
2010-Fusion413-of-418-Version-2.jpg from: http://tomclynes.photoshelter.com/image/I0000VTl_9pHcyfI
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the
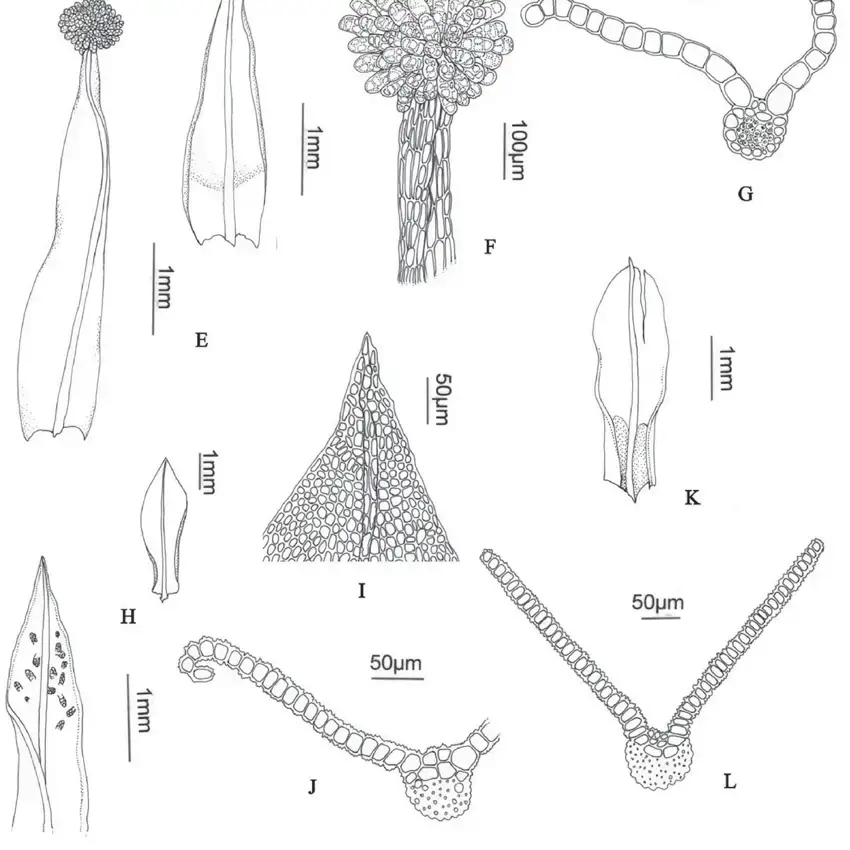
A-D-Streptopogon-brasiliensis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Leaf-apex-D-Leaf-section.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Streptopogon-brasiliensis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Leaf-apex-D-Leaf-section_fig6_281820899
Streptopogon erythrodontus (Taylor) Wilson moss, belonging to the Pottiaceae family. Also known simply as Streptopogon, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Streptopogon erythrodontus is a member of the phylum Bryophyta, which encompasses all mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Within this phylum, it belongs to the class Bryopsida, commonly referred to as the “true mosses.”
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Streptopogon erythrodontus is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the stems. Its leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and often have a reddish tinge, particularly at the tips – a characteristic that gives rise to its specific epithet, “erythrodontus” (meaning “red-toothed”). The stems are typically unbranched and can reach heights of up to a few centimeters.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from exposed soil and rock surfaces to disturbed areas, such as roadsides and construction sites. Streptopogon erythrodontus is particularly well-adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, making it a hardy and resilient species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

taylor-wilson_10.jpg from: https://www.mentalfloss.com/article/28576/mad-scientist-month-whos-afraid-taylor-wilson
Despite its diminutive size, Streptopogon erythrodontus plays crucial ecological roles. As a pioneer species, it is often among the first to colonize bare or disturbed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and pave the way for other plant species to establish themselves. Additionally, mosses like Streptopogon contribute to the overall biodiversity of their ecosystems, providing microhabitats for various invertebrates and serving as food sources for some organisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Streptopogon erythrodontus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This trait allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable or scarce.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Mojave Desert, researchers found that Streptopogon erythrodontus played a crucial role in stabilizing soil and facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize and create a protective mat helped prevent erosion and provided a suitable microenvironment for seedling germination.

b6da067fd87b22af53f9445945c26bac.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/440930619749353775/

a08f48898b700307e340afde728558cf.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/440930619749353749/

wilson-taylor-image.jpg from: https://www.famousbirthdays.com/people/taylor-wilson.html

taylor-wilson-5.jpg from: https://helena.org/members/taylor-wilson/

taylor-wilson-centred.png from: https://thenewnow.org/digital-futures/taylor-wilson-centred/

20867744133_1f6920dea7_b.jpg from: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/prithwirajdutta/royalsdeck-frontend-code/master/blogs/story_of_taylor_wilson.php
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Streptopogon |
| Species | erythrodontus |
Conclusion
Streptopogon erythrodontus (Taylor) Wilson moss, a member of the Pottiaceae family, may be small in stature, but its ecological significance is undeniable. From its unique morphological features to its remarkable adaptations and global distribution, this moss species continues to captivate enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we delve deeper into the intricate world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and resilience of these often-overlooked organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of reddish-tipped moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the wonders of Streptopogon erythrodontus
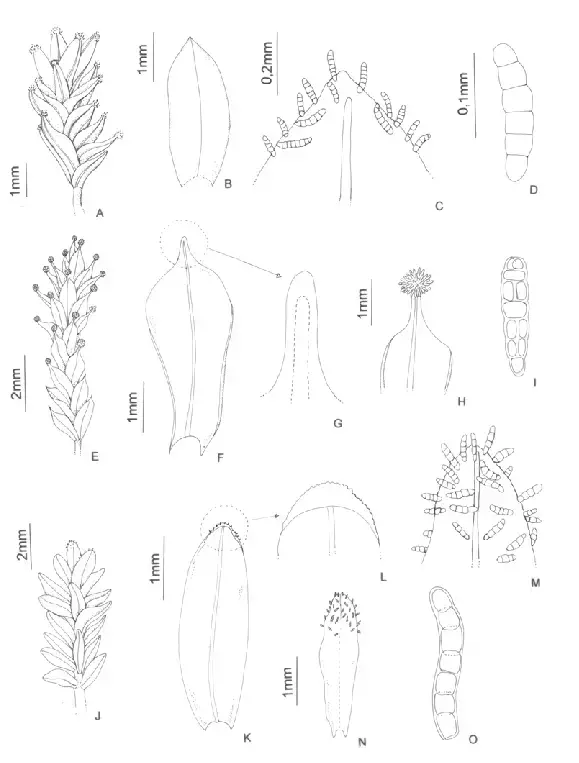
A-D-Streptopogon-brasiliensis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Detail-of-leaf-apex-with-marginal.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Streptopogon-brasiliensis-A-Habit-B-Leaf-C-Detail-of-leaf-apex-with-marginal_fig1_255709419
.