
image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jorgil/27510425776/
Introduction
Prepare to embark on a captivating journey into the realm of Bryophyta, the enchanting world of mosses. Among the myriad species that adorn our planet, one stands out as a true marvel: Lepidopilum diaphanum (Sw. ex Hedw.) Mitt., a member of the Pilotrichaceae family, commonly known as Lepidopilum. This unassuming yet extraordinary moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide, and today, we’ll delve into its fascinating intricacies.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Lepidopilum diaphanum

image from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/16114511150197922/
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These diminutive plants belong to the Bryophyta division, a group of non-vascular plants that play a crucial role in various ecosystems. Mosses are often overlooked, but their significance cannot be overstated, as they contribute to soil formation, water retention, and provide habitats for countless microorganisms.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lepidopilum diaphanum is a true masterpiece of nature, with its delicate fronds and intricate structures. This moss is characterized by its slender, creeping stems that form dense mats or cushions. Its leaves are small, ovate to lanceolate, and acuminate, with a distinctive diaphanous (translucent) appearance. The leaf margins are finely serrated, adding to the moss’s intricate beauty.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lepidopilum diaphanum is widely distributed across various regions, including tropical and subtropical areas of Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. This moss thrives in humid, shaded environments, often found growing on tree trunks, rocks, and soil in tropical rainforests and cloud forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

image from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/mossgardenbycheriechi-cheriechisgarden-moss-collection-bryum-capillare-lex-hedw–557390891371776183/
Despite its diminutive size, Lepidopilum diaphanum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a

image from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5685
microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lepidopilum diaphanum is its ability to withstand desiccation
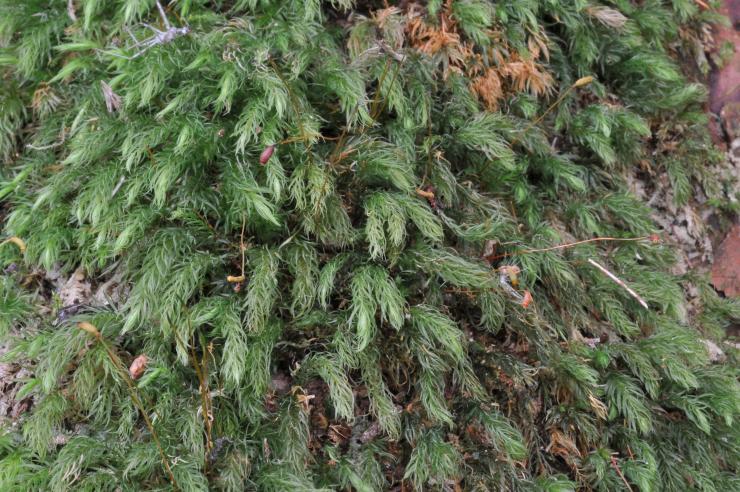

image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/dd18a1d727ae9348b279c46e3323b4a5
. During dry periods, the moss can
image from: https://moonmoths.blogspot.com/2011/04/melin-mynach-epiphytes.html
curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to survive in diverse environments and contributes to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve in Costa Rica, Lepidopilum diaphanum is a prominent component of the epiphytic moss community, adorning the trunks and branches of trees. Its presence contributes to the rich biodiversity of this unique ecosystem, providing habitat for various invertebrates and playing a crucial role in nutrient cycling.

image from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5685
Technical Table

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pogonatum-urnigerum-Hedw-P-Beauv-A-fresh-habit-B-male-gametophyte-with-perigonia_fig10_331675612

image from: https://www.pinterest.es/pin/mossgardenbycheriechi-cheriechisgarden-moss-bryum-capillare-lex-hedw-and-funaria-hygrometrica-hedw-collection–557390891371715761/

image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/dd18a1d727ae9348b279c46e3323b4a5
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lepidopilum diaphanum (Sw. ex Hedw.) Mitt. |
| Family | Pilotrichaceae |
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate, acuminate |
| Leaf Margin | Finely serrated |
| Habitat | Humid, shaded environments (tropical rainforests, cloud forests) |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions (Central and South America, Africa, Asia, Oceania) |