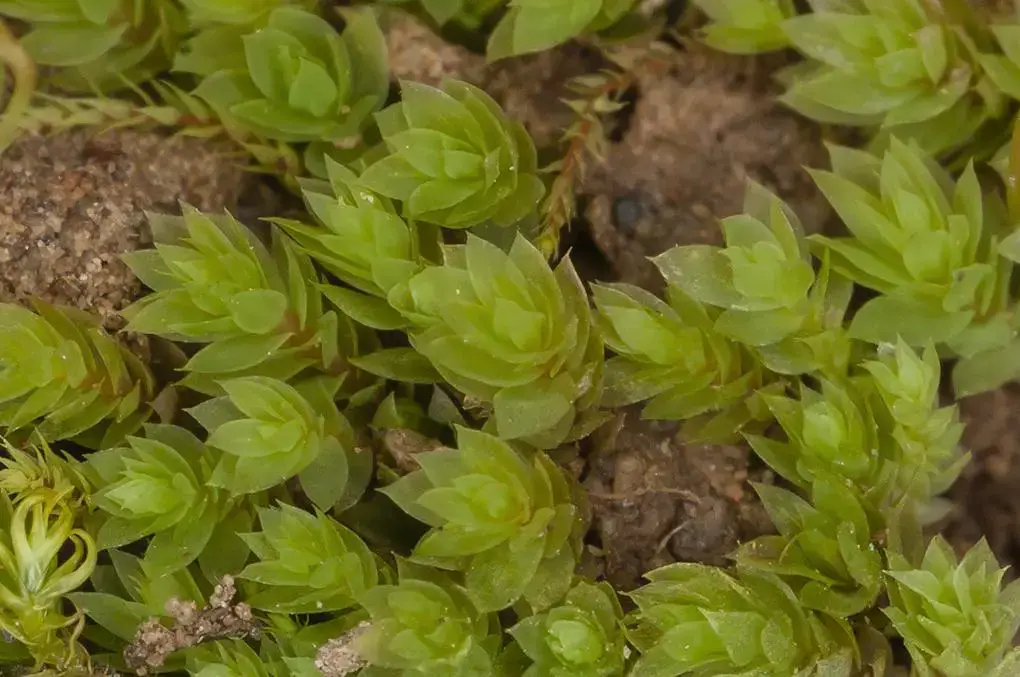

2604.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org//cgi-bin/species_query.cgi?where-calrecnum=12459
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Epipterygium tozeri (Grev.) Lindb. moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Mniaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss, commonly referred to as Epipterygium, has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this intriguing bryophyte.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of
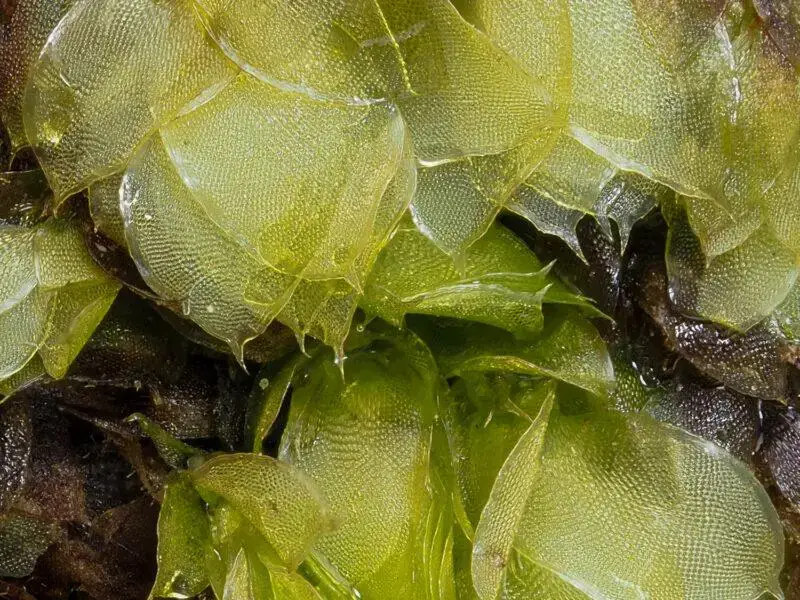

