
051f92efc684fd48548d6d2da5143add.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/81e0b54b26986b46d5ddb276c7ba1eba
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Erythrodontium julaceum (Schwägr.) Paris. Belonging to the Entodontaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as Erythrodontium. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant and explore its remarkable traits.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Erythrodontium julaceum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
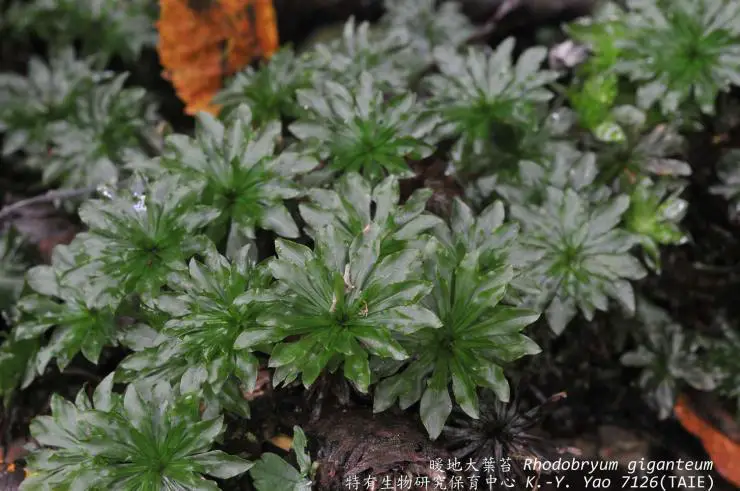
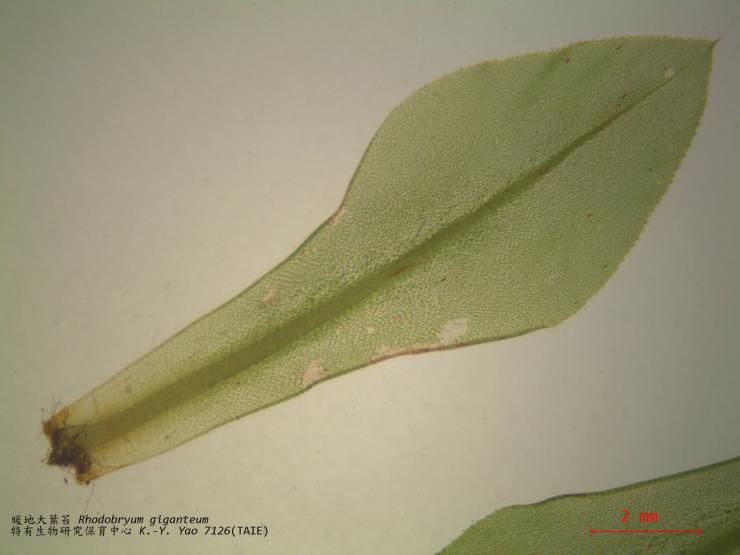
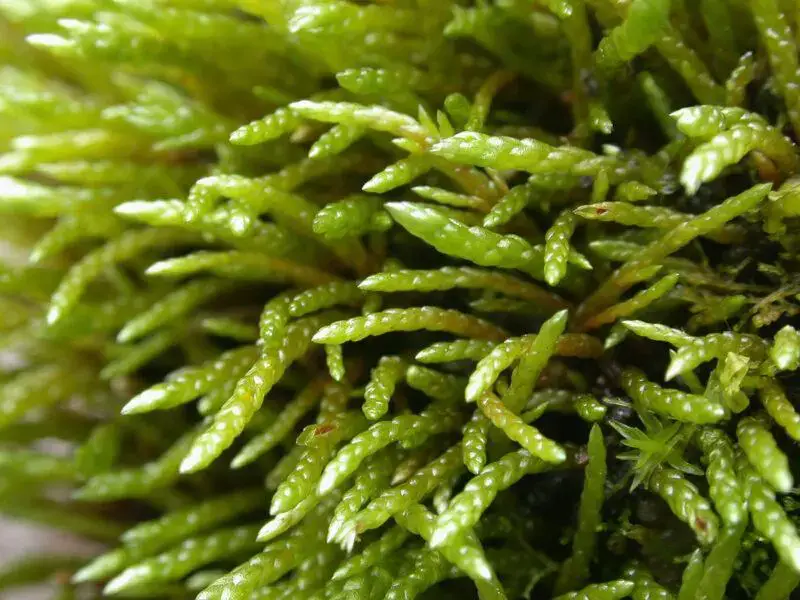
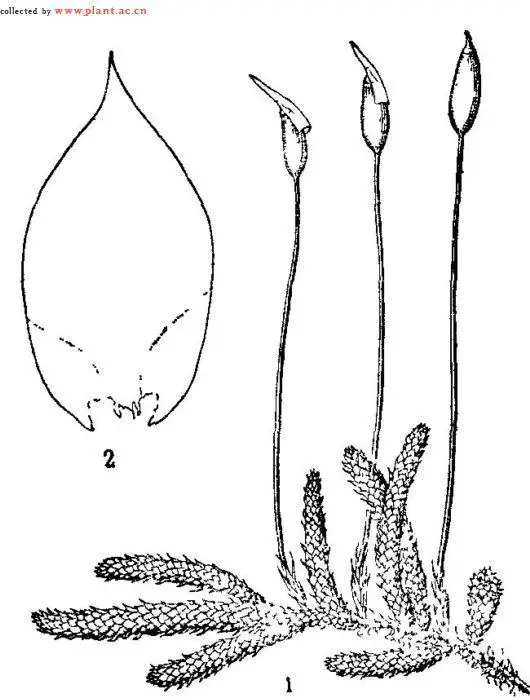
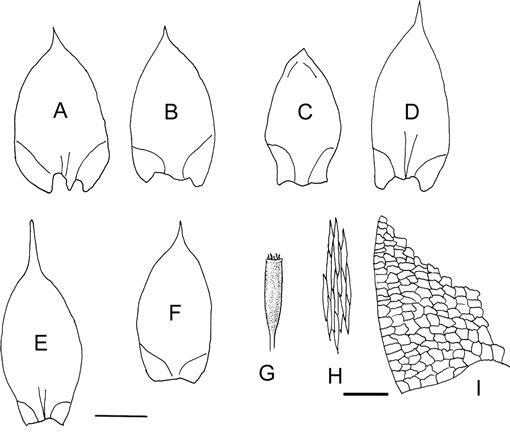
Erythrodontium julaceum is a striking moss species characterized by its vibrant red to reddish-brown coloration. This hue is derived from the presence of pigments called carotenoids, which protect the moss from harmful UV radiation. The plants form dense

