295728.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5004/tab/fiche
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Timmia norvegica J.E.Zetterst. moss stands out as a true marvel. Belonging to the Timmiaceae
295729.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5004
family, this unassuming yet extraordinary moss species has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/243259-Timmia-norvegica-norvegica
Bryopsida member.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Timmia norvegica, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, comprising mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
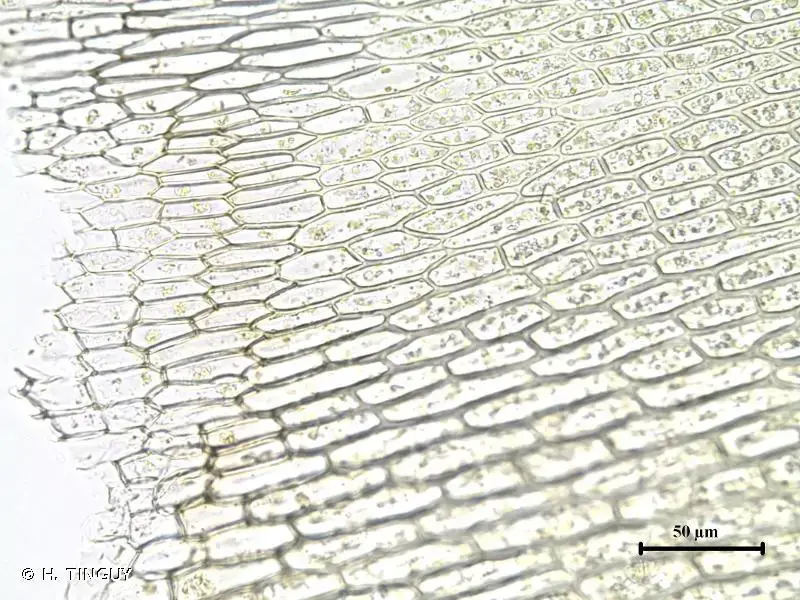
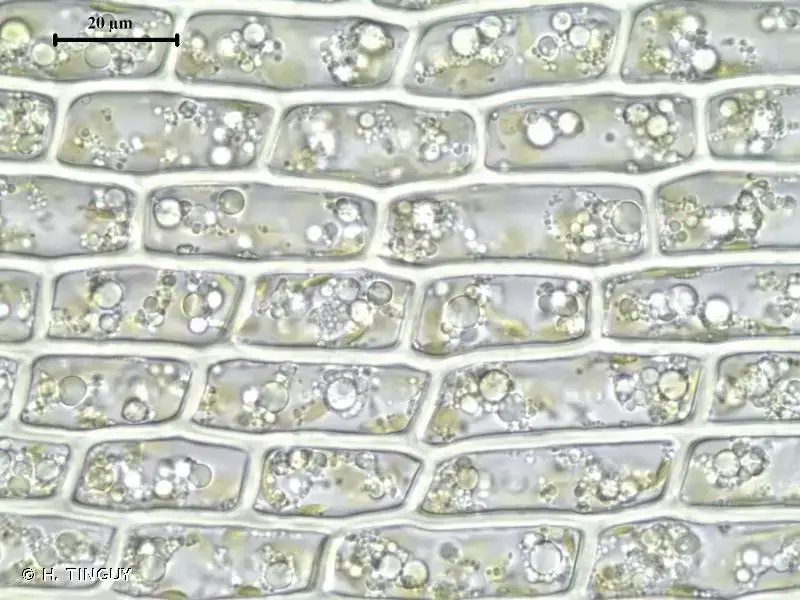
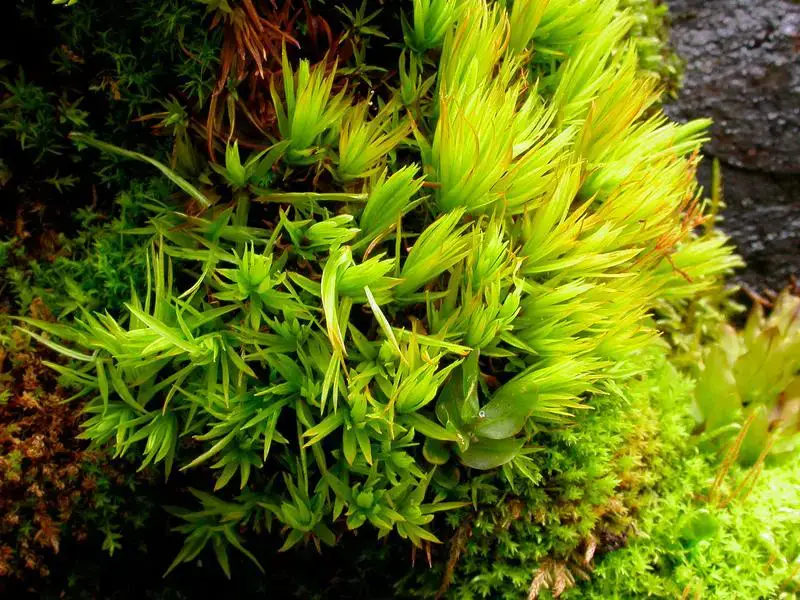
Timmia norvegica is a striking moss species that can be easily identified by its distinctive features. The plants form dense, cushion-like tufts, with erect stems reaching heights of up to 5 centimeters. The leaves are lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like structure known as the awn
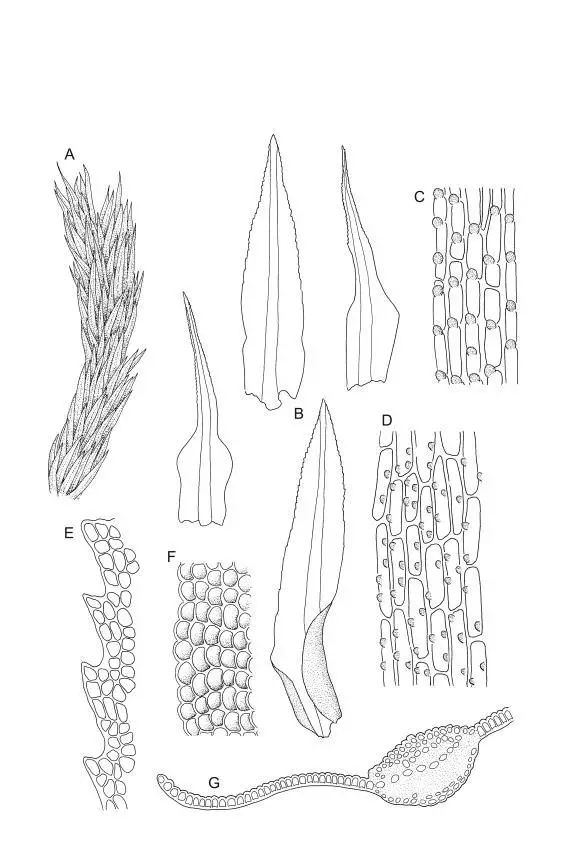
Image2AM3large.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Timmia-norvegica.html
. This characteristic awn is a defining feature of the Timmiaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Timmia norvegica is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in various habitats. It can be found in moist, shaded areas, such as coniferous and mixed forests, rock crevices, and even on decaying logs. This moss species is particularly abundant in regions with cool, temperate climates, such as Northern Europe, North America, and parts of Asia.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Timmia norvegica plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. They contribute to soil formation, moisture retention, and nutrient cycling, creating favorable conditions for larger plants to thrive.

