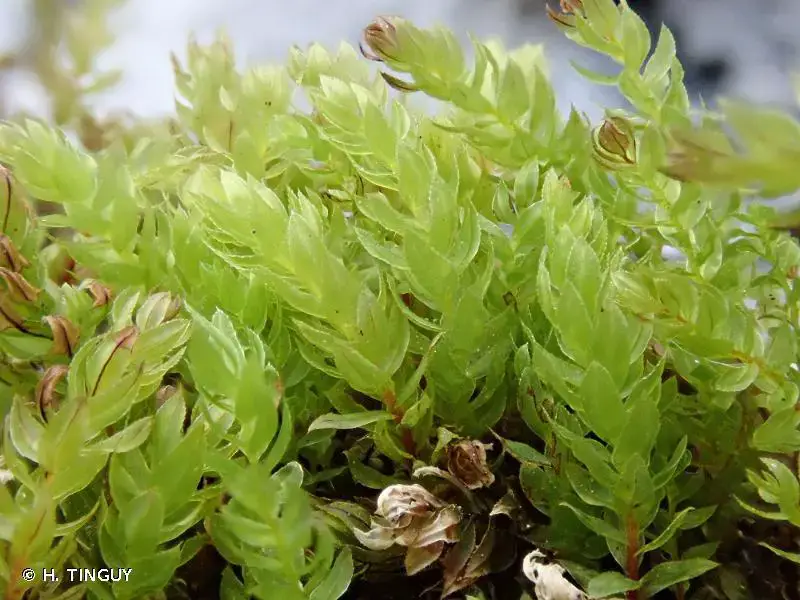

297426.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4927/tab/taxo?lg=en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Mnium thomsonii Schimp. moss stands out as a true marvel of nature. Belonging to the Mniaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Mnium thomsonii Schimp., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as

211847.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4927
Bryophyta or Bryopsida, are among the oldest and most resilient life forms on our planet. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to the intricate web of life.