CH-Frenchmans-Creek-Calyptrochaeta-apiculata-3-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/epipterygium-tozeri/
Epipterygium tozeri, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments, from moist forests to arid deserts.
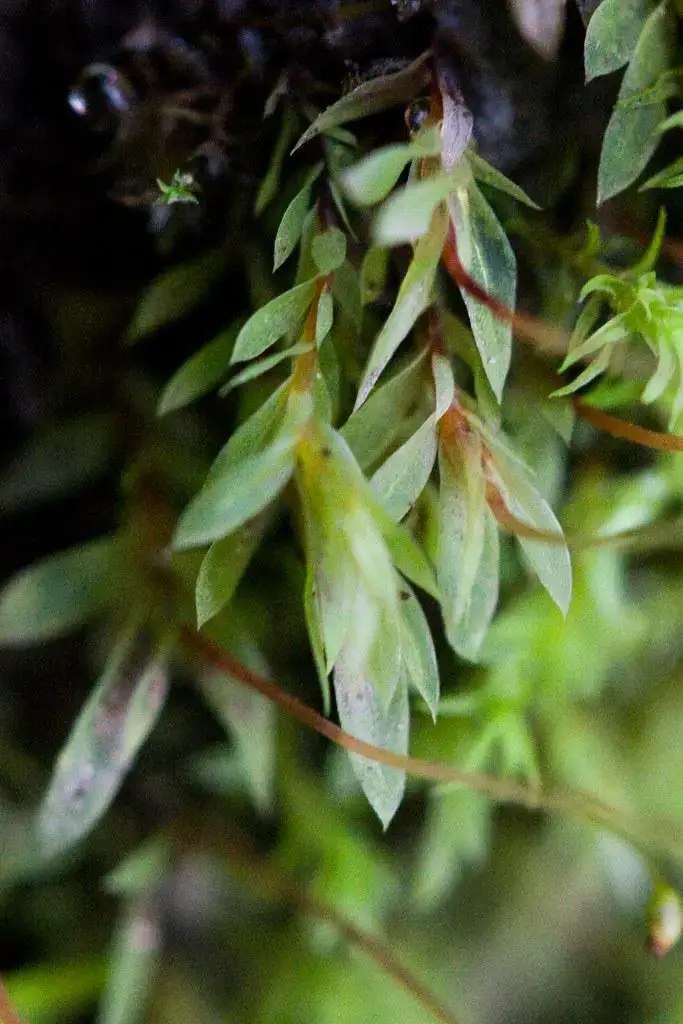

