
B038-02_0.jpg from: http://taibif.tw/zh/namecode/200142
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt., commonly known as Diphyscium. This remarkable member of the Diphysciaceae family has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique features and fascinating biology.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt., it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as Bryophyta, encompass mosses (Bryopsida), liverworts, and hornworts. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

Diphyscium-foliosum2-MB-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/diphyscium-foliosum/
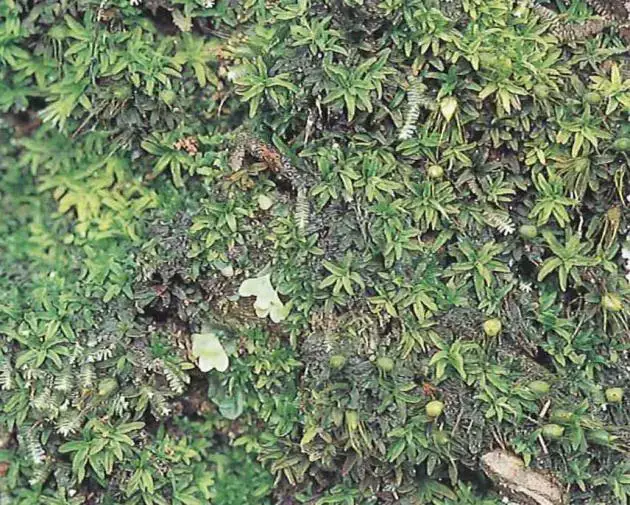
Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt. is a striking moss species that immediately catches the eye with its distinctive appearance. Its gametophytes

overall-sporophyte-300×290.png from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=2556
(the haploid, gamete-producing phase) consist of upright, unbranched stems adorned with spirally arranged leaves