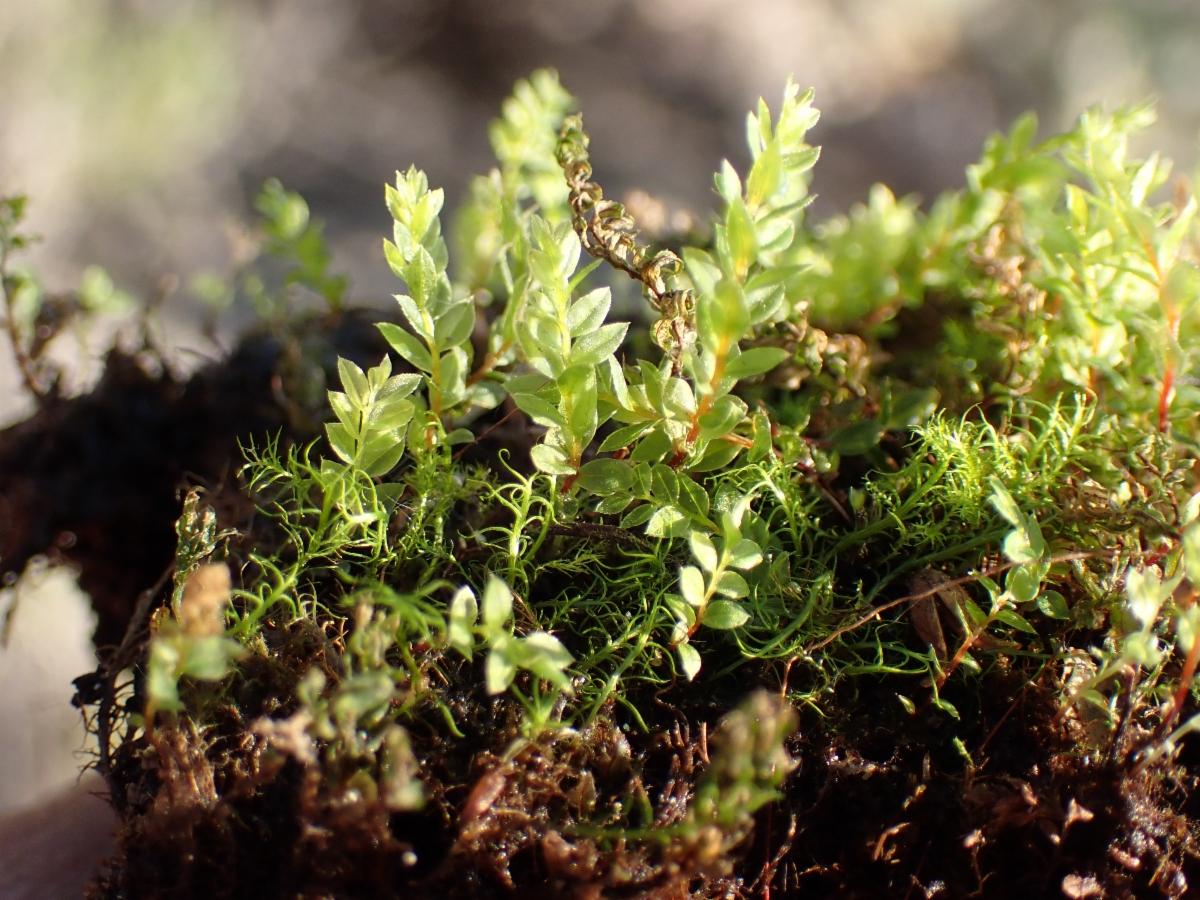

141794.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=13986
Main Content
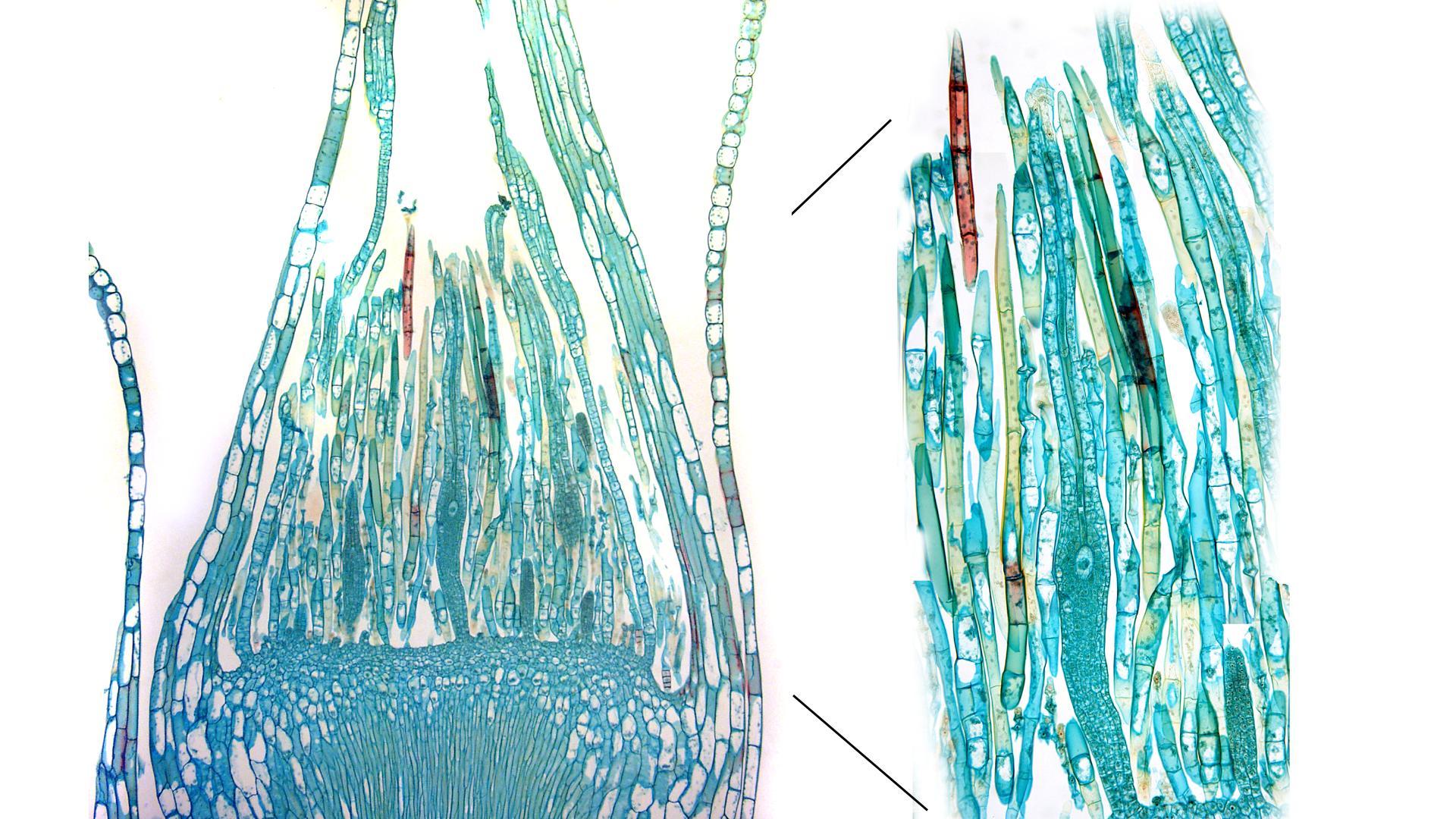
Morphology and Identification
Mnium thomsonii Schimp., commonly referred to as Mnium, is a acrocarpous moss species characterized by its distinctive features. Its gametophytes form dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, with stems that can reach up to several centimeters in height. The leaves are ovate to lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. When mature, the moss produces capsules (sporophytes) atop slender setae, which aid in spore dispersal.