5524183783_eff27a50e7_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/ken-ichi/5524183783
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Epipterygium tozeri is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are erect and can reach up to 2 centimeters in height. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like structure known as an awn. This characteristic feature is a key identifier for the species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Epipterygium tozeri has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, including calcareous soils, rock crevices, and even disturbed areas such as old quarries and roadsides. This moss is often found in association with other bryophyte species, forming intricate and diverse communities.
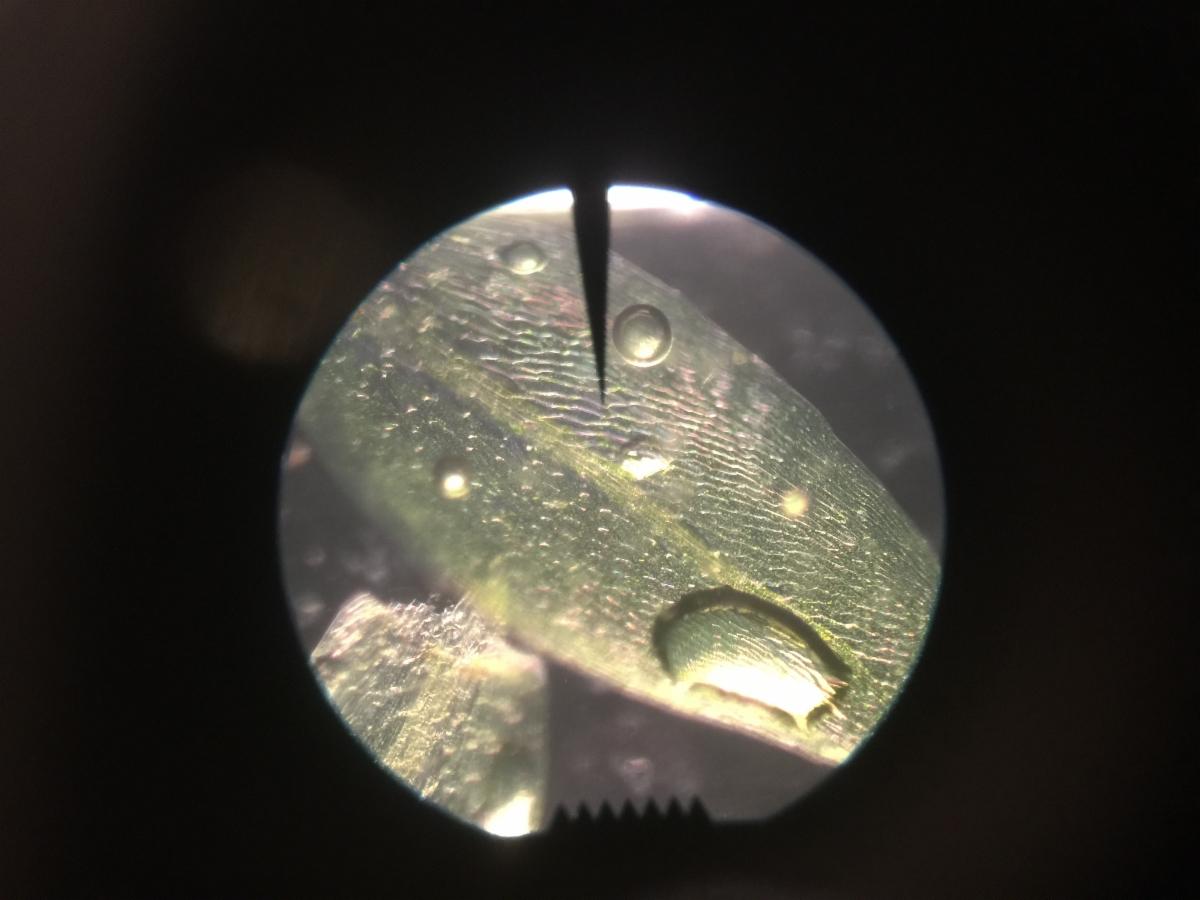

84093.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=12459
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Epipterygium tozeri plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, these mosses act as efficient water reservoirs, helping to regulate moisture levels in their immediate surroundings.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Epipterygium tozeri is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is intermittent.

37087213154_461cf3ed53.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/23980231@N07/37087213154/
Repartition-dEpipterygium-tozeri-Grev-Lindb-a-Porquerolles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Repartition-dEpipterygium-tozeri-Grev-Lindb-a-Porquerolles_fig41_328841440
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the United Kingdom, researchers investigated the impact of Epipterygium tozeri on soil stabilization in an abandoned quarry. The results showed that the presence of this moss significantly reduced erosion rates and facilitated the establishment of other plant species, contributing to the overall restoration of the site.
Technical Table

38299695214_0fa25e45bc.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/23980231@N07/38299695214/
akasujigoke-huti.jpg from: https://mikawanoyasou.org/koke/akasujigoke.htm

