
655372_2c34ee86.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/655372.html
Exploring the Fascinating World of Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche Moss
Introduction
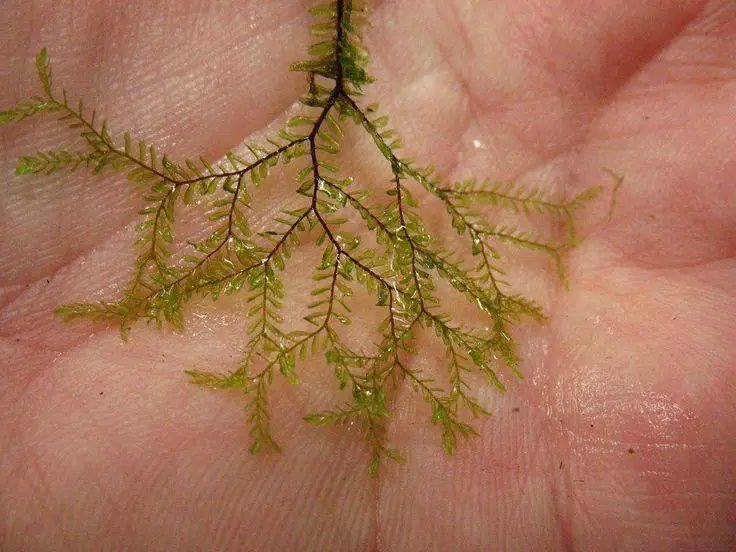

a33343a8ad0be7ecb9cd164fa427426b.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/a-liverwort-in-my-hand-closely-related-to-plagiochila–116882552818198230/
Have you ever stopped to admire the tiny, intricate plants growing on trees and rocks in the forest? One of these miniature wonders is Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche, a species of moss in the Plagiochilaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the captivating world of this unique moss and learn about its