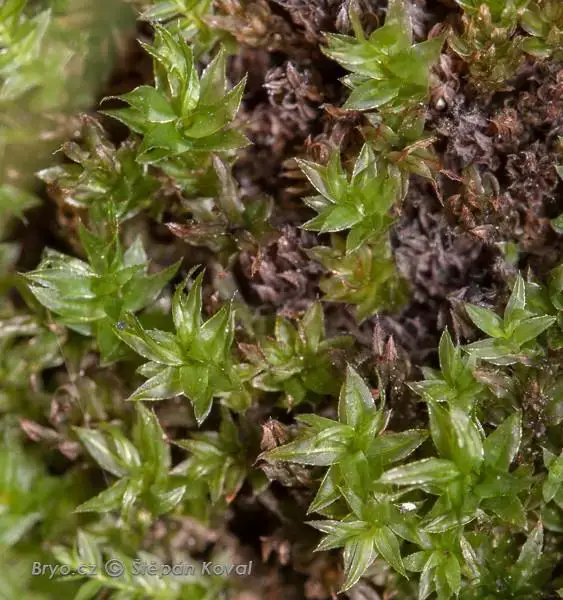

3569_Mnium_thomsonii_2008_07_29_0533.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=mnium_thomsonii&id=3569
Global Distribution and Habitat
Mnium thomsonii Schimp. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in a diverse range of habitats. From moist, shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, this resilient moss can adapt to a variety of conditions. Its ability to colonize new areas and withstand environmental stresses contributes to its widespread distribution.
