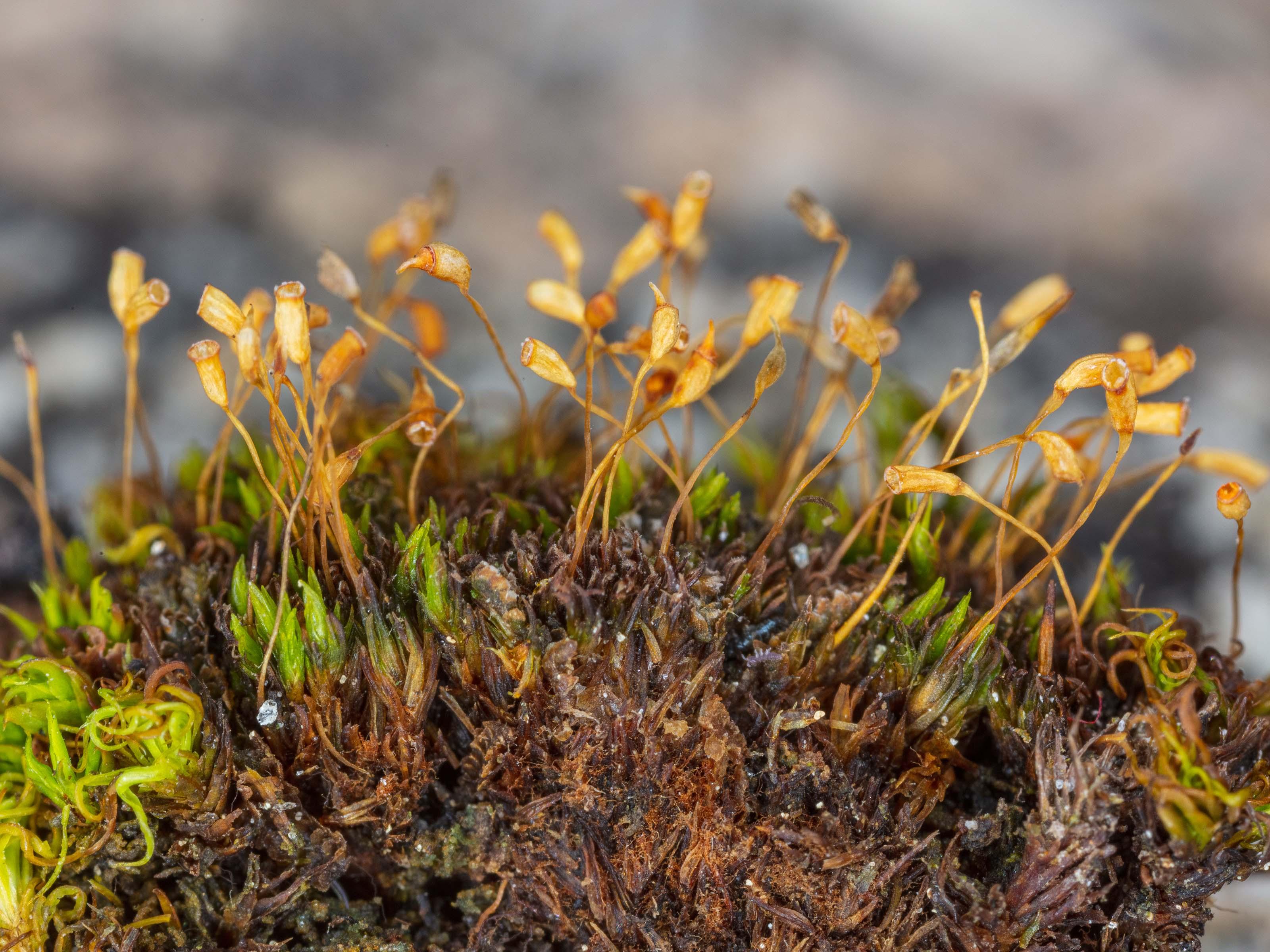

cnestrum_alpestre.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/dicranaceae/index.html
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts, to an enchanting exploration of the Cnestrum alpestre (Wahlenb. ex Huebener) Nyholm ex Mogensen moss, a captivating member of the Rhabdoweisiaceae
0.jpg from: https://plant.depo.msu.ru/open/public/item/MW9029490
family. Prepare to embark on a journey through the intricate world of this remarkable Bryophyte, where we’ll unravel its secrets and unveil the wonders that make it a true gem in the realm of mosses.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Cnestrum alpestre