morphology, habitat, ecological roles, and more. Get ready to be amazed by the hidden beauty of Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche!
Background on Plagiochila Mosses
Plagiochila is a genus of leafy liverworts in the Plagiochilaceae family. There are over 400 species of Plagiochila found worldwide, mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. These mosses are characterized by their flattened, translucent leaves arranged in two rows on either side of the stem. Plagiochila mosses play important ecological roles as pioneer species and in nutrient cycling in their habitats.
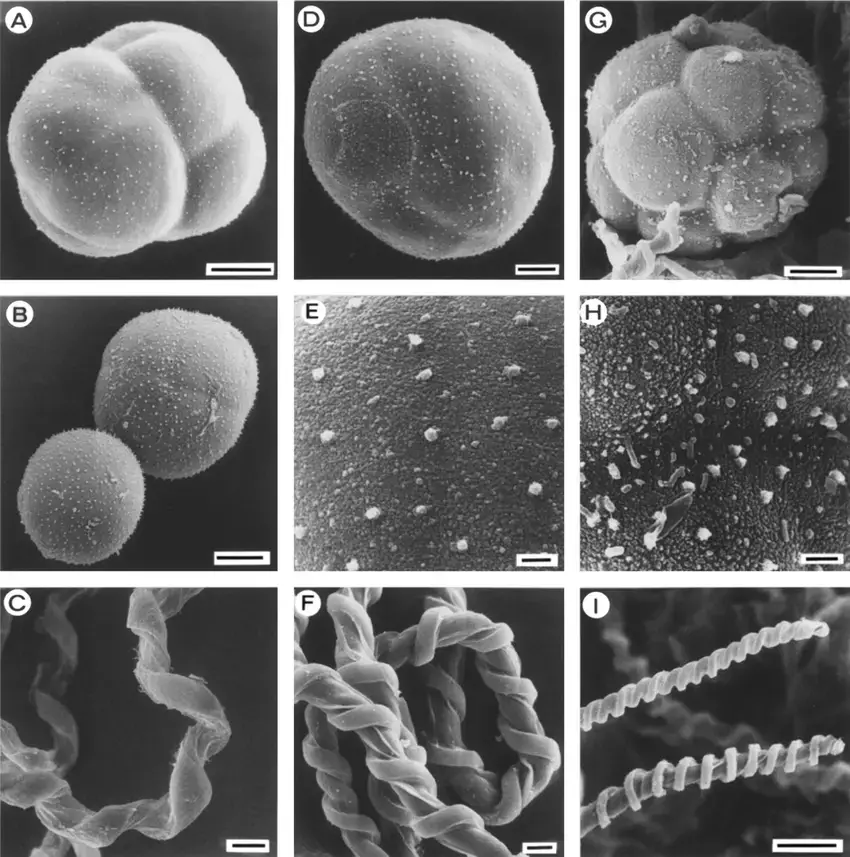
