2021-09-19-18-28-48-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sematophyllum-demissum/
Introduction
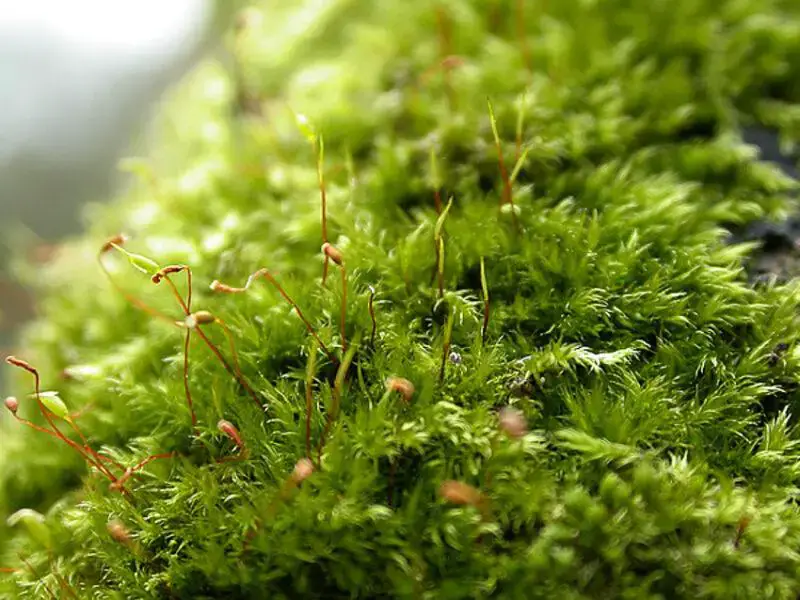

SemsubKV-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sematophyllum-substrumulosum/
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the Sematophyllum demissum (Wilson) Mitt., a moss belonging to the Sematophyllaceae family, commonly known as Sematophyllum. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of the Bryophyta (mosses) and Bryopsida (true mosses) divisions.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Sematophyllum demissum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of mosses. These ancient plants have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Mosses are non-vascular, meaning they lack specialized tissues for transporting water and nutrients, relying instead on a simple structure and the ability to absorb moisture directly from their surroundings.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Sematophyllum demissum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems can reach lengths of several centimeters, adorned with delicate, ovate-lanceolate leaves that are typically less than 2 millimeters long. These leaves are characterized by their distinctive midrib, which extends nearly to the leaf apex, and their finely serrated margins.
One of the key identifying features of Sematophyllum demissum is its sporophyte, the reproductive structure that produces spores. The seta (stalk) supporting the capsule is relatively short, and the capsule itself is curved and asymmetrical, often with a distinct neck region. This unique capsule shape is a hallmark of the Sematophyllaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Sematophyllum demissum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock outcrops to stream banks and even urban areas, where it can be found growing on tree bark, rotting logs, and soil.
This moss’s ability to adapt to diverse environments is a testament to its resilience and versatility. It can tolerate a range of moisture levels and light conditions, making it a successful colonizer of various substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Sematophyllum demissum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture retention for a myriad of tiny invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Sematophyllum demissum is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, resuming its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Study: Urban Moss Gardens
In recent years, the concept of urban moss gardens has gained popularity, particularly in cities where traditional gardening can be challenging due to limited space and harsh conditions. Sematophyllum demissum, with its tolerance for urban environments and ability to thrive on various substrates, has become a prime candidate for these unique green spaces.
Urban moss gardens not only add a touch of natural beauty to concrete jungles but also serve as miniature ecosystems, providing habitat for insects and other small creatures. They can be created on vertical surfaces, such as walls or fences, or incorporated into larger landscaping designs, offering a low-maintenance and sustainable alternative to traditional gardens.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Genus | Sematophyllum |
| Species | demissum |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Midrib | Extending nearly to apex |
| Leaf Margins | Finely serrated |
| Capsule Shape | Curved, asymmetrical |
| Habitat | Moist forests, shaded rocks, stream banks, urban areas |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, Africa, North America |
| Ecological Role | Soil stabilization, moisture retention, biodiversity support |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
The Sematophyllum demissum (Wilson) Mitt. moss, a member of the Sematophyllaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. From its intricate morphology and global distribution to its ecological roles and unique adaptations, this unassuming plant offers a wealth of knowledge and inspiration.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of mosses, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: In a world where urbanization and environmental challenges persist, how can we leverage the resilience of species like Sematophyllum demissum to create more sustainable and biodiverse urban landscapes?