
nardia_geoscyphus3.jpg from: http://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/savikkosiiransammal.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Nardia geoscyphus (De Not.) Lindb. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Gymnomitriaceae
Habrodon-perpusillus-De-Not-Lindb-from-Adler-Ignatov-Ignatova-9VIII2002-MHA.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Habrodon-perpusillus-De-Not-Lindb-from-Adler-Ignatov-Ignatova-9VIII2002-MHA_fig3_275607409
family. Also known simply as Nardia, this unassuming yet resilient plant has carved its niche in various ecosystems, playing a vital role in the intricate web of life. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this remarkable moss.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Nardia geoscyphus, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and leafy mosses. These bryophytes are often overlooked, but they are crucial components of many ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, water retention, and providing microhabitats for countless other organisms.

Solenostoma_gracillimum_002.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Solenostoma_gracillimum.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

2022-03-29-12-42-16.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/tortula-pallida/
Nardia geoscyphus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the ground or rocks. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with overlapping leaves arranged in two rows. The leaves are deeply divided into two or three lobes, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. When mature,
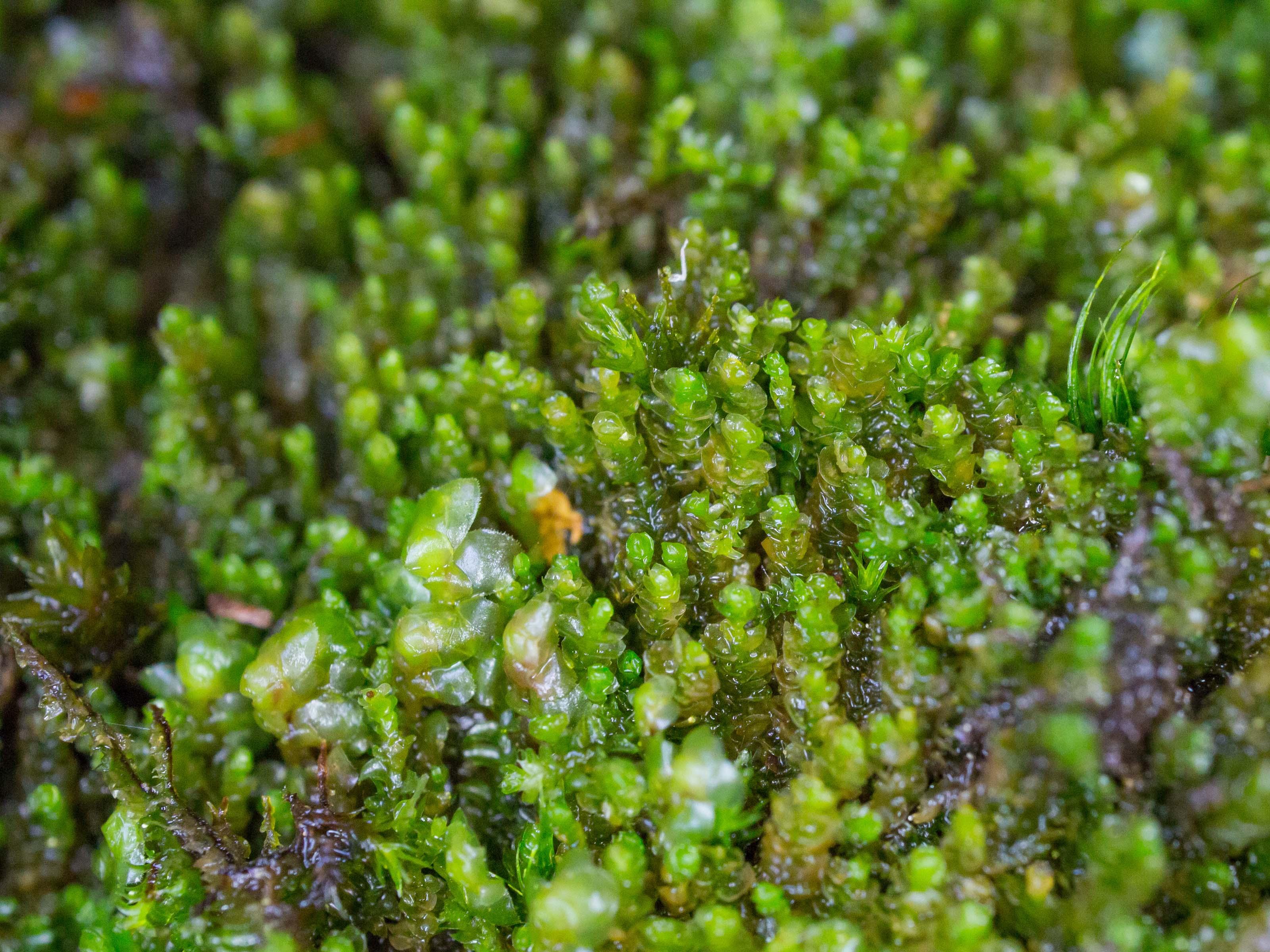