nut%2Bmoss%2Bpicture.jpg from: https://bigworldtinyorganisms.blogspot.com/2015/10/nut-moss.html
. These leaves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and taper to a fine point, giving the moss a delicate yet striking silhouette.
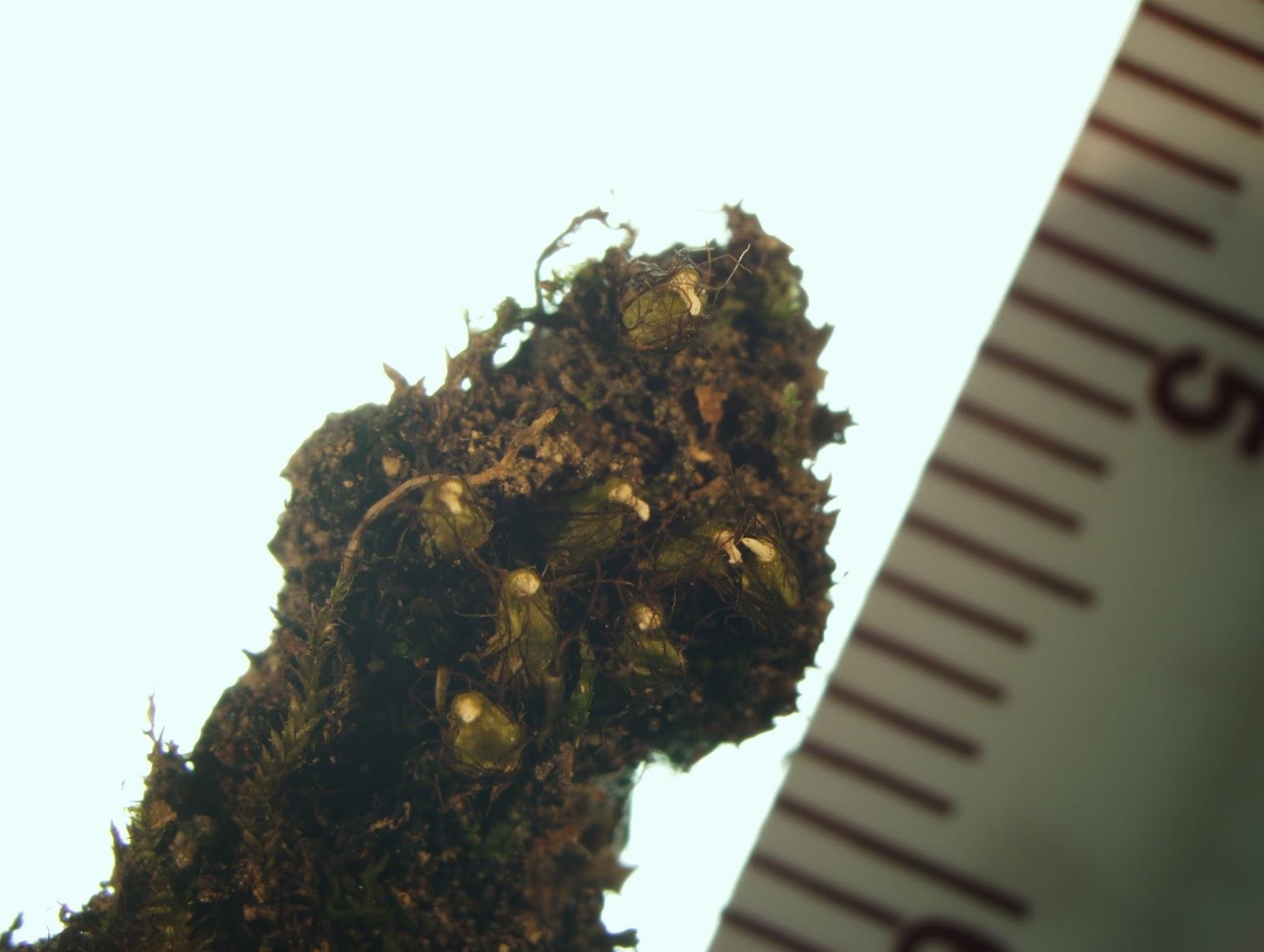
One of the most remarkable features of Diphyscium is its inflated, pouch-like structures found at the base of each leaf. These structures, known as leaf axils, are unique to this genus and serve as water reservoirs, allowing the moss to thrive in dry environments.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and cliffs. This moss is particularly well-adapted to environments with fluctuating moisture levels, thanks to its specialized leaf axils.
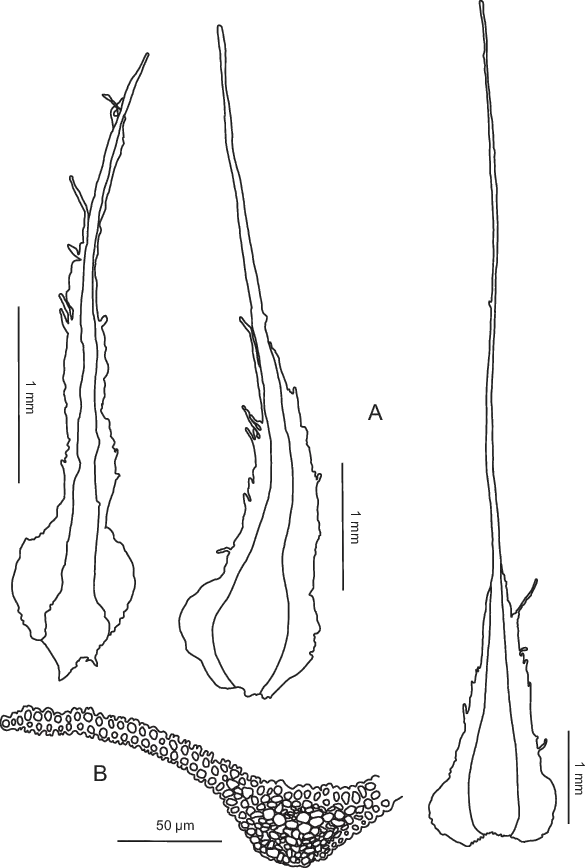
Diphyscium-fulvifolium-from-Enroth-70603-A-Three-inner-perichaetial-leaves-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Diphyscium-fulvifolium-from-Enroth-70603-A-Three-inner-perichaetial-leaves-B_fig3_47935239
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
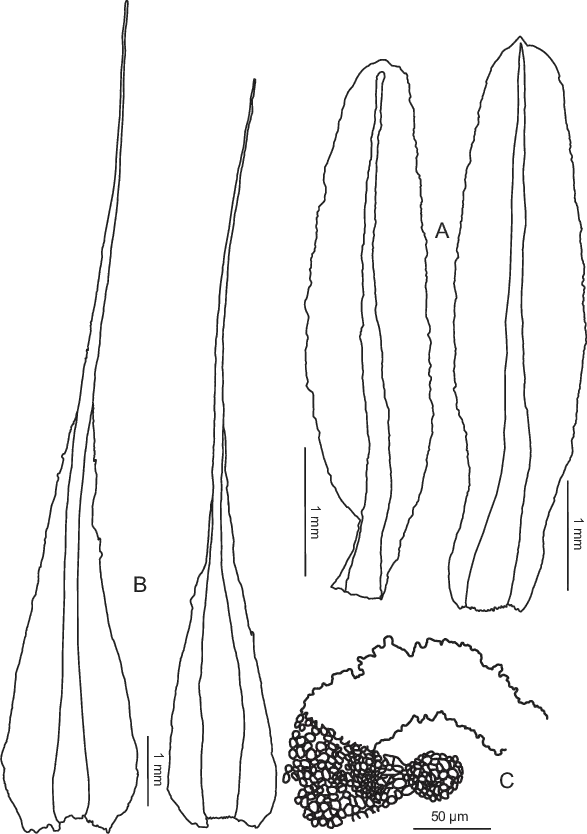