Plagiochila-diversifolia-Lindenb-and-Gottsche-A-D-F-P-longispina-Lindenb-and.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-diversifolia-Lindenb-and-Gottsche-A-D-F-P-longispina-Lindenb-and_fig1_226186164
Morphology and Identification
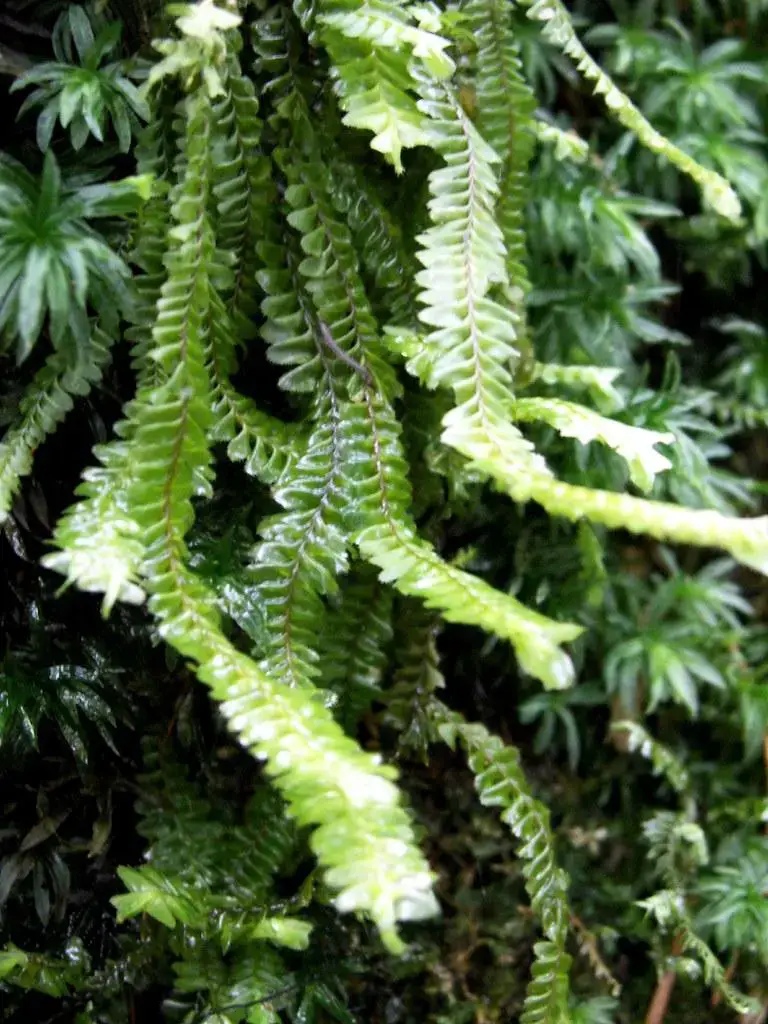
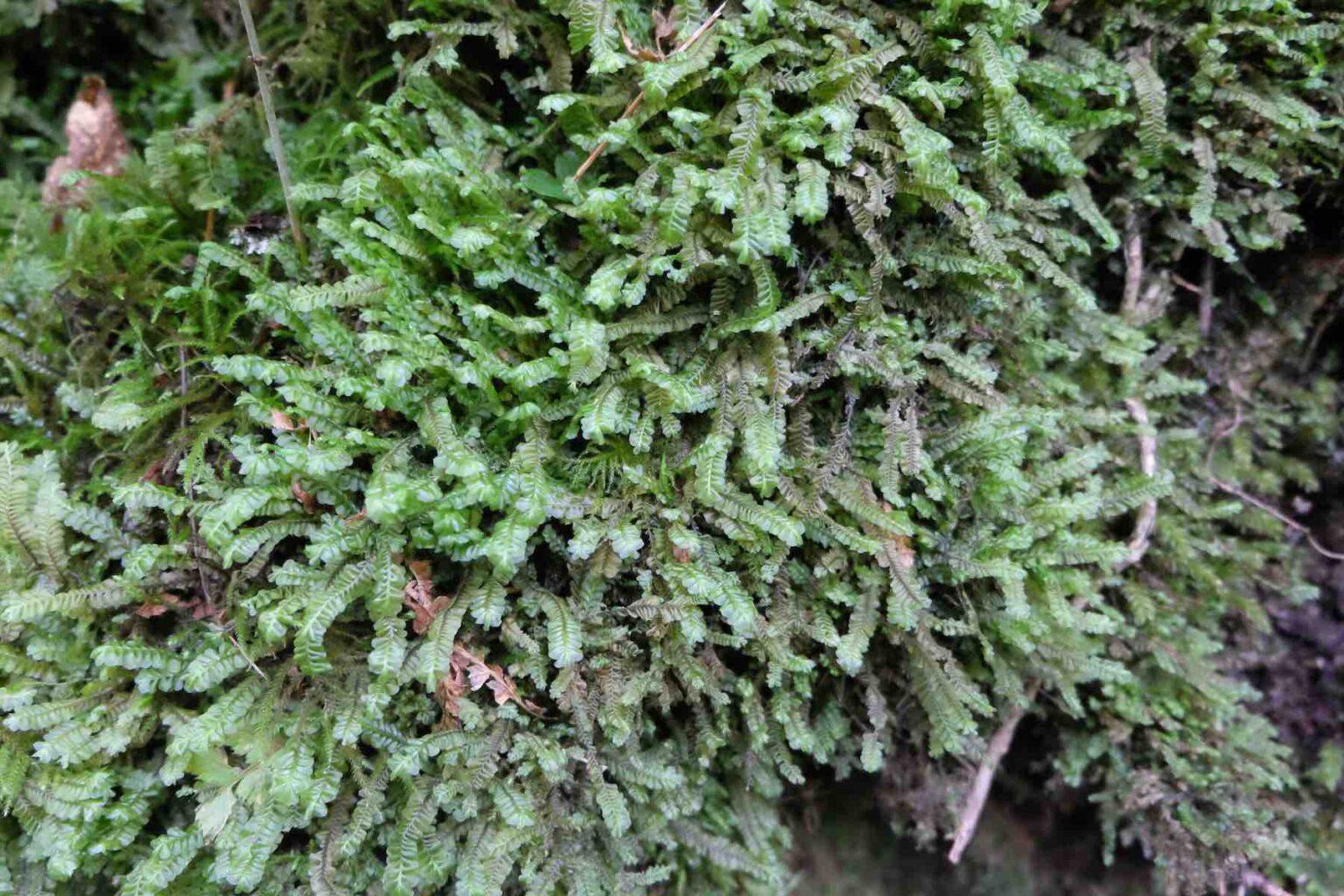
Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche is a small to medium-sized moss, typically growing in dense mats. The

4141241857_842346e043_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/costarica1/4141241857/
stems are creeping to ascending, irregularly branched, and can reach 2-5 cm long. The leaves are oblong to obovate, 1.5-2.5 mm long, with a rounded to truncate apex. They are translucent, yellowish-green in color, and have no underleaves. The leaf margins are entire to slightly toothed.

