
40237726441_6c0e2a2960_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/40237726441/
Introduction
Welcome, fellow enthusiasts, to an exploration of the captivating world of

2021-09-12-15-51-13.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/riccia-subbifurca/
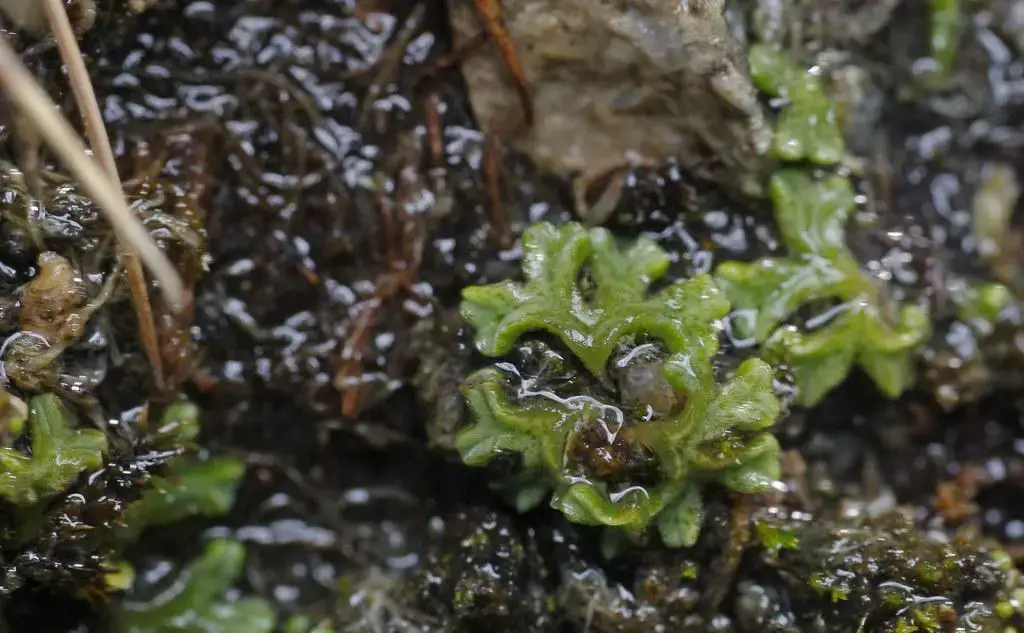
Riccia subbifurca Warnst. ex Croz., a remarkable moss species belonging to the Ricciaceae family. Often referred to simply as Riccia, this unassuming plant holds a wealth of fascinating secrets waiting to be uncovered.