Diphyscium-fulvifolium-from-Enroth-70603-A-Leaves-B-Outer-perichaetial-leaves.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Diphyscium-fulvifolium-from-Enroth-70603-A-Leaves-B-Outer-perichaetial-leaves_fig2_47935239
Like many bryophytes, Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation,

Diphyscium_foliosum.jpg from: https://wildflowersearch.org/search?&tsn=16616
water retention, and nutrient cycling, while also providing a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Diphyscium is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to survive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
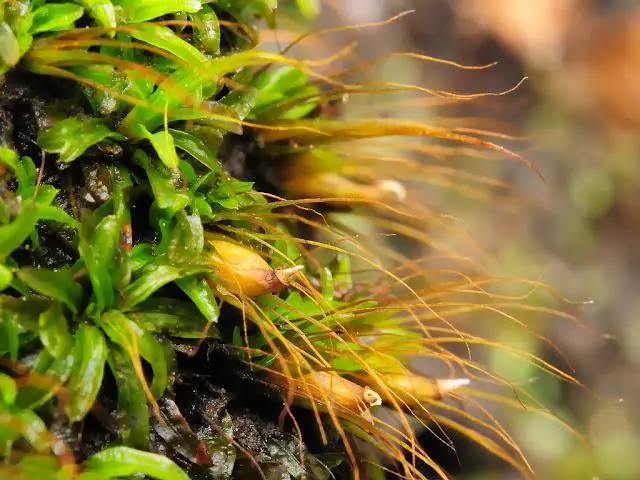

ikubigoke120307_1.jpg from: https://soyokaze2jp.blogspot.com/2019/02/blog-post_23.html
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt. growing on moist, shaded rock faces. The study highlighted the moss’s ability to colonize and thrive in these unique habitats, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Diphysciales |
| Family | Diphysciaceae |
| Genus | Diphyscium |
| Species | Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt. |
| Common Name | Diphyscium Moss |
Conclusion
Diphyscium fulvifolium Mitt., the remarkable Diphyscium moss, is a true testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, this unassuming yet extraordinary moss reminds us of the intricate beauty that can be found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the microscopic marvels around us, what other hidden gems might we be missing, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?