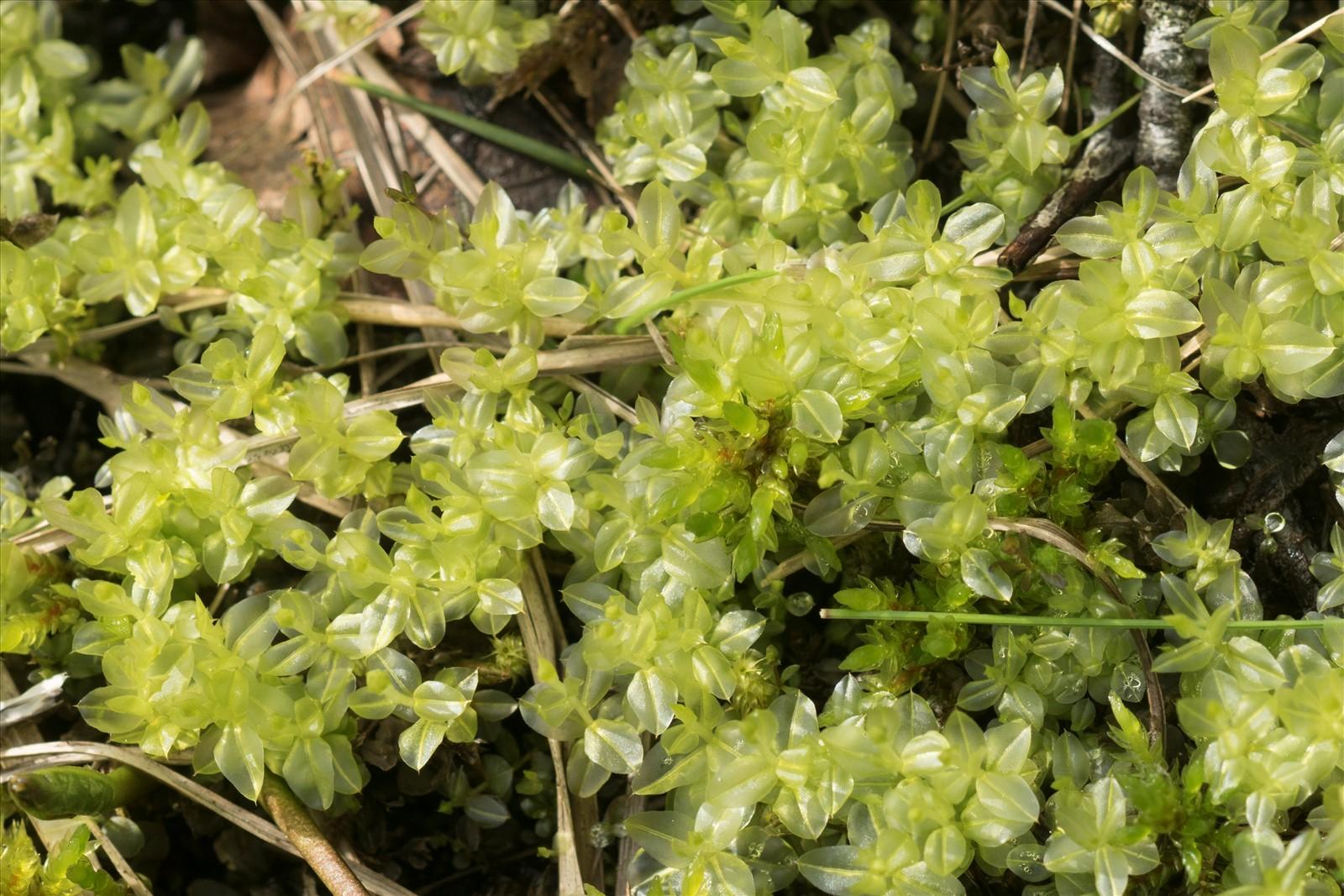

DSC02314_1600.jpg from: https://www.preservons-la-nature.fr/flore/taxref/27155.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Mnium thomsonii Schimp. plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize soil and create favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, mosses like Mnium act as efficient water reservoirs, retaining moisture and preventing soil erosion.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Mnium thomsonii Schimp. is its ability to undergo desiccation and revive when water becomes available again. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive in harsh environments and contributes to its resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest ecosystem, researchers found that Mnium thomsonii Schimp. played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of seedlings and promoting biodiversity. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and create a favorable microclimate supported the growth of various plant species, contributing to a thriving and diverse ecosystem.
