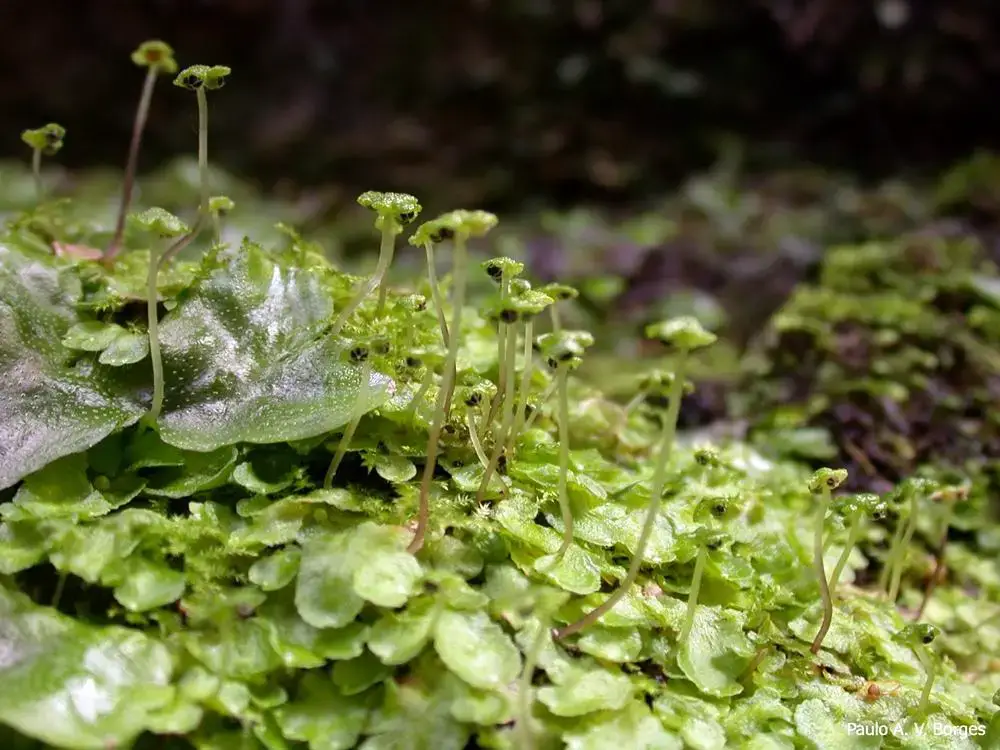

Asterella-africana-2824-136714964298971.jpg from: https://naturdata.com/especie/Asterella-africana/2824/0/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular species stands out as a true marvel – the Asterella africana (Mont.) Underw. ex A.Evans moss. Belonging to the Aytoniaceae family and commonly referred to as Asterella, this remarkable moss has captured the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on an exciting journey to unravel the secrets of this extraordinary plant.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Asterella africana, it’s essential to understand its place within the Marchantiophyta (liverworts) division of the Marchantiopsida class. These fascinating organisms are often overlooked, yet they play a crucial role in various ecosystems, serving as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to the intricate web of life.
