2020-10-15-16-41-29-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/heterocladium-heteropterum/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance:

2975_Heterocladium_heteropterum_2015_04_10_4462.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=heterocladium_heteropterum&id=2975
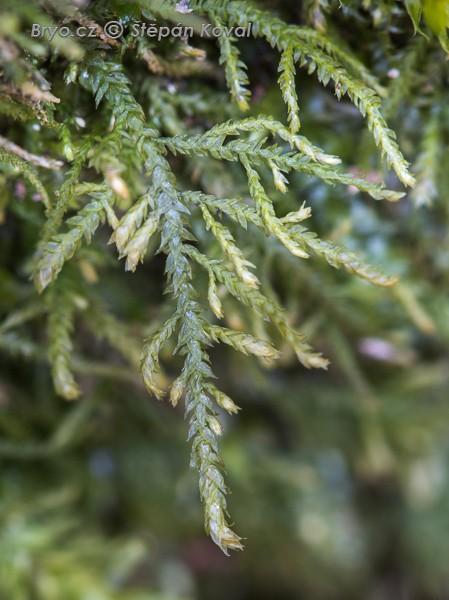
Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp., a member of the Lembophyllaceae family. Often referred to simply as Heterocladium, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its delicate beauty and remarkable adaptations.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.

2969_Heterocladium_heteropterum_2015_03_08_4240.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=heterocladium_heteropterum&id=2969
