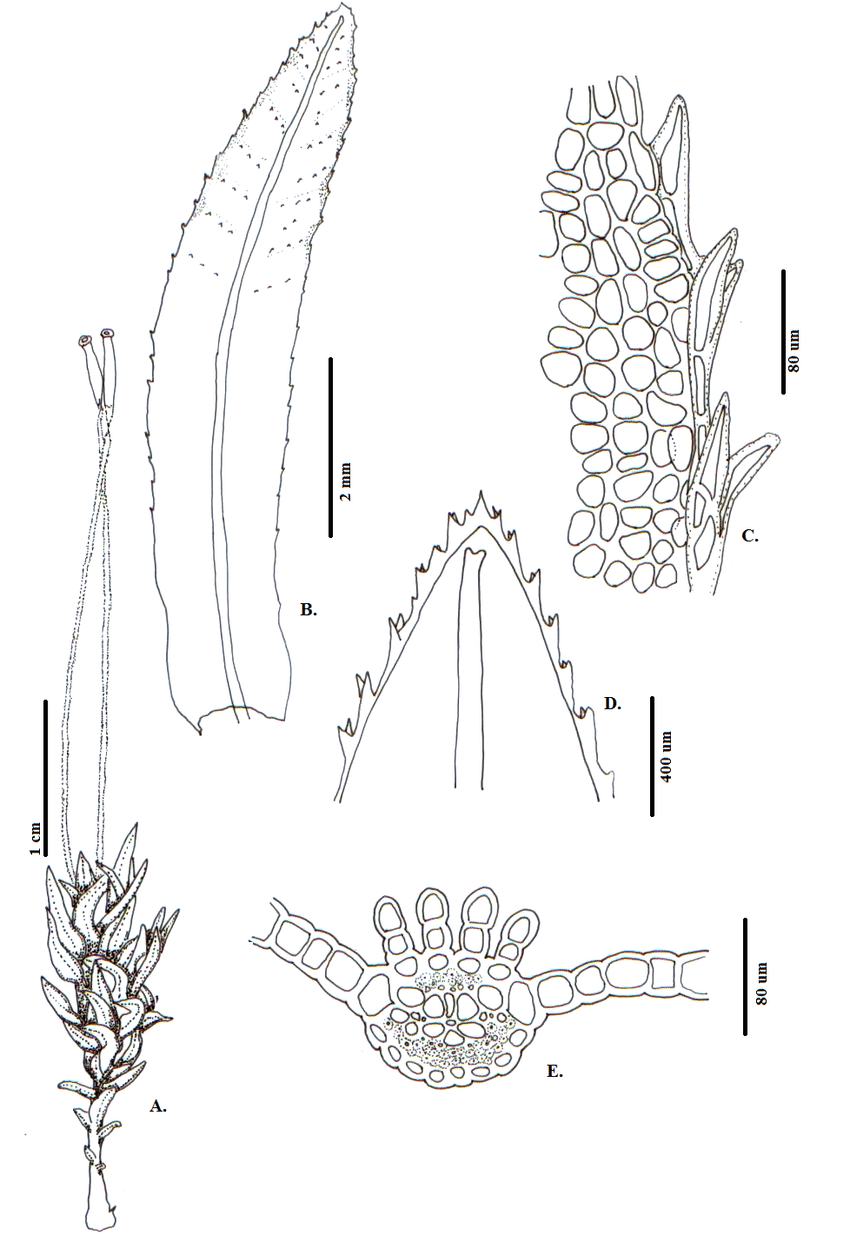
Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Atrichum-androgynum-MuellHal-Jaeger-A-Habito-B-E-Hoja-B-Vista-ventral-C_fig1_318217800
Global Distribution and Habitat
Leucoloma dichelymoides is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from tropical and subtropical forests to montane regions, often growing on tree trunks, rocks, and soil.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to humid and shaded environments, where it can take advantage of the moisture and protection provided by the canopy. However, it also exhibits remarkable resilience, capable of surviving in drier conditions by entering a dormant state until favorable conditions return.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
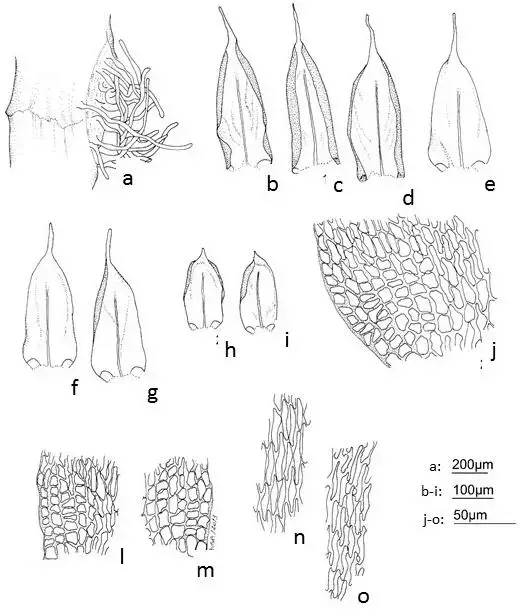
Figura-11-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Pseudoparafilos-filamentosos.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-11-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Pseudoparafilos-filamentosos_fig11_309232610
Despite its diminutive size, Leucoloma dichelymoides plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Leucoloma dichelymoides is its ability to absorb and retain water through its leaves and stems. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought by entering a state of dormancy and reviving when water becomes available again.
