
1115152.jpg from: https://www.forestryimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=1115152
Schlotheimia balfourii Mitt.: A Fascinating Moss of the Orthotrichaceae Family
A-y-B-Stictolejeunea-balfourii-Mitt-EW-Jones-A-Habito-B-Detalle-de-celulas.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-y-B-Stictolejeunea-balfourii-Mitt-EW-Jones-A-Habito-B-Detalle-de-celulas_fig4_262478045
Introduction
The world of mosses is full of fascinating species, each with their own unique characteristics and ecological roles. One such moss is Schlotheimia balfourii Mitt., a member of the Orthotrichaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this intriguing moss, exploring its morphology, global distribution, habitat preferences, and ecological adaptations. Get ready to be amazed by the miniature world of Schlotheimia balfourii!
Background
Schlotheimia balfourii Mitt., commonly known as just Schlotheimia, is a species of moss belonging to the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. It was first described by the British bryologist William Mitten in 1863. The Orthotrichaceae family, to which Schlotheimia belongs, contains over 900 species worldwide.

Schlotheimia%2Brugifolia%2Bcapsule.jpg from: https://botanyprofessor.blogspot.com/2018/02/mosses-of-central-florida-48.html
Image2FDGlarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Schlotheimia.html
Morphology and Identification
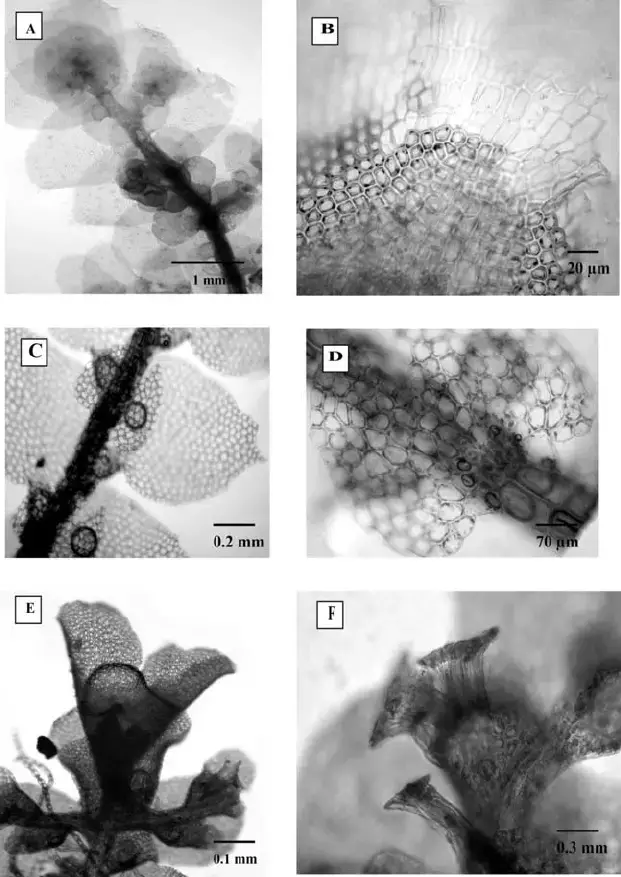
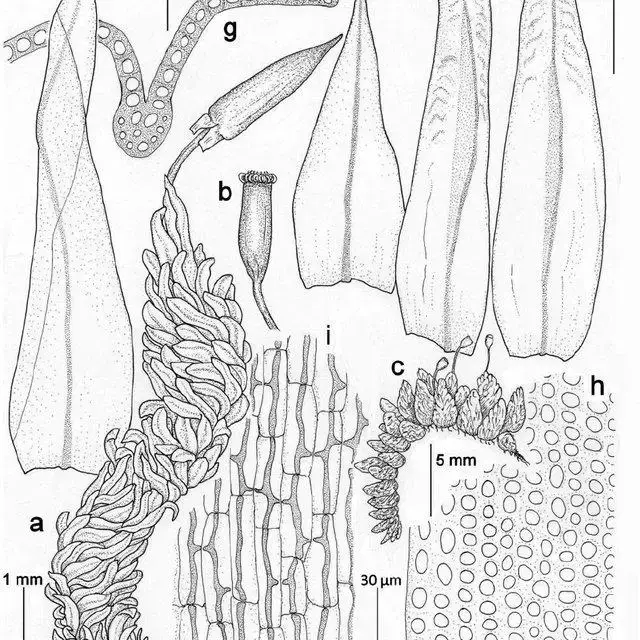
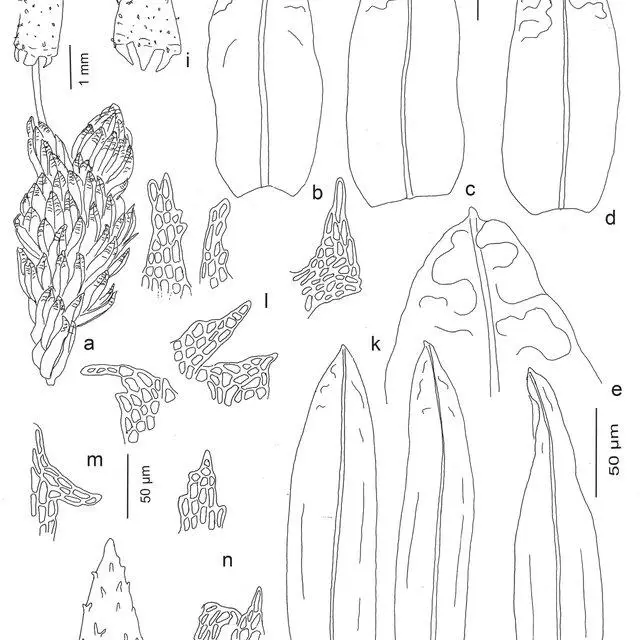
Schlotheimia balfourii is a small to medium-sized moss, typically growing in dense tufts or cushions. Its stems are erect, reaching 5-20 mm in height. The leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a pointed apex and margins that are often recurved. A key identifying feature is the presence of multicellular gemmae on the leaf tips, which aid in vegetative reproduction.
The sporophytes of S. balfourii are erect and emerge from the tips of the stems. The capsules are cylindrical and have a peristome with 16 teeth. Spores are small, ranging from 10-15 μm in diameter.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Schlotheimia balfourii has a wide global distribution, found on several continents:
Schlotheimia-badiella-Besch-a-c-habit-dry-b-capsule-d-branch-leaves-e_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schlotheimia-badiella-Besch-a-c-habit-dry-b-capsule-d-branch-leaves-e_fig2_281108486