marsupella_emarginata_habitus.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/jungermanniaceae/index.html
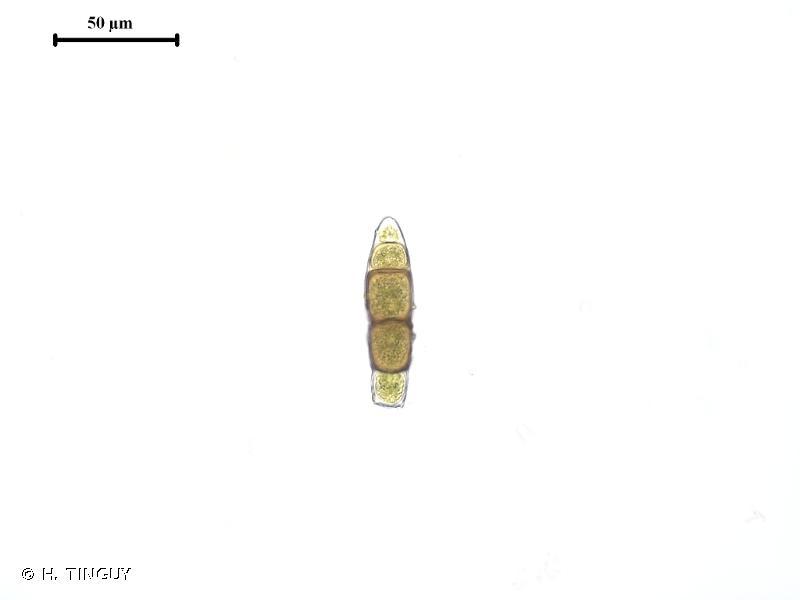