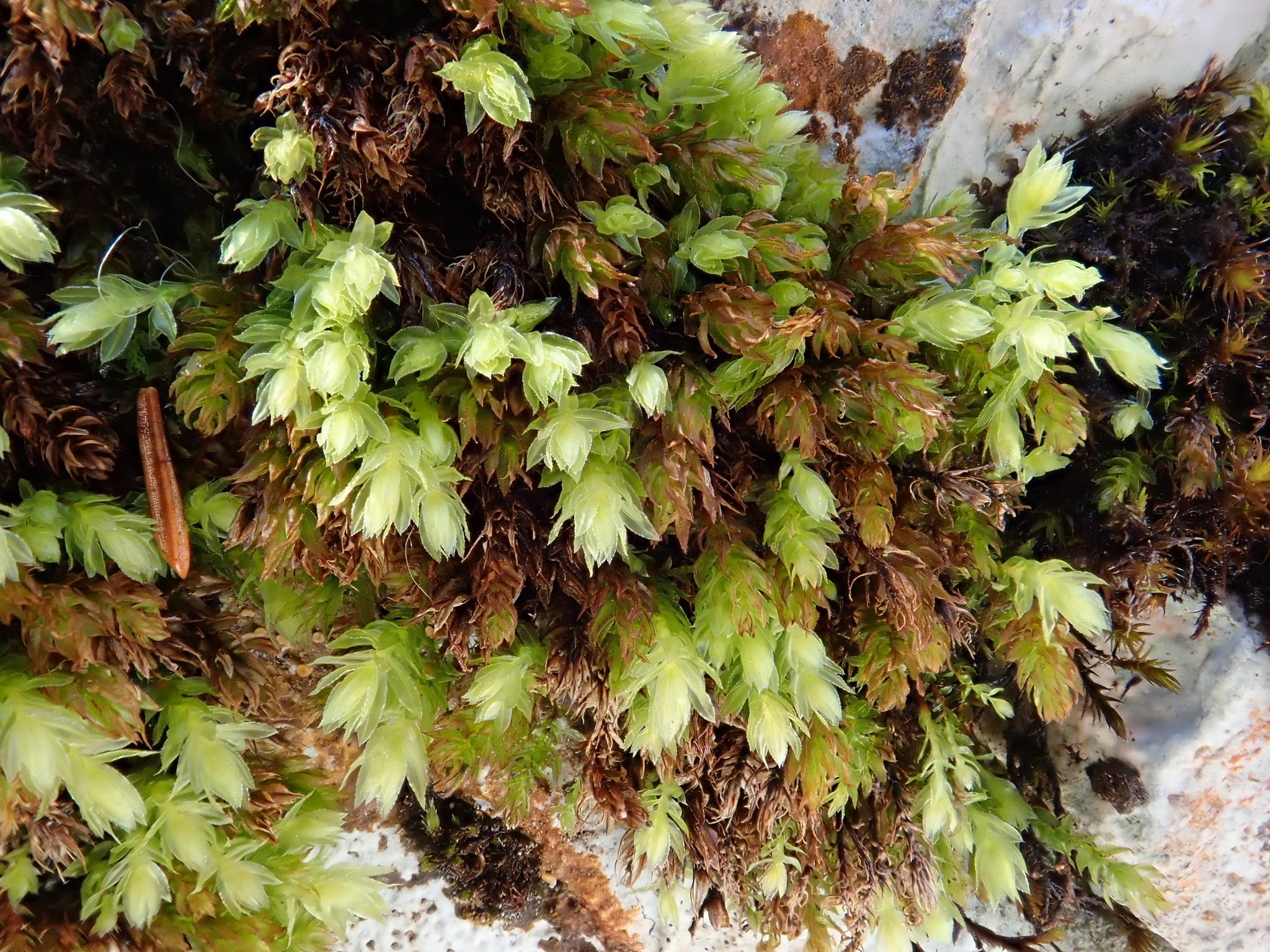

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/5282700

C0116209-Mnium_moss.jpg from: https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/439362/view/mnium-moss

240px-Mnium_thomsonii_(a%2C_142806-474610)_8707.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Mnium_thomsonii
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Family | Mniaceae |
| Genus | Mnium |
| Species | Mnium thomsonii Schimp. |
| Common Name | Mnium |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded forests, rocky outcrops, urban environments |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
Conclusion