3cc4000d2306c698feef42e1fcfe8816.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/819e99de6aebe5cefffd014f5b702f85
cushions or tufts, with slender stems and tiny, overlapping leaves that create a velvety appearance.
One of the key identifying features of Erythrodontium julaceum is its distinctive double peristome – a set of tooth-like structures surrounding the opening of the capsule (spore-bearing structure). This intricate peristome aids in the controlled release of spores, ensuring successful reproduction and dispersal.

JULACEUM-B-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/bryum-julaceum/
188.jpg from: https://www.zhiwutong.com/dan_tu/9/7559.htm
Global Distribution and Habitat
Erythrodontium julaceum is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Europe, Asia, and New Zealand
cdbf6c81800a19d8bc3ef25f63aa958ba61ea8d3e813-bkimg-process,v_1,rw_1,rh_1,pad_1,color_ffffff from: https://baike.baidu.com/item/异叶提灯藓/50007391
. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
This moss species often grows on decaying logs, tree trunks, and soil, forming vibrant carpets that add a touch of natural beauty to its surroundings. Its ability to colonize diverse substrates and tolerate varying moisture levels contributes to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

PHH0034014b.png from: https://cryptogam-phh.hcmus.edu.vn/index.php/en/bryophtes?page=30
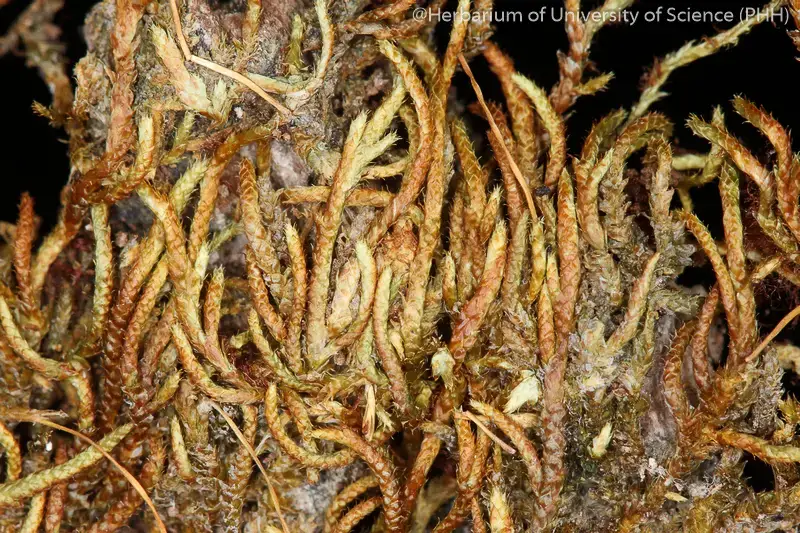
Despite its diminutive size, Erythrodontium julaceum plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. These mosses act as
i0007-2745-112-4-804-f04.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/The-Bryologist/volume-112/issue-4/0007-2745-112.4.804/A-taxonomic-revision-of-span-classgenus-speciesErythrodontiumspan-Entodontaceae/10.1639/0007-2745-112.4.804.full
pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species by creating a suitable microclimate and retaining moisture.
Additionally, Erythrodontium julaceum serves as a crucial habitat for various microscopic organisms, such as tardigrades (water bears) and rotifers, which find refuge within the intricate structure of the moss cushions. This symbiotic relationship highlights the interconnectedness of life and the importance of preserving even the smallest components of an ecosystem.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Erythrodontium julaceum is a common sight in old-growth forests, where it thrives on decaying logs and tree trunks. Its vibrant red hue adds a striking contrast to the lush green surroundings, creating a visually captivating scene for nature enthusiasts and photographers alike.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Gametophyte | Cushion or tuft-forming, reddish-brown |
| Leaves | Ovate-lanceolate, acuminate, with a single costa |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, erect, with a double peristome |
| Spores | Spherical, finely papillose |
| Habitat | Decaying logs, tree trunks, soil, rocks |
Conclusion
Erythrodontium julaceum is a true marvel of nature, a testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. From its striking appearance to its ecological significance, this moss species captivates the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?