medium-19969.jpeg from: https://plantdollar.com/plant/timmia-norvegica/
Moreover, Timmia norvegica exhibits remarkable adaptations to its environment. Its dense tufts help retain moisture, while the awn on the leaves aids in water absorption and dispersal of spores. The moss’s ability to withstand desiccation and revive upon rehydration is a testament to its resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Timmia norvegica played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as wildfires or logging. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas facilitated the establishment of other plant species, accelerating the process of ecological succession.
Technical Table

25200_2423_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/timmia-norvegica-2423
240px-Timmia_norvegica_(a%2C_133246-471443)_4427.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Timmia_norvegica
330947.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434128
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Timmiaceae |
| Genus | Timmia |
| Species | Timmia norvegica J.E.Zetterst.
 120px-Timmia_norvegica_(c%2C_124559-470456)_2725.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Timmia_norvegica |
| Common Name | Timmia moss |
| Growth Form | Dense, cushion-like tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Distinctive Feature | Awn (hair-like extension of the costa) |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, coniferous and mixed forests, rock crevices, decaying logs |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, North America, Asia) |
Conclusion
The Timmia norvegica J.E.Zetterst. moss, a member of the Timmiaceae family, is a true testament to the wonders of the bryophyte world. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems await discovery in the realm of bryophytes, and how can we better protect and conserve these invaluable components of our ecosystems?

A-D-Dicranum-spadiceum-JE-Zetterst-habit-dry-A-from-Austria-Ignatov_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Dicranum-spadiceum-JE-Zetterst-habit-dry-A-from-Austria-Ignatov_fig1_283845670