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Riccia subbifurca, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to the world of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems.

Riccia_subbifurca_003.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Riccia_subbifurca.html
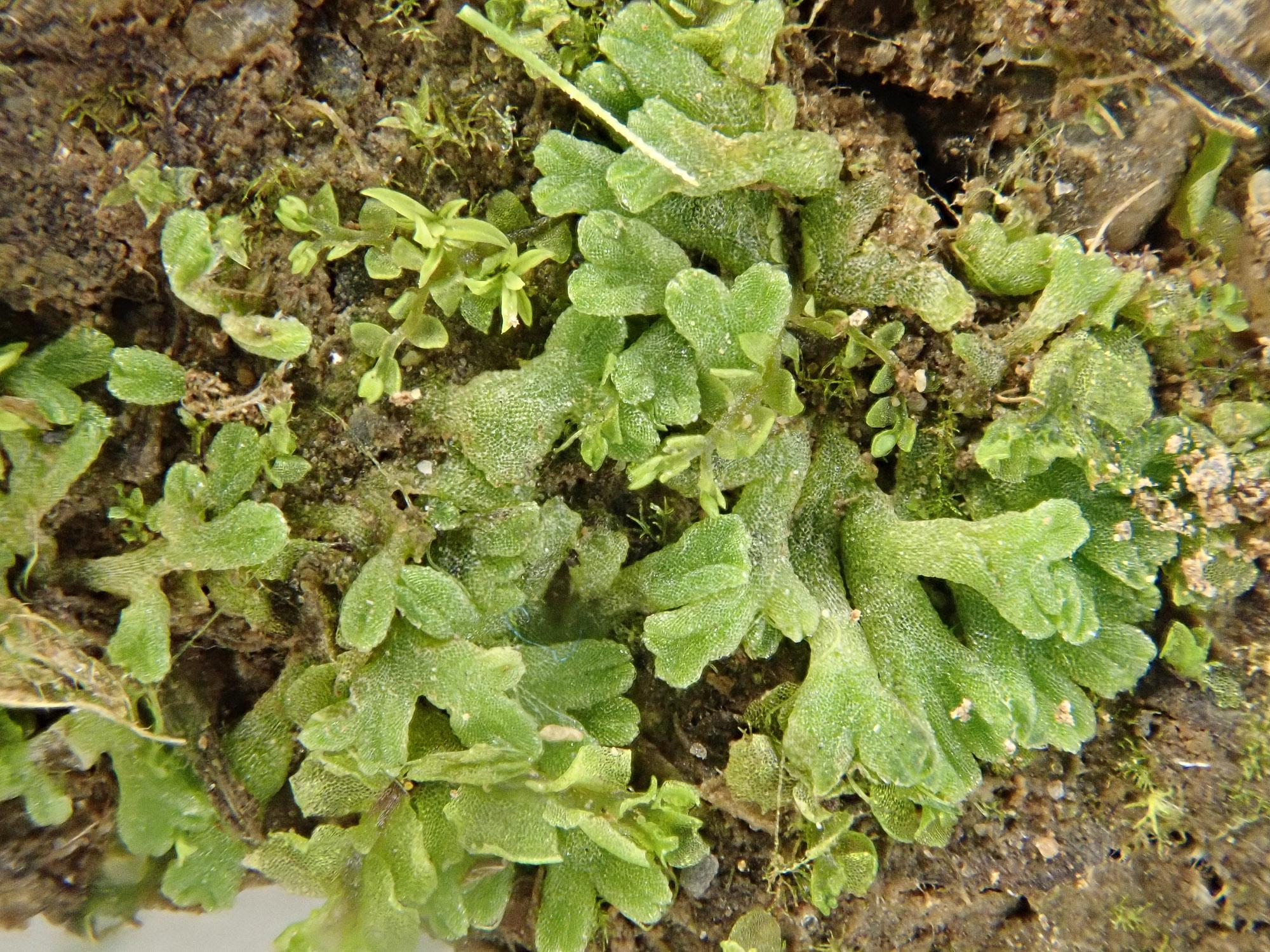
Riccia subbifurca is a member of the Marchantiophyta division, also known as liverworts, which are among the oldest lineages of land plants.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

40237725061_9e8870a3b7_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/40237725061/
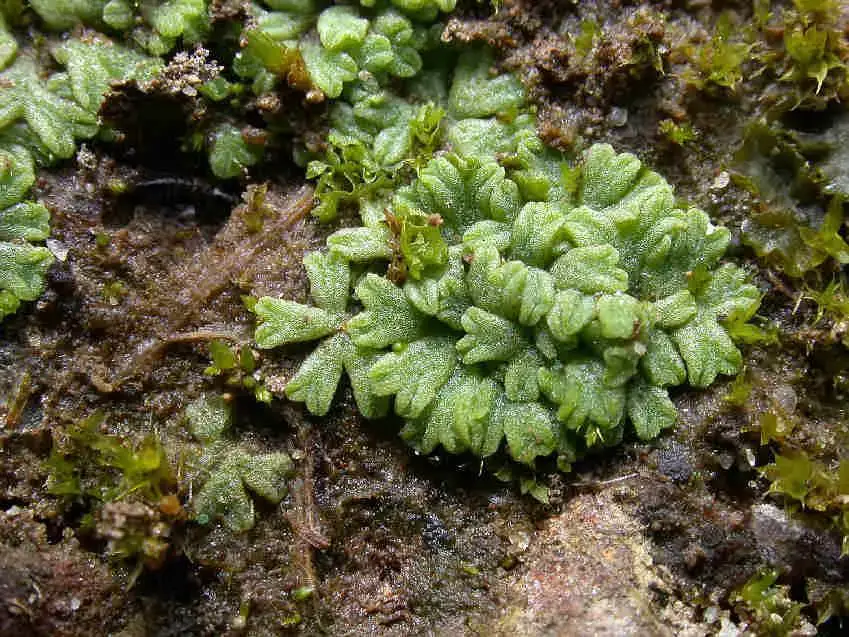