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
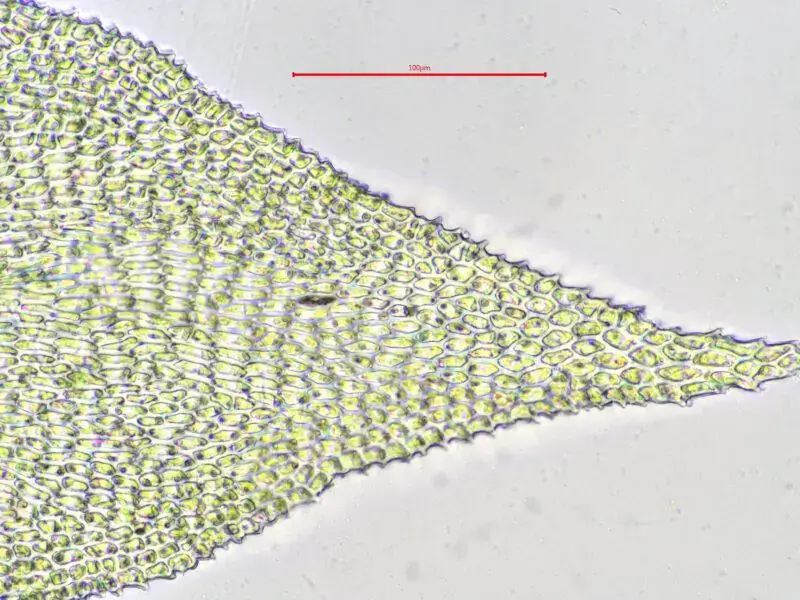
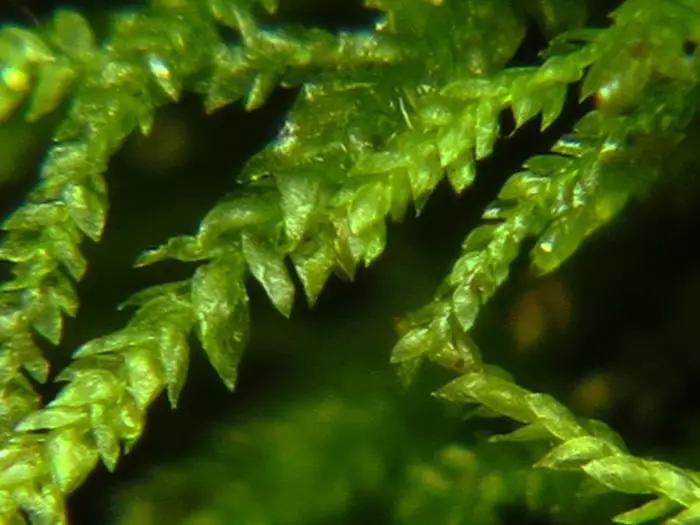
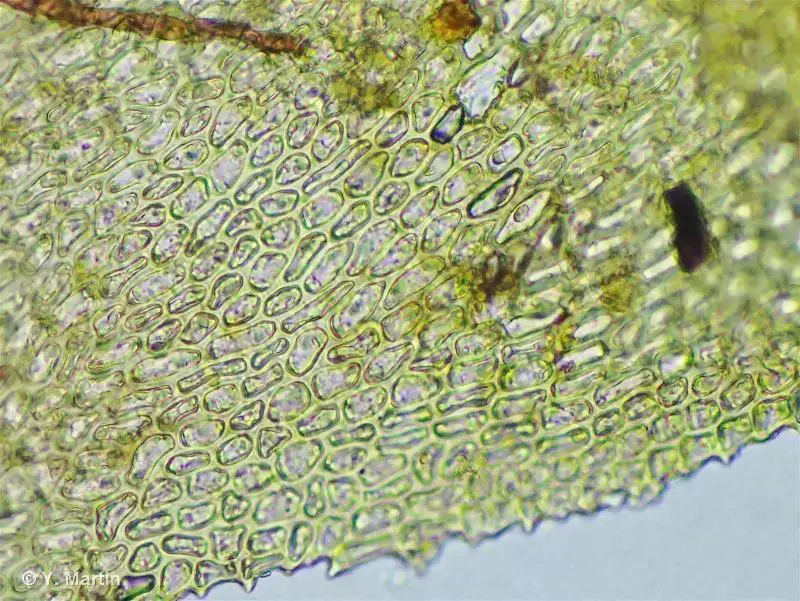
Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp. is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, feathery branches that create a lush, carpet-like appearance. The leaves are small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem.

Heterocladium%2Bheteropterum%2Bvar%2Bflaccidum%2B11.3.16%2BCwm%2BNofydd%2BP1070867.JPG from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/03/heterocladium-heteropterum-var-flaccidum.html
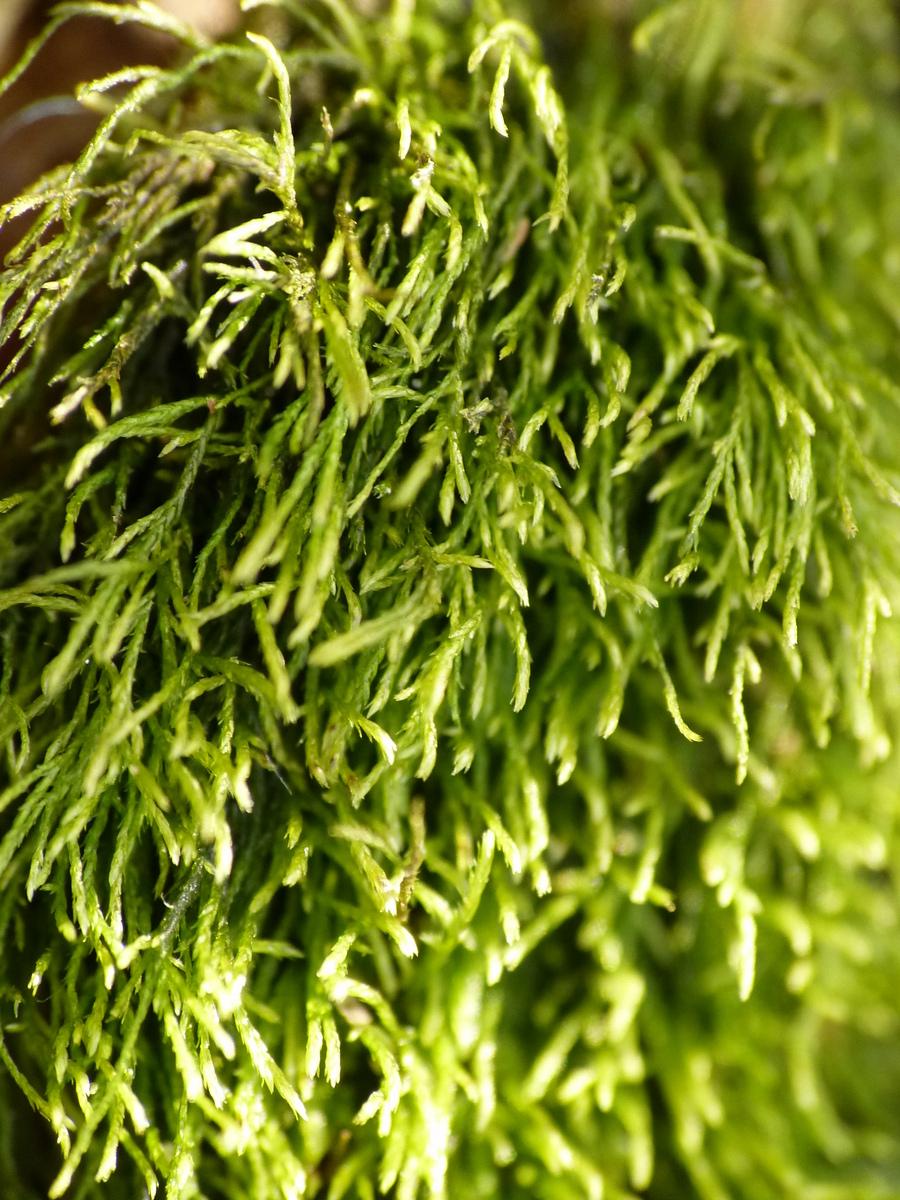