Plagiochila-asplenioides-08-10-23-1536×1024.jpg from: https://www.plantlife.org.uk/whats-that-moss-id-tips-for-beginners/
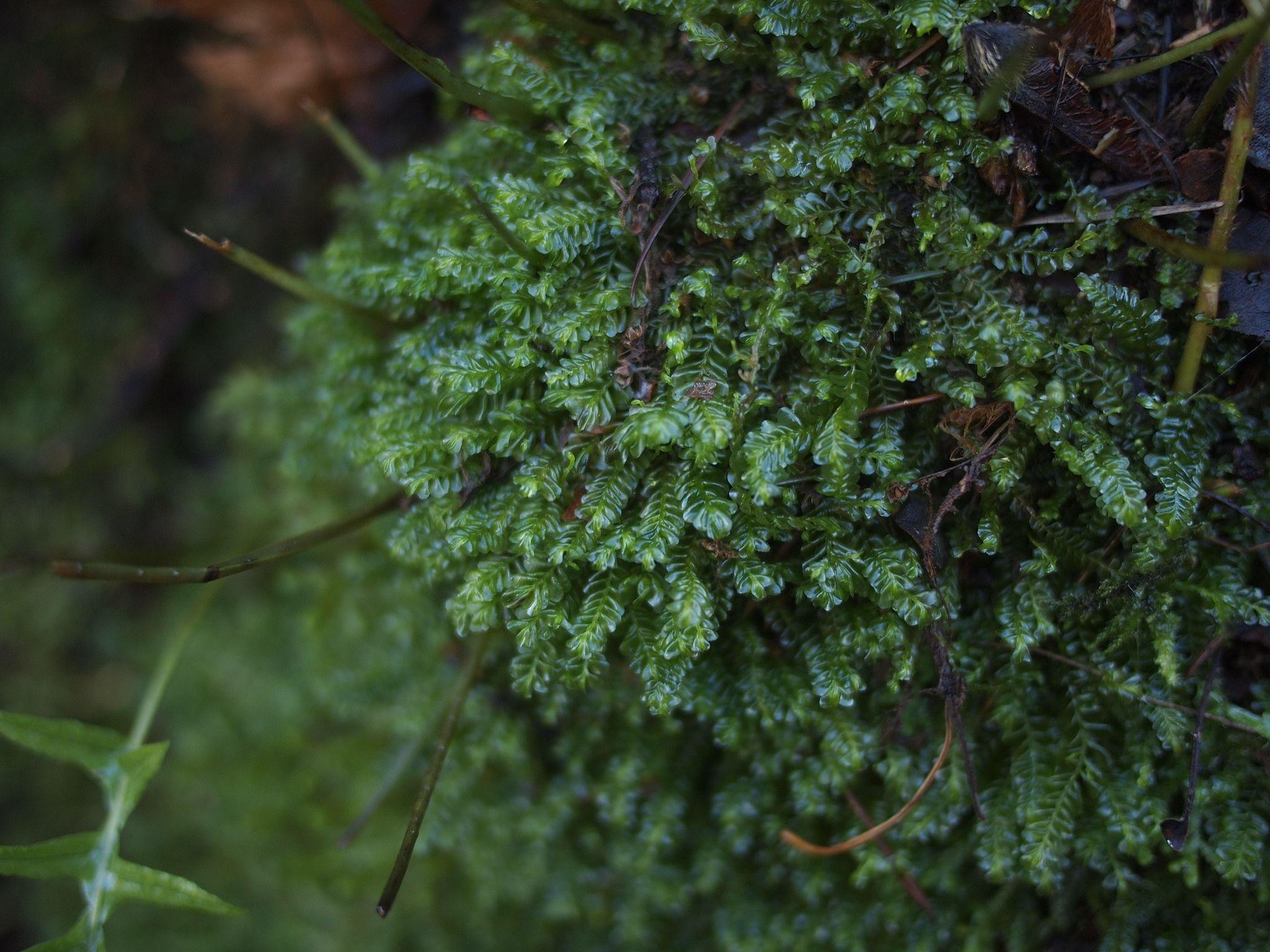
Plagiochila salacensis is

f2c4f6990d80e93f891c198db364f783.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/161637074119075917/
dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants. The perianths, which enclose the female reproductive structures, are oblong to cylindrical and have a truncate mouth with small teeth.
Global Distribution and Habitat

2b876b43051231be7fb8bceead12d953.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/plagiochila-asplenioides–291045194657579944/
Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions of Central and South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. It grows on tree trunks, branches, and rocks in moist, shaded habitats such as rainforests and cloud forests. In Southeast Asia, it is commonly found in montane forests at elevations of 1000-2500 meters.