Epipterygiumtozeri.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/event/spring-meeting-2002-isle-of-wight/
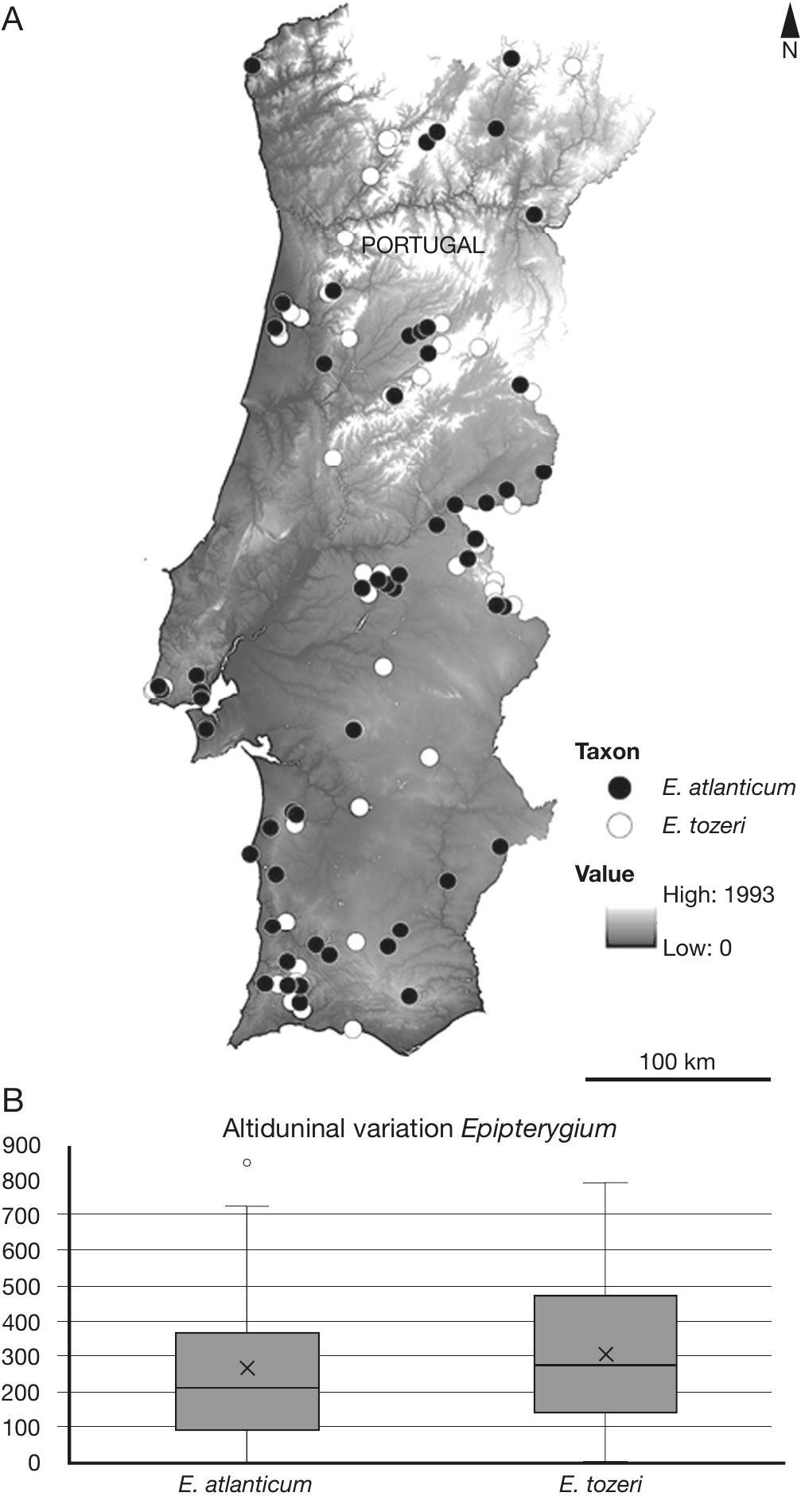
img-z7-13_195.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/cryptogamie-bryologie/volume-43/issue-13/cryptogamie-bryologie2022v43a13/Observations-on-the-Taxonomy-and-Distribution-of-Epipterygium-atlanticum-Hanusch/10.5252/cryptogamie-bryologie2022v43a13.full
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Mniaceae |
| Genus | Epipterygium |
| Species | tozeri |
| Common Name | Epipterygium moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Distinctive Feature | Awn (hair-like structure extending from leaf apex) |
Conclusion
The Epipterygium tozeri (Grev.) Lindb. moss, a member of the Mniaceae family, is a remarkable species that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better understand and protect these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?