4891658387_be0a1182d6.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/30512307@N03/4891658387

liparoceras-cheltiensis.jpg from: https://www.paleo-passion.com/ammonites-jurassique/2194-liparoceras-cheltiensis.html
| Continent | Countries/Regions |
|---|---|
| Africa | Madagascar, Réunion, Mauritius |
| Asia | India, Sri Lanka, China, Japan, Indonesia |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand, Pacific Islands |
This moss typically grows as an epiphyte on the bark of trees and shrubs in humid forests, from lowland to montane elevations. It prefers shaded, moist habitats with high humidity and moderate temperatures.
Schlotheimia-spinomitria-A-Plants-with-capsule-B-D-Vegetative-leaves-E-Apex-of_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schlotheimia-spinomitria-A-Plants-with-capsule-B-D-Vegetative-leaves-E-Apex-of_fig1_316553428
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many mosses, Schlotheimia balfourii plays important ecological roles in its habitats. It contributes to

momigoke230512_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2023/05/blog-post_18.html
nutrient cycling, helps retain moisture, and provides shelter for small invertebrates. The dense cushions formed by this moss also aid in preventing soil erosion on tree trunks and branches.
S. balfourii has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its epiphytic habitat. The presence of multicellular gemmae enables efficient vegetative reproduction, allowing the moss to spread quickly on suitable substrates. Additionally, the recurved leaf margins help retain moisture, a crucial adaptation in the often-dry epiphytic environment.
Conclusion
Schlotheimia balfourii Mitt. is a remarkable moss species with a fascinating morphology, wide global distribution, and important ecological roles. Its adaptations to the epiphytic lifestyle showcase the resilience and diversity of bryophytes. The next time you find yourself in a humid forest, keep an eye out for the small but mighty Schlotheimia balfourii. Who knows what other miniature wonders await discovery in the world of mosses?

schlan_schrugweb1.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/schlotheimialancifolia.html