The Mnium thomsonii Schimp. moss, a member of the Mniaceae family, is a true testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. From its distinctive morphology to its global distribution and ecological significance, this unassuming plant continues to captivate moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the intricate beauty and complexity that nature holds, even in its smallest forms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush, verdant carpet of moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the wonders of
h1380-23b41.jpg from: https://search.library.wisc.edu/digital/A4NQEQTAFSBKMV8P
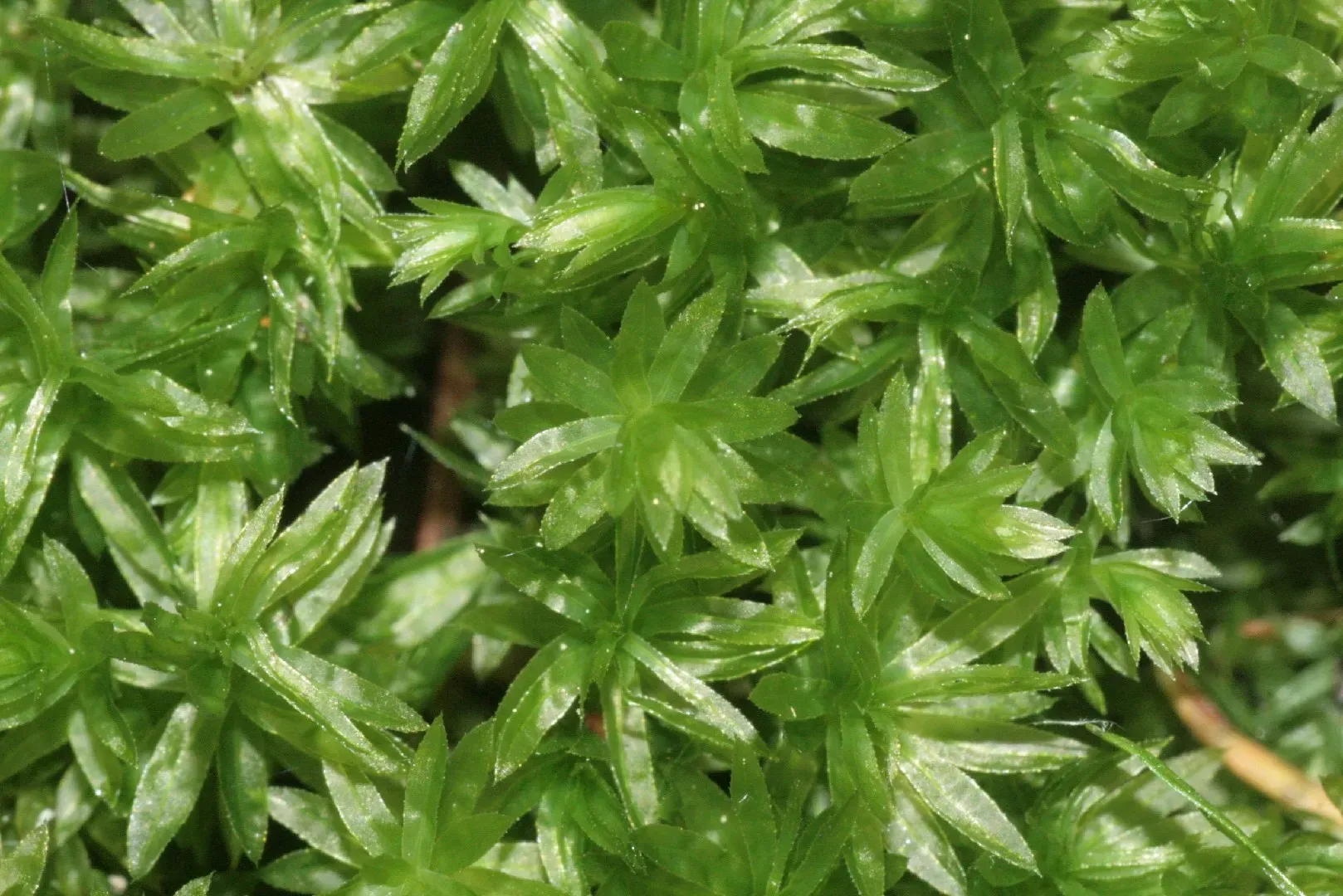

152364759436492800.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/wiki/Mnium.html
Mnium thomsonii Schimp., a true marvel of the plant kingdom.