Riccia subbifurca is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form without distinct stems or leaves. Its thalli are typically green to yellowish-green in color and can reach up to 2 cm in length. One of the defining features of this species is the presence of bifurcate (forked) thalli, which give it its distinctive appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This diminutive moss has a widespread distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including damp soil, rock crevices, and disturbed areas such as paths and lawns. Riccia subbifurca is particularly well-adapted to temporary and ephemeral habitats, making it a true survivor in the ever-changing world of bryophytes.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
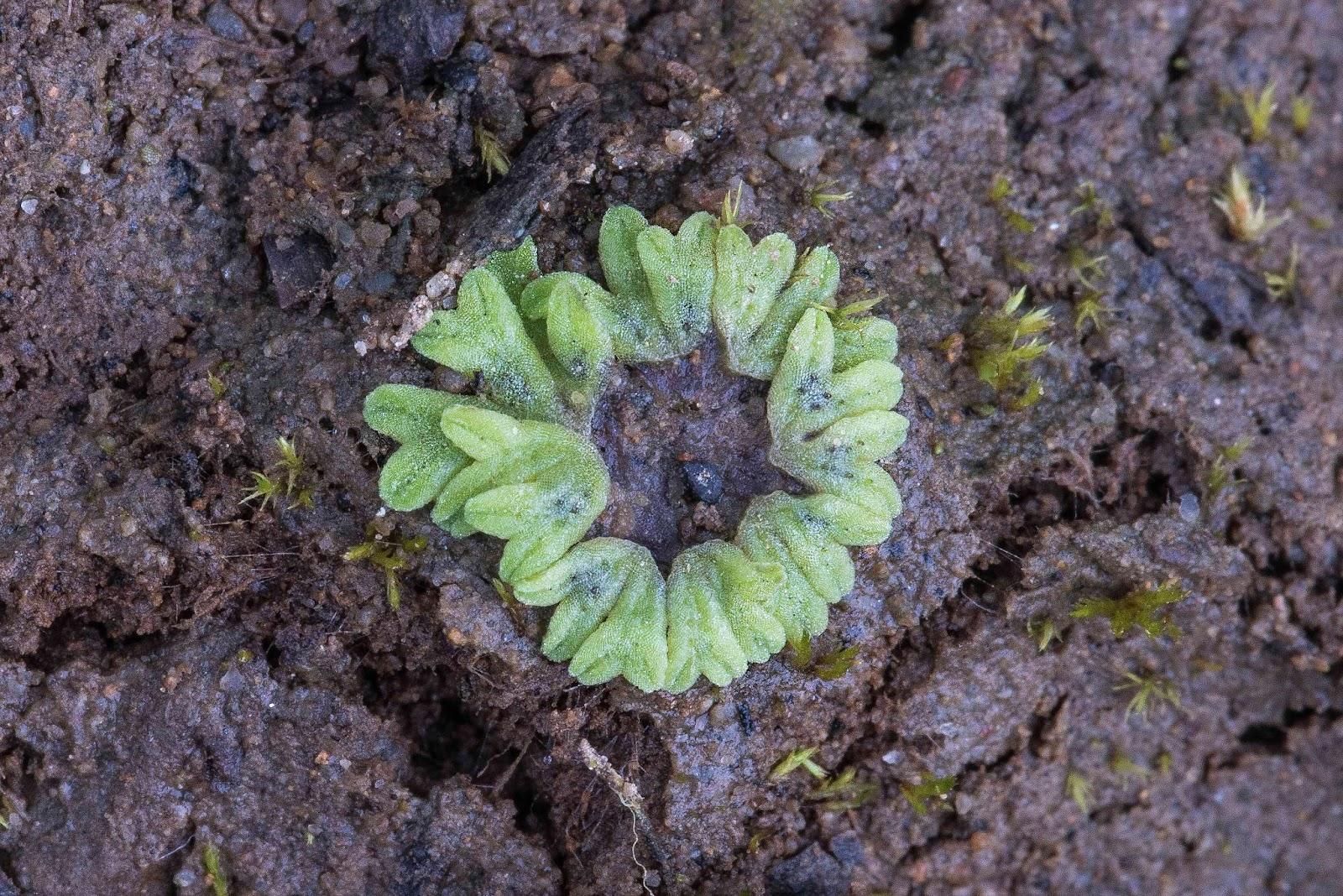

Riccia%2Bsubbifurca%2BPelenna%2Blowres.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/09/riccia-subbifurca-along-pelenna-forest.html
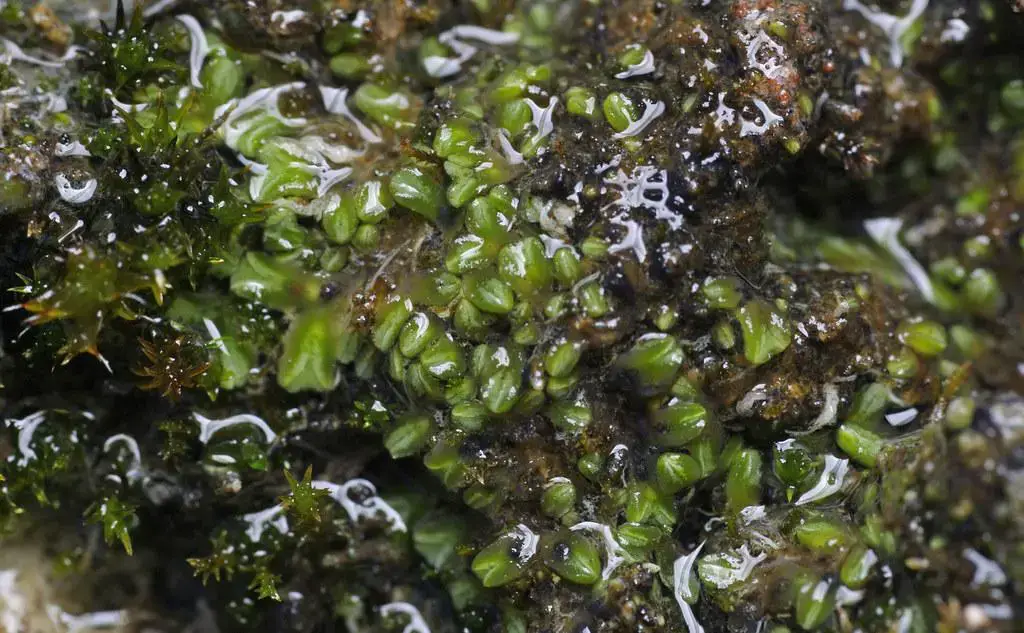
Despite its small stature, Riccia subbifurca plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a pioneer species, colonizing disturbed areas and paving the way for more complex plant communities to establish themselves.
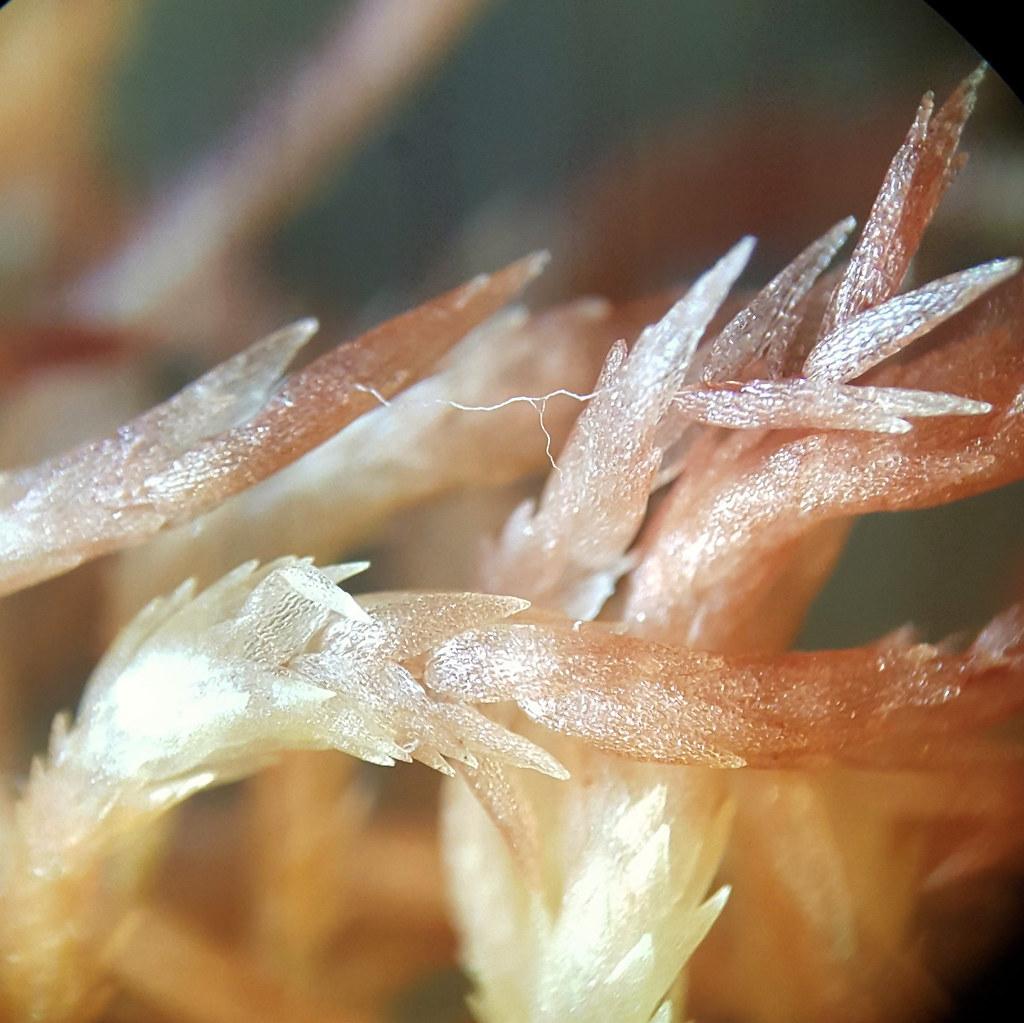