One of the most distinctive features of Heterocladium is its heteromorphic branching pattern, which gives rise to its scientific name. The primary stems produce two types of branches: vegetative branches, which are shorter and more densely leaved, and flagelliform branches, which are longer, more slender, and sparsely leaved. This unique branching pattern is a key identifying characteristic of the species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
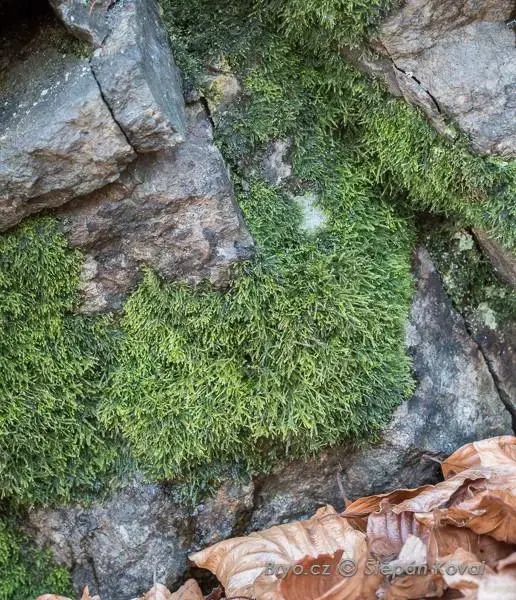
Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp. is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in temperate and boreal regions. It can be found in various habitats, including moist and shaded areas in forests, on rotting logs, and on the bark of trees. This moss prefers acidic substrates and is often associated with coniferous or mixed forests.