235036.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5149
Nardia produces tiny, urn-shaped sporophytes that release spores, ensuring its propagation.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This resilient moss has a widespread distribution, thriving in various regions across the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It can be found in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and quarries. Nardia geoscyphus is well-adapted to survive in these environments, thanks to its ability to withstand desiccation and its tolerance for a wide range of pH levels.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Nardia geoscyphus plays a crucial role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Exostome-teeth-of-Habrodon-perpusillus-De-Not-Lindb-France-H-Buch-29XII1930-H.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Exostome-teeth-of-Habrodon-perpusillus-De-Not-Lindb-France-H-Buch-29XII1930-H_fig1_275607409
One of the remarkable adaptations of Nardia is its ability to survive periods of drought by entering a state of dormancy. During dry spells, the moss curls up and appears lifeless, but as soon as moisture becomes available, it quickly revives and resumes its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Study: Nardia geoscyphus in Boreal Forests
In the vast boreal forests of the Northern Hemisphere, Nardia geoscyphus thrives on decaying logs and moist soil. Its presence is often an indicator of a healthy and undisturbed forest ecosystem. Researchers have found that this moss plays a vital role in nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients back into the soil, supporting the growth of other plants and trees.
Technical Table
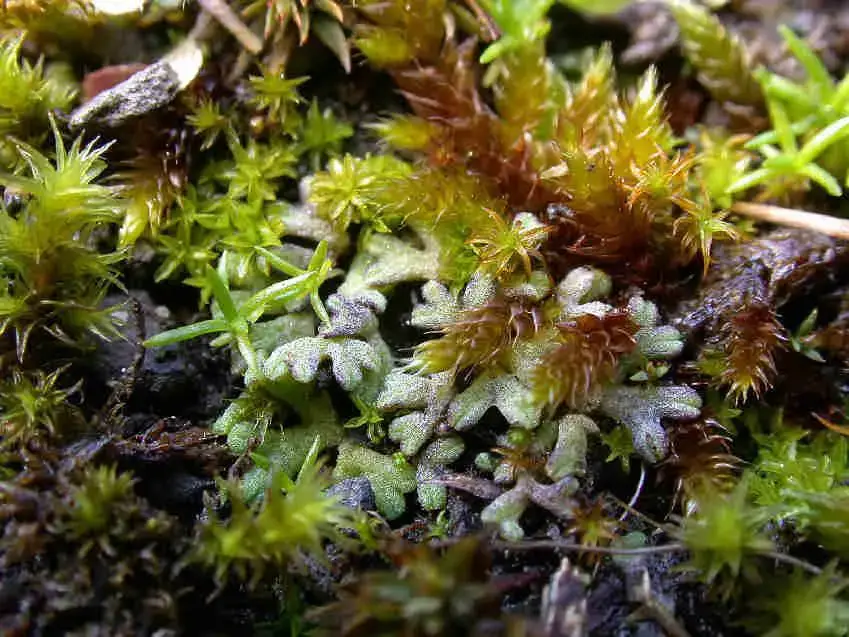

Riccia_nigrella_002.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Riccia_nigrella.html
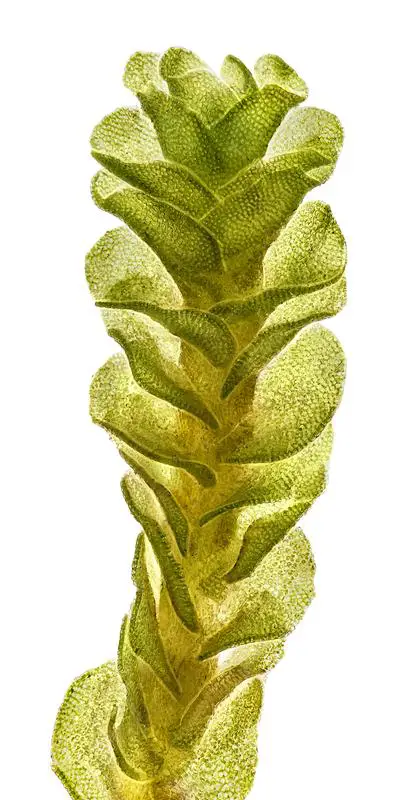

54146_2380_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/nardia-geoscyphus-2380

Nardia_berge.jpg from: https://bryologiewallonie.blogspot.com/2022/07/nardia-insecta-lindb.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Gymnomitriaceae |
| Genus | Nardia |
| Species | Nardia geoscyphus (De Not.) Lindb. |
| Growth Form | Creeping moss, forming dense mats or cushions |
| Leaf Arrangement | Leaves arranged in two rows, deeply divided into two or three lobes |
| Sporophyte | Tiny, urn-shaped sporophytes |
| Habitat | Moist and shaded areas, rocky outcrops, disturbed sites |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Nardia geoscyphus moss may be small, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is profound. From stabilizing soils and providing microhabitats to contributing to nutrient cycling, this unassuming bryophyte plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How many other overlooked organisms are silently shaping the environments we call home?