Case Study: Tropical Rainforest Ecosystem
In the lush and biodiverse tropical rainforests, Leucoloma dichelymoides plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of these ecosystems. Its ability to colonize tree trunks and branches creates a unique microhabitat for other organisms, such as insects, spiders, and even small amphibians.
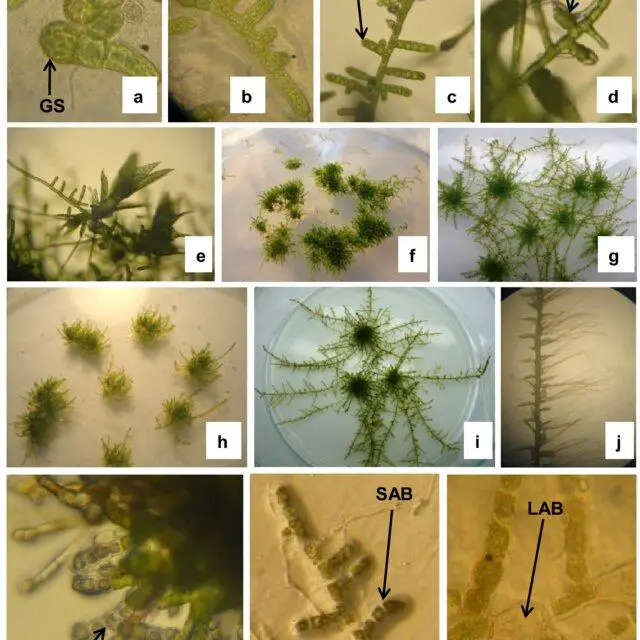

a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914
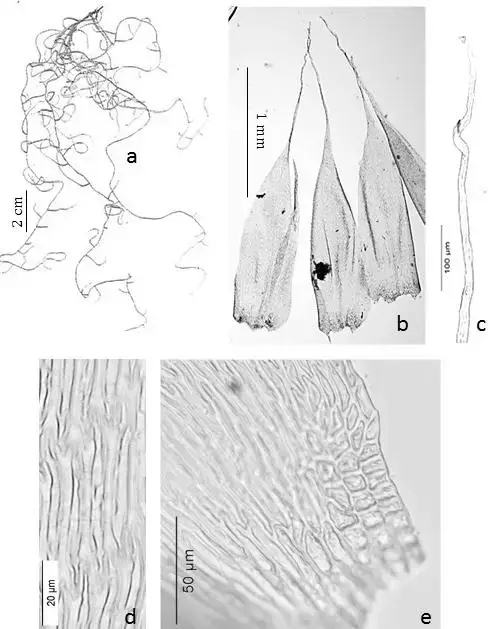
Figura-12-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-12-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-c_fig12_309232610
Furthermore, the moss acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, which helps regulate the humidity levels within the forest canopy. This, in turn, supports the growth and survival of other plant species, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Technical Table
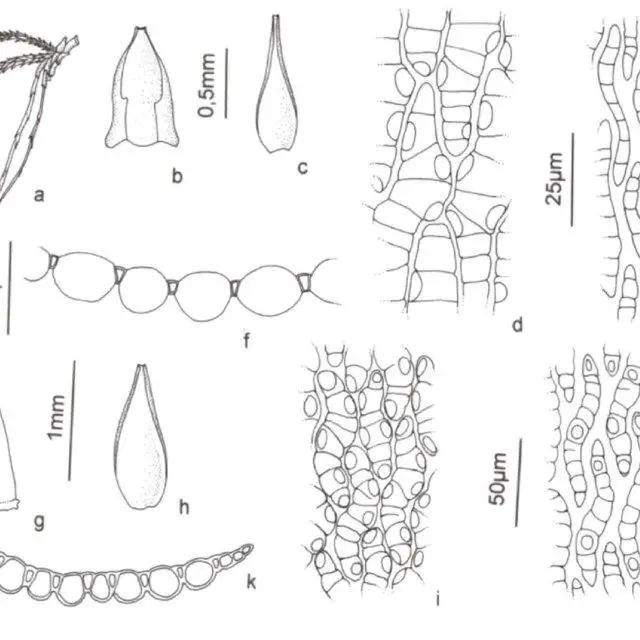
Sphagnum-aciphyllum-Muell-hal-A-Fascicle-B-Stem-leaves-C-Branch-leaves-D-Cells-of_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sphagnum-aciphyllum-Muell-hal-A-Fascicle-B-Stem-leaves-C-Branch-leaves-D-Cells-of_fig1_324655306
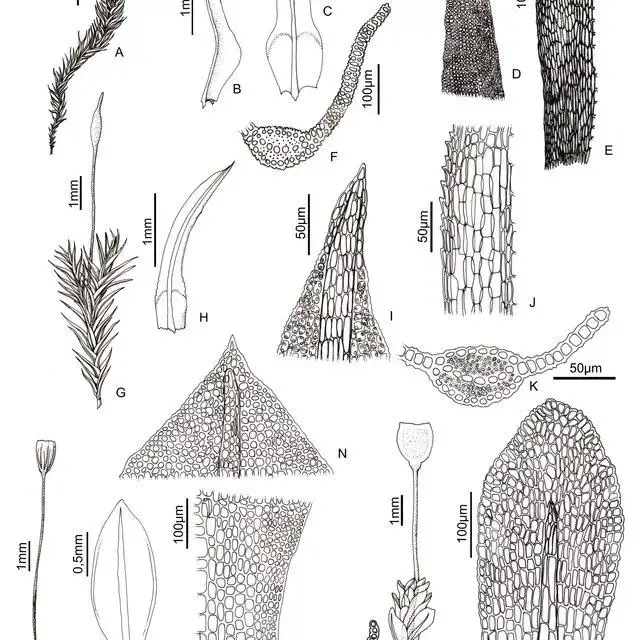