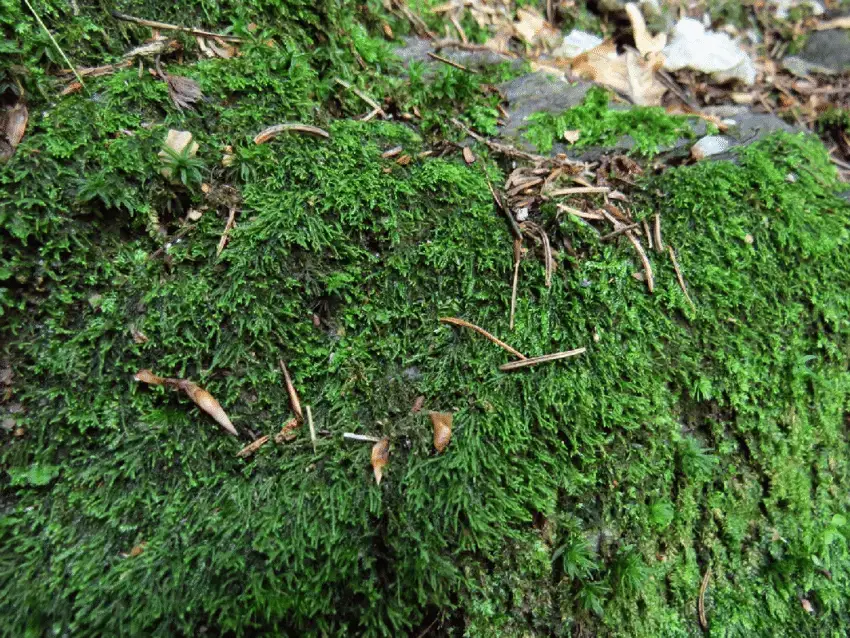

Habit-of-Heterocladium-heteropterum.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Habit-of-Heterocladium-heteropterum_fig4_311879137
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Heterocladium plays a vital role in forest ecosystems. Its dense mats help retain moisture, create microhabitats for other organisms, and contribute to nutrient cycling. Additionally, the moss serves as a food source and nesting material for various invertebrates and small mammals.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Heterocladium
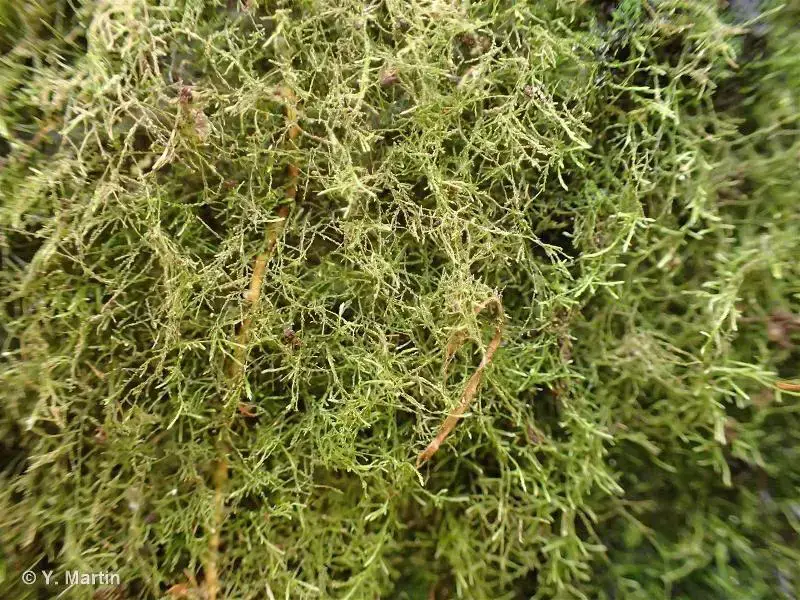

382044.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/388800
is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp. is a common sight in old-growth forests, where it forms lush carpets on decaying logs and tree trunks. These moss mats provide crucial habitat for a diverse array of invertebrates, including mites, springtails, and beetles, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.

842949.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/842946.html
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Lembophyllaceae |
| Genus | Heterocladium |
Species
 382045.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5190 |
heteropterum Schimp. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Branching | Heteromorphic |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded forests |
| Substrate | Rotting logs, tree bark |
Conclusion
Heterocladium heteropterum Schimp., a unassuming yet remarkable moss, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, Heterocladium reminds us of the beauty and complexity that can be found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where towering trees and vibrant wildflowers often steal the spotlight, how can we cultivate a deeper appreciation for the unsung heroes like Heterocladium, whose quiet presence sustains entire ecosystems?