50260254972_5d4056d75c_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/50260254972/
One of the remarkable adaptations of
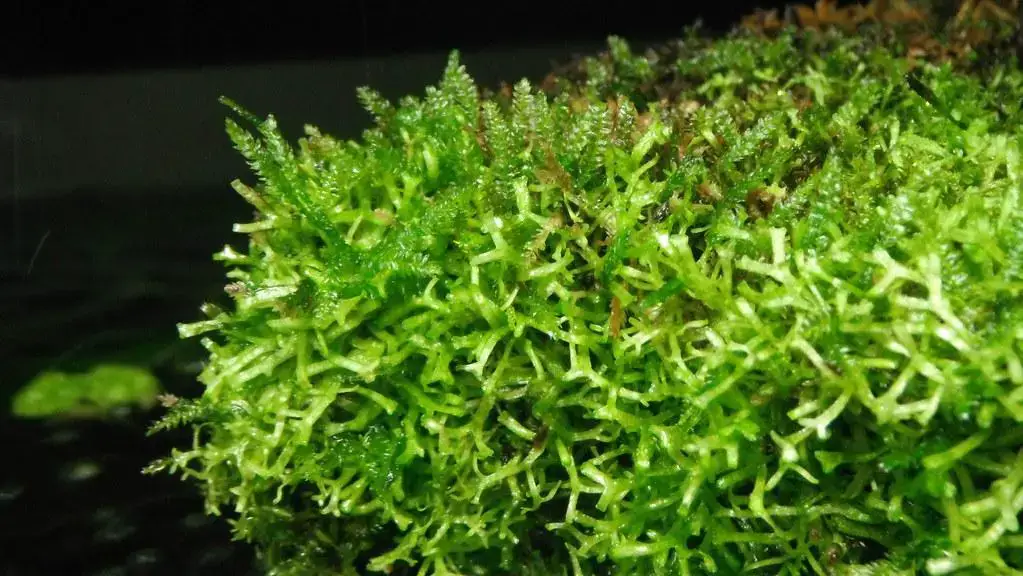

14441185564_b69bac8a76_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/ursus_sapien/14441185564
Riccia subbifurca is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the thalli can curl up and enter a dormant state, only to revive and continue growing when moisture returns. This resilience is a testament to the incredible evolutionary strategies employed by bryophytes to thrive in challenging environments.