Main Content

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236850858_Asterella_africana_Mont_A_Evans_grown_on_Madeira_and_in_mainland_Portugal_morphological_data_and_composition_of_the_essential_oil
Morphology and Identification
Asterella africana is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form. Its thallus is typically green to yellowish-green in color, with a distinct midrib running along its length. The thallus can reach up to 5 cm in length and is adorned with purple to brownish-purple scales on the underside. One of the most striking features of this moss is its umbrella-like reproductive structures called archegoniophores, which bear the female reproductive organs.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Asterella africana is a cosmopolitan species, found on various continents, including Africa, Asia, Europe, North America
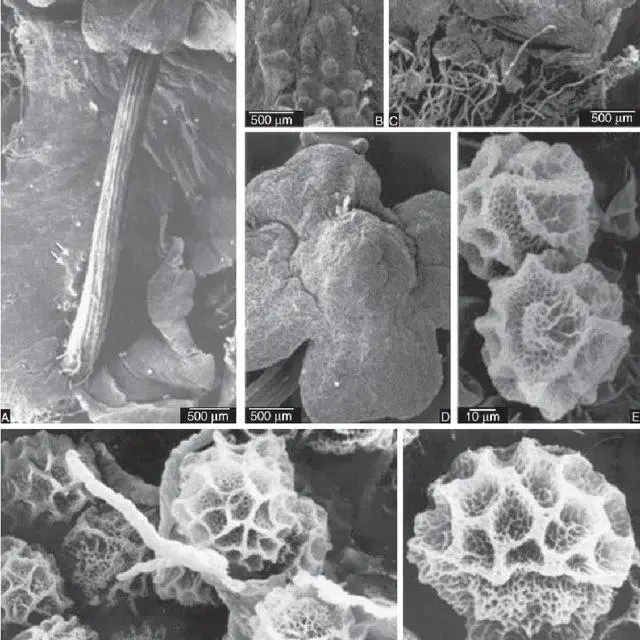
Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Asterella-africana-from-Madeira-A-E-and-mainland_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Asterella-africana-from-Madeira-A-E-and-mainland_fig1_236850858
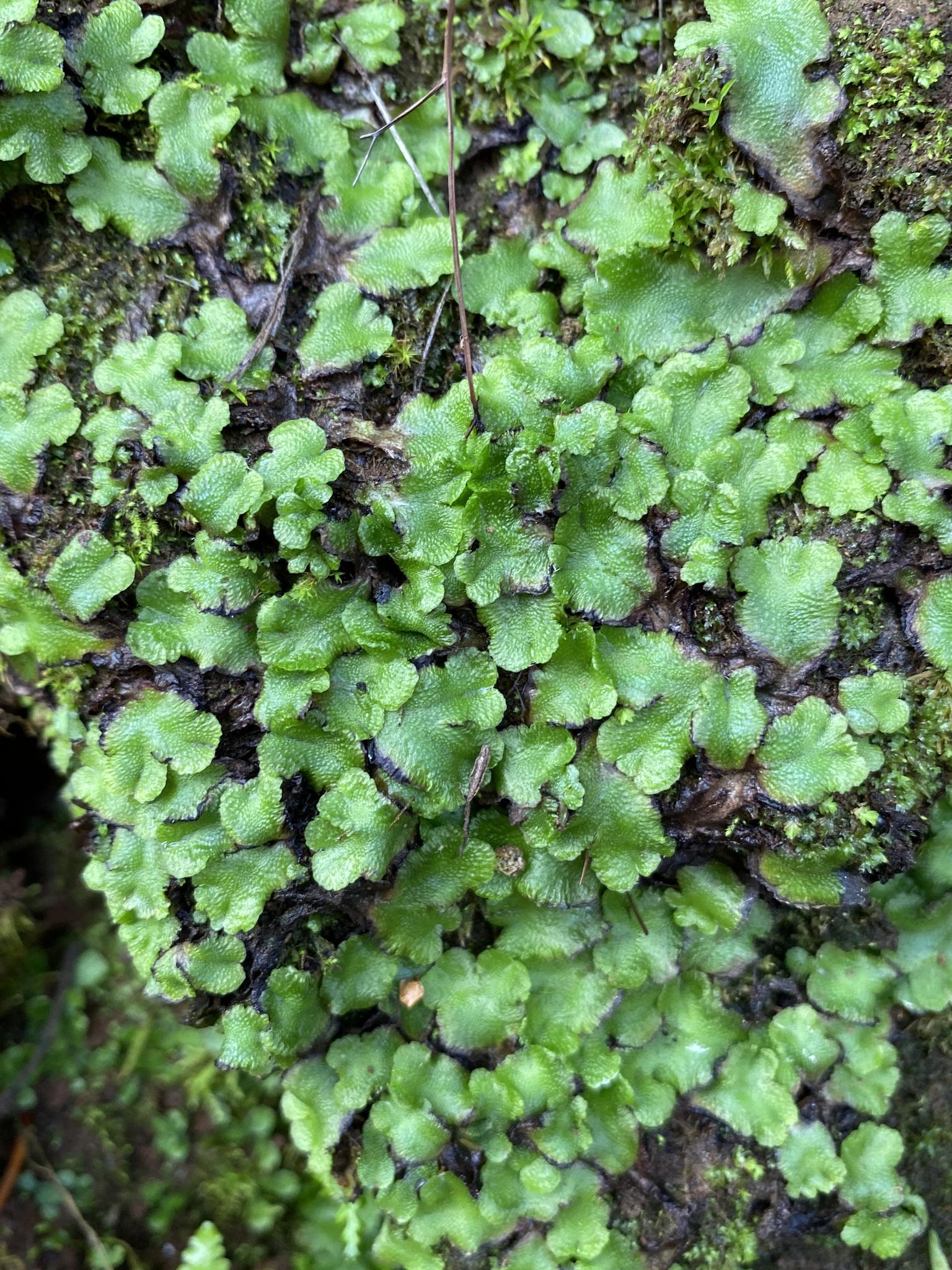

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/5710097
, and South America. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from moist soil and rock crevices to decaying logs and tree bark. This moss is particularly fond of shaded, humid environments, making it a common sight in forests, woodlands, and gardens.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Asterella africana plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of
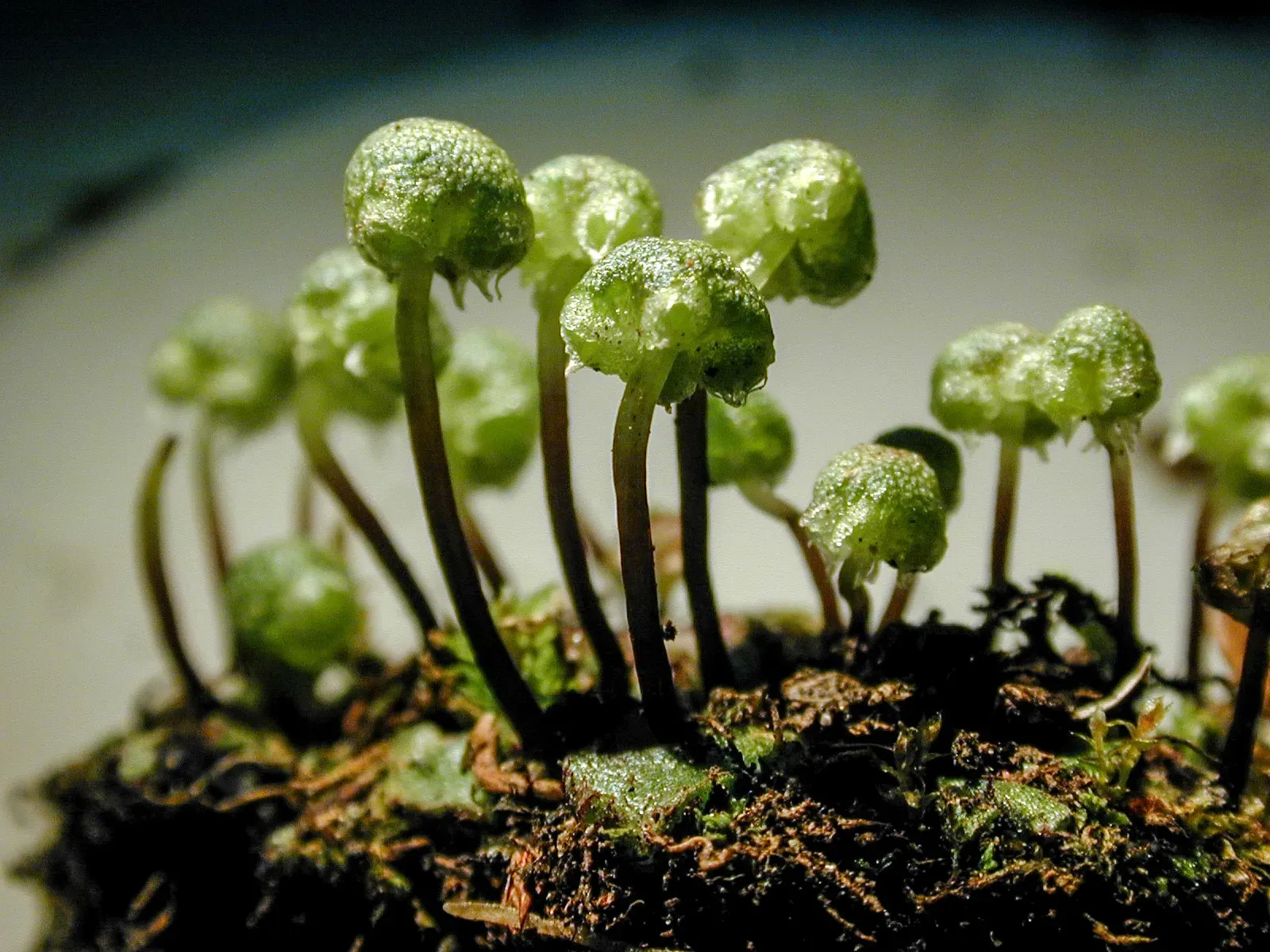