Erythrophyllopsis-andina-Sull-RH-Zander-A-Habit-B-C-Leaves-D-Leaf-apex-E_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Streptopogon-calymperes-Muell-Hal-A-B-Leaves-C-Leaf-apex-D-Leaf-section_fig7_296705710
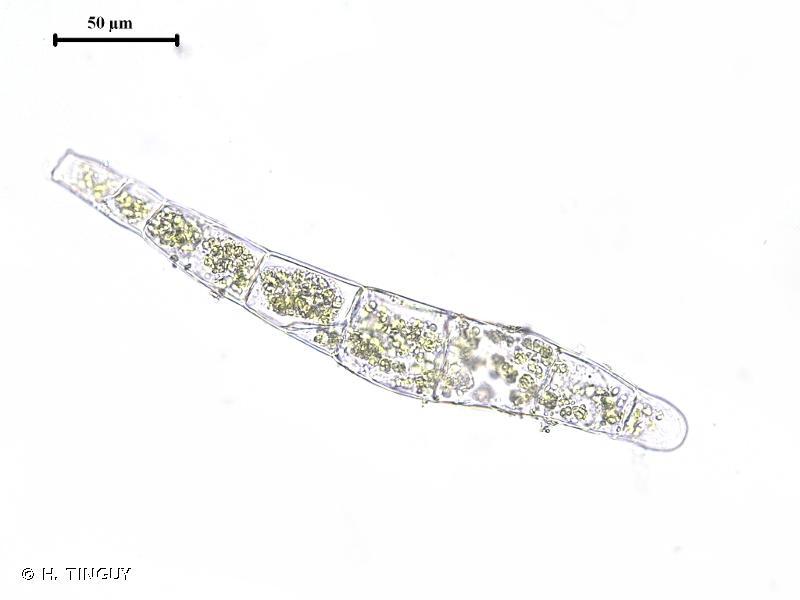
239258.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786477
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Genus | Leucoloma
 209936.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4771/tab/fiche |
| Species | dichelymoides |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lanceolate, often curved or falcate |
| Sporophyte | Slender seta with curved, cylindrical capsule |
| Habitat | Tree trunks, rocks, soil in humid and shaded environments |
| Distribution | Asia, Africa, Australia, South America |
| Adaptation | Poikilohydry (ability to survive drought) |
Conclusion
The Leucoloma dichelymoides (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger moss, or simply Leucoloma, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this bryophyte plays a vital role in various ecosystems, contributing to soil stabilization, providing microhabitats, and regulating moisture levels.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate web of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve the often-overlooked yet essential components of our ecosystems, like the humble Leucoloma dichelymoides?