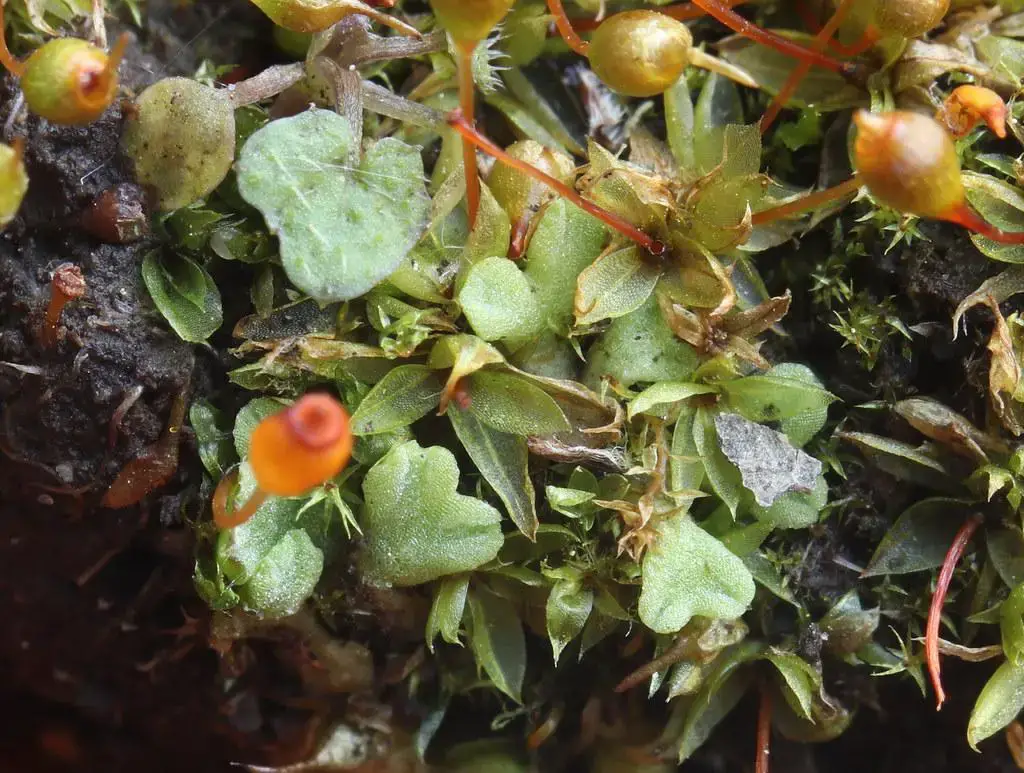

41711177244_769fc894d1_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/picassofish/41711177244/
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered that
f01_83.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Cryptogamie-Bryologie/volume-32/issue-1/cryb.v32.iss1.2011.083/Riccia-Subbifurca-Warnst-ex-Croz-Ricciaceae-New-to-Turkey/10.7872/cryb.v32.iss1.2011.083.full
Riccia subbifurca played a crucial role in the recovery of forest understories after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas helped stabilize the soil and create favorable conditions for the establishment of other plant species, ultimately contributing to the restoration of the ecosystem.
Technical Table

riccia-moss.jpg from: https://himadriaquatics.com/products/riccia-fluitans-floating-crystalwort-riccia-moss/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta (Liverworts) |
| Class | Marchantiopsida |
| Order | Marchantiales |
| Family | Ricciaceae |
| Genus | Riccia |
| Species | Riccia subbifurca Warnst. ex Croz. |
| Thallus Form | Thallose, bifurcate (forked) |
| Color | Green to yellowish-green |
| Habitat | Damp soil, rock crevices, disturbed areas |
| Distribution | Widespread, found on all continents except Antarctica |
Conclusion
Riccia subbifurca may be small, but its impact on the natural world is anything but insignificant. This remarkable moss serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that exists all around us, even in the most unassuming of places. As we bid farewell to this fascinating species, let us ponder the following question: What other hidden wonders await discovery in the realm of bryophytes, and how can we better appreciate and protect these often-overlooked members of our ecosystems?