Astegra-carpocephala.jpg from: https://www.wildflowerjournal.net/tag/asterella-gracilis/
Asterella africana is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in challenging environments and ensures its long-term survival.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered that Asterella africana
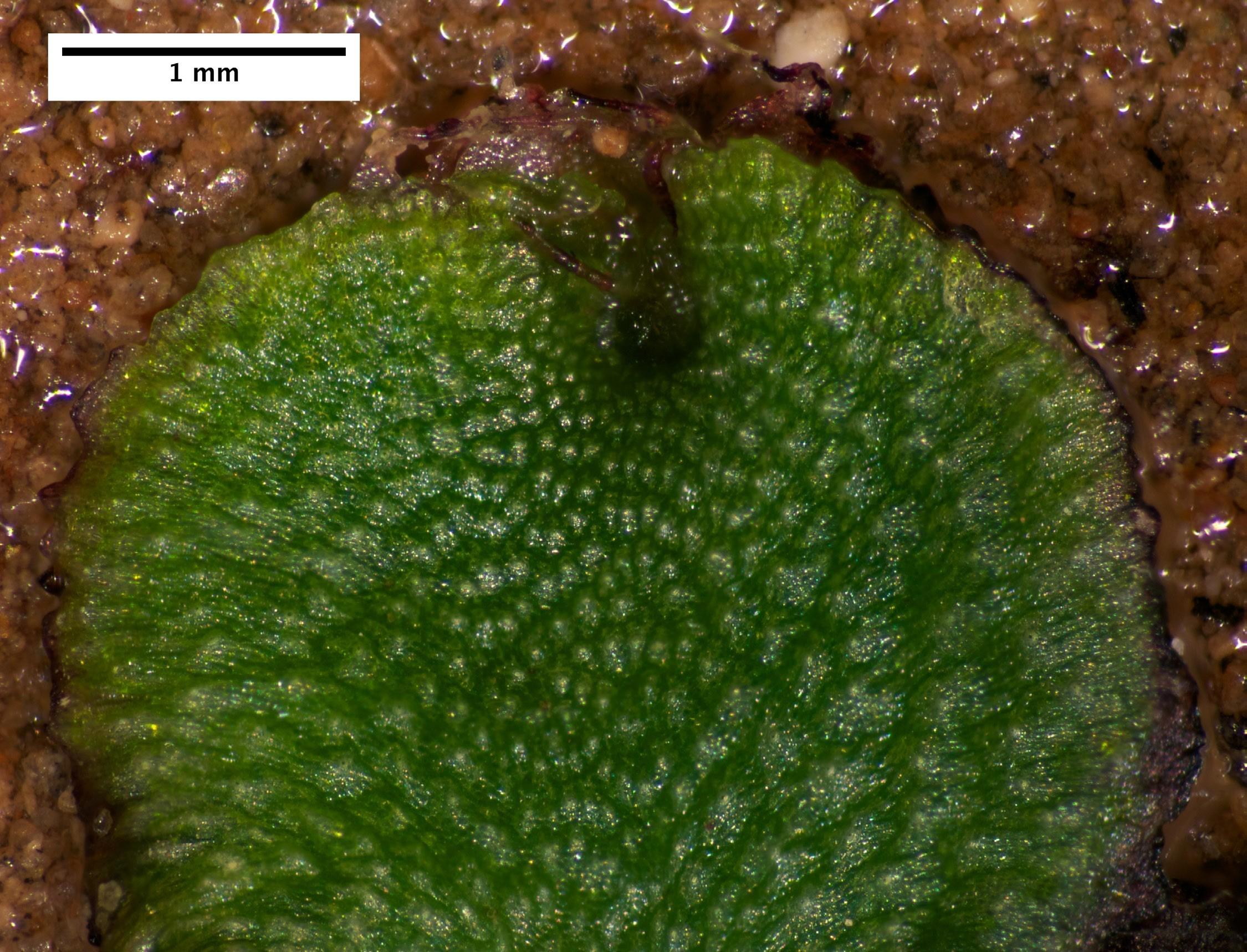

Astrella-californica-wet.jpg from: https://www.nps.gov/para/learn/nature/asterella-californica.htm
played a crucial role in the regeneration of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as
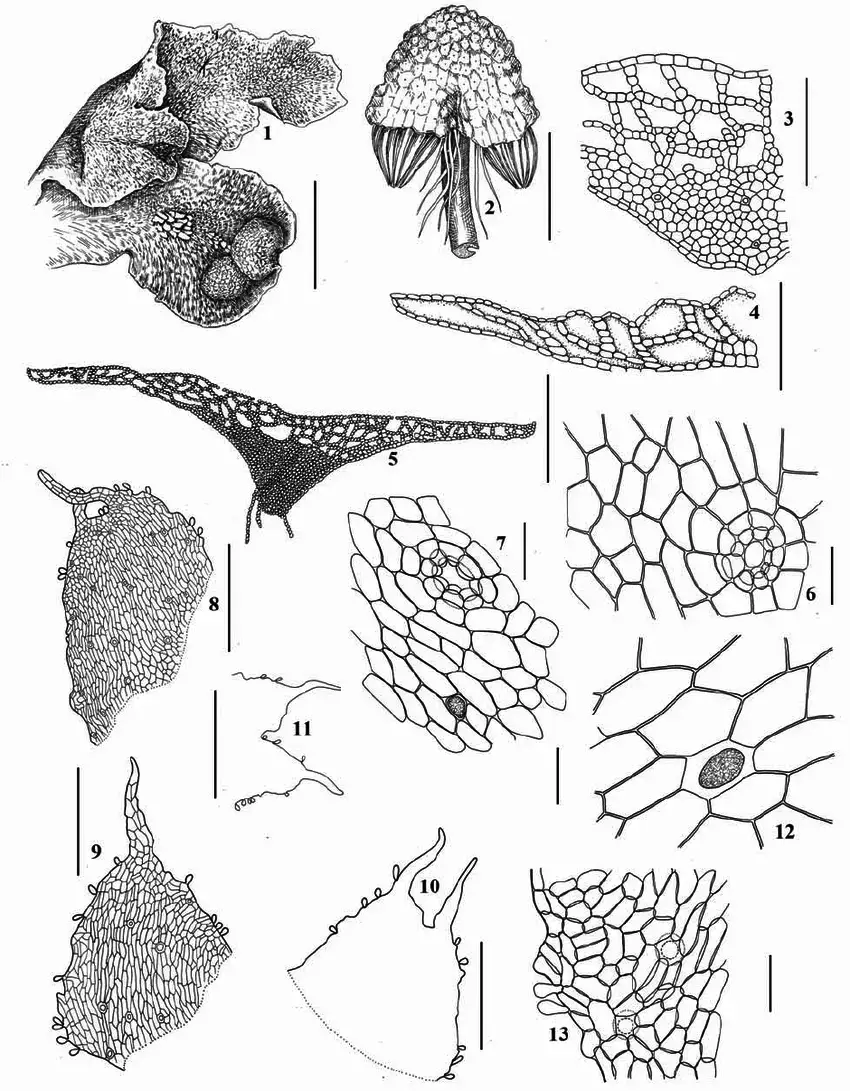
Asterella-lindenbergiana-Corda-ex-Nees-Arnell-1-4-9-11-13-from-Republic-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Asterella-lindenbergiana-Corda-ex-Nees-Arnell-1-4-9-11-13-from-Republic-of_fig3_283442870
logging or wildfires. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas and create a suitable microclimate facilitated the establishment of other plant species, accelerating the recovery process.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Marchantiopsida |
| Family | Aytoniaceae |
| Genus | Asterella |
| Species | africana |
| Thallus | Green to yellowish-green, with a midrib |
| Scales | Purple to brownish-purple on the underside |
| Reproductive Structures | Umbrella-like archegoniophores |
| Habitat | Moist soil, rock crevices, decaying logs, tree bark |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
Conclusion
Asterella africana is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its striking morphology to its vital ecological roles, this moss captivates and inspires. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these often-overlooked yet invaluable organisms for generations to come?