0.jpg from: https://plant.depo.msu.ru/open/public/item/MW9029482
, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to the fascinating world of mosses. These diminutive yet resilient plants belong to the Bryophyta division, a group of non-vascular plants that have been around for millions of years. Mosses play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and providing habitats for countless other organisms.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Cnestrum alpestre is a true marvel of nature, with its delicate yet intricate structure. This moss forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, adorned with slender, erect stems that reach heights of up to 5 centimeters. Its leaves are

5973174959_1d5d4e8071_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/7208148@N02/5973174959/in/photostream/
lanceolate in shape, tapering to a fine point, and arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem. The leaf margins are entire, meaning they lack teeth or serrations, while the leaf cells are elongated and smooth.
One of the most distinctive features of Cnestrum alpestre is its capsule, which is erect and cylindrical, supported by a reddish-brown seta (stalk). This capsule houses the reproductive spores, ensuring the continuation of this remarkable species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Cnestrum alpestre is a true globetrotter, found across various regions of the world, including

carex-glareosa-schkur-ex-wahlenb-carex-glareosa-schkur-ex-wahlenb-2C1MFAX.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/carex-glareosa-schkur-ex-wahlenb-carex-glareosa-schkur-ex-wahlenb-image362483490.html
Europe, Asia, North America, and even parts of South America. This moss thrives in a wide range of habitats, from alpine and arctic regions to boreal forests and tundra environments

original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2727875
. It often grows on soil, rocks, or decaying wood, showcasing its adaptability and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Cnestrum alpestre plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It acts as a pioneer species, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a habitat and food source for numerous microscopic organisms, contributing to the intricate web of life.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Cnestrum alpestre is its ability to withstand extreme conditions, such as drought, freezing temperatures, and high levels of UV radiation. This resilience is attributed to its unique physiological and structural characteristics, including the ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available.
Case Studies/Examples

5973174961_b6043d9c21.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/7208148@N02/5973174961/in/photostream/
To illustrate the significance of Cnestrum alpestre, let’s explore a fascinating case study from the Arctic tundra. In this harsh environment, where vegetation is sparse and conditions are unforgiving, Cnestrum alpestre plays a crucial role in stabilizing the soil and providing a microhabitat for other organisms. Its dense mats help retain moisture and create a protective layer, allowing other plants to establish themselves and contributing to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Technical Table

julka_ftorkova_420592_o.jpg from: https://www.nahuby.sk/obrazok_detail.php?obrazok_id=420592

cnestrum_schisti1.jpg from: https://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/kalliotopposammal.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cnestrum alpestre (Wahlenb. ex Huebener) Nyholm ex Mogensen |
| Family | Rhabdoweisiaceae |
| Common Name | Cnestrum
 14388477891_422437e51a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/100087631@N08/14388477891/ |
| Growth Form | Dense cushions or mats |
| Stem Height | Up to 5 cm |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, tapering to a fine point |
| Leaf Margin | Entire (smooth) |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated and smooth |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical |
| Seta | Reddish-brown |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |
| Habitat | Alpine, arctic, boreal forests, tundra |
| Substrate | Soil, rocks, decaying wood |
| Ecological Role | Pioneer species, habitat provider, soil stabilizer |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, UV resistance, freezing tolerance |
Conclusion
As we bid farewell to the captivating world of Cnestrum alpestre, we are left with a profound appreciation for the resilience and adaptability of this remarkable moss. Its ability to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and ingenuity of nature.
Ponder this: If such a tiny organism can withstand the extremes of the Arctic tundra or the scorching rays of alpine regions, what other wonders might be hidden in the intricate tapestry of life? Perhaps the next time you encounter a seemingly insignificant patch of moss, you’ll pause and reflect on the extraordinary journey of these ancient and resilient plants.