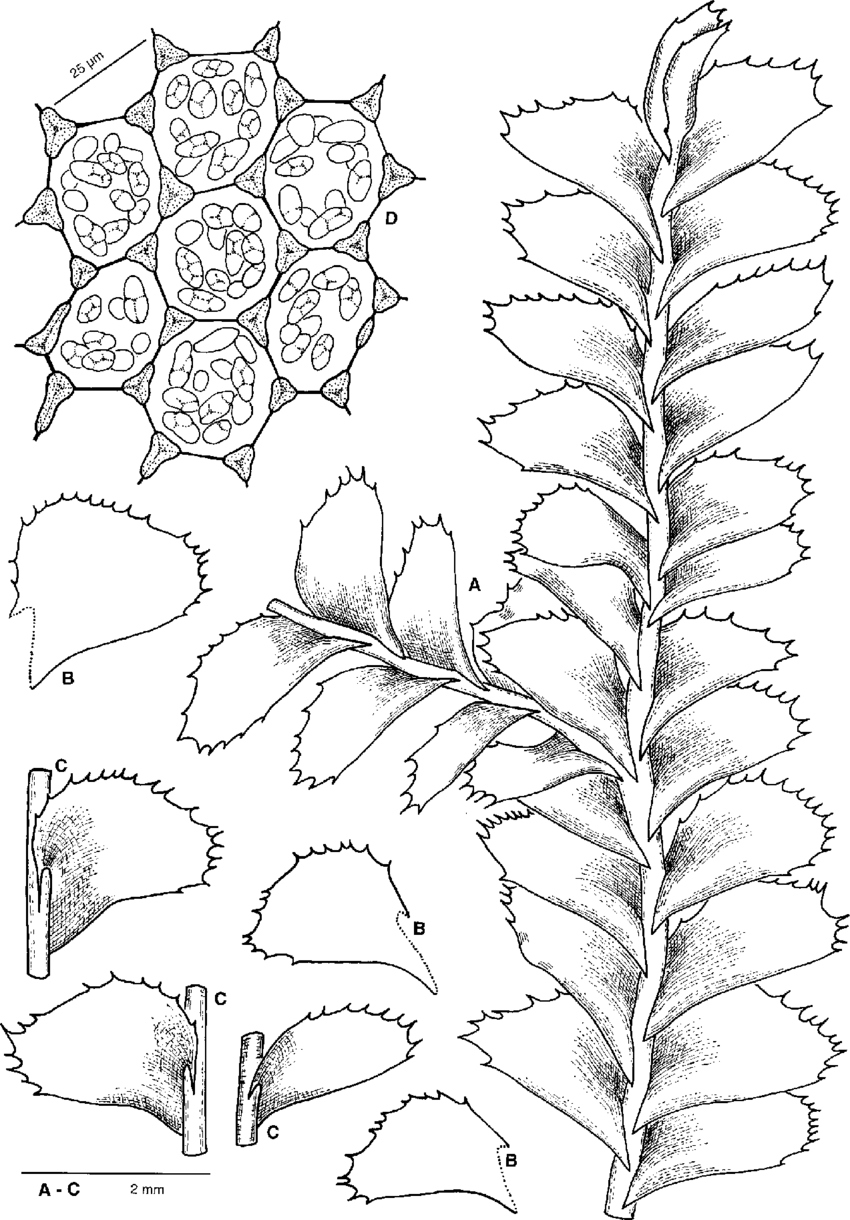
Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal_fig2_29813448
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other Plagiochila mosses, P. salacensis plays important ecological roles in its habitat. As an epiphyte growing on trees, it helps to intercept and retain moisture, providing a microhabitat for various invertebrates. The dense mats of moss also contribute to nutrient cycling by trapping organic debris and releasing nutrients as the plant material decomposes.

Plagiochila-trichostoma-Gottsche-A-Transverse-section-of-capsule-wall-B-Part-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-trichostoma-Gottsche-A-Transverse-section-of-capsule-wall-B-Part-of_fig1_232695596

41fe9edb6b4feeecd3976279ac633711.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/plagiochila-asplenioides–346988346302434872/
Plagiochila salacensis has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its moist, shaded habitat:
- Flattened, translucent leaves that maximize light capture for photosynthesis
- Leaves arranged in two rows for efficient water conduction
- Rhizoids (root-like structures) that anchor the plant to its substrate
- Ability to reproduce asexually via fragmentation, allowing for quick colonization of new areas
Conclusion
Plagiochila salacensis Gottsche may be small, but it is a fascinating and ecologically important moss species. From its intricate leaf structure to its role in nutrient cycling, this tropical moss has much to teach us about the wonders of the plant kingdom. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the mosses and liverworts around you – you might just spot a patch of Plagiochila salacensis! What other secrets do you think these tiny plants hold?