
27229842528_b3f8534fd2_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/27229842528/
Introduction
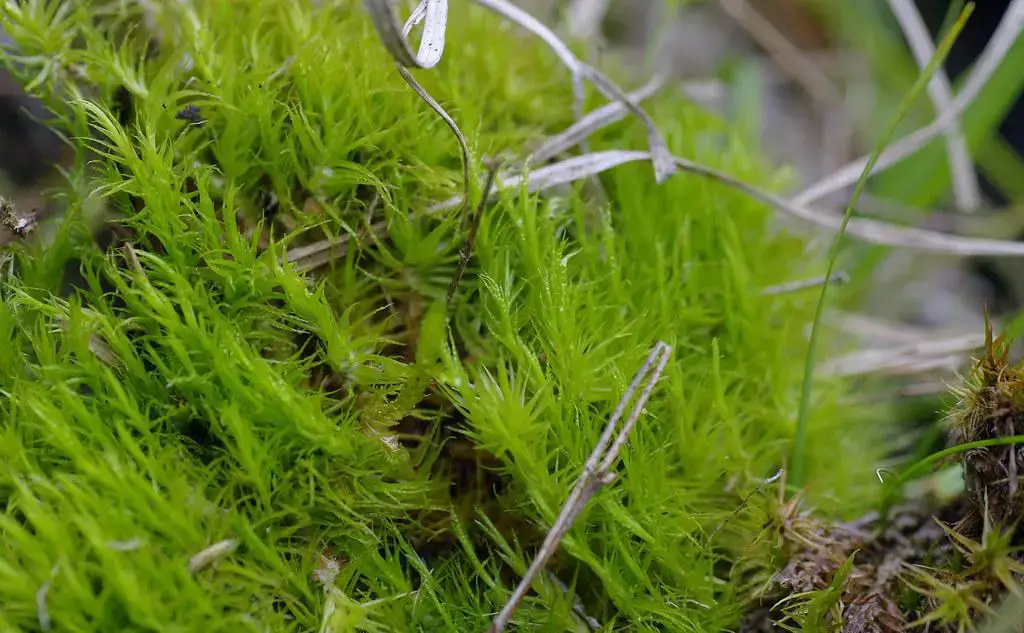
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Dicranum bonjeanii De Not. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Dicranaceae family. Often referred to simply as Dicranum, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of

229046.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4741
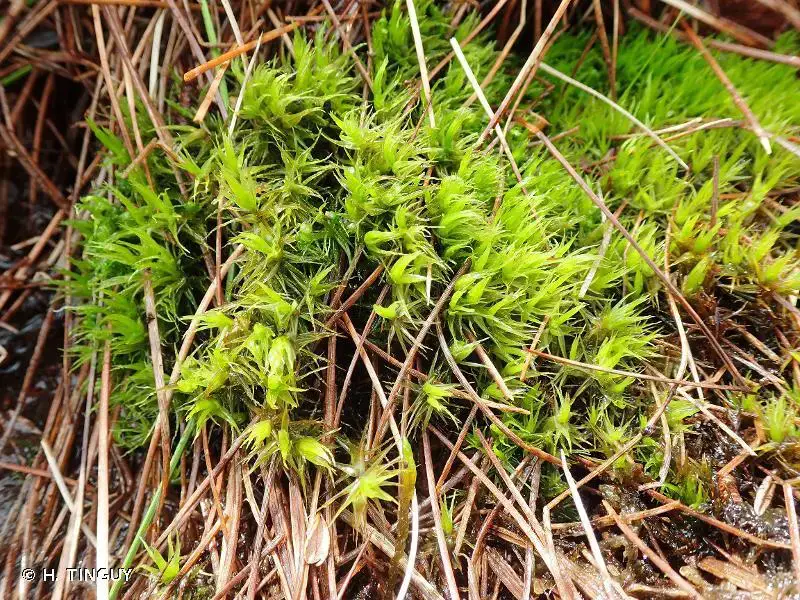
Dicranum bonjeanii, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

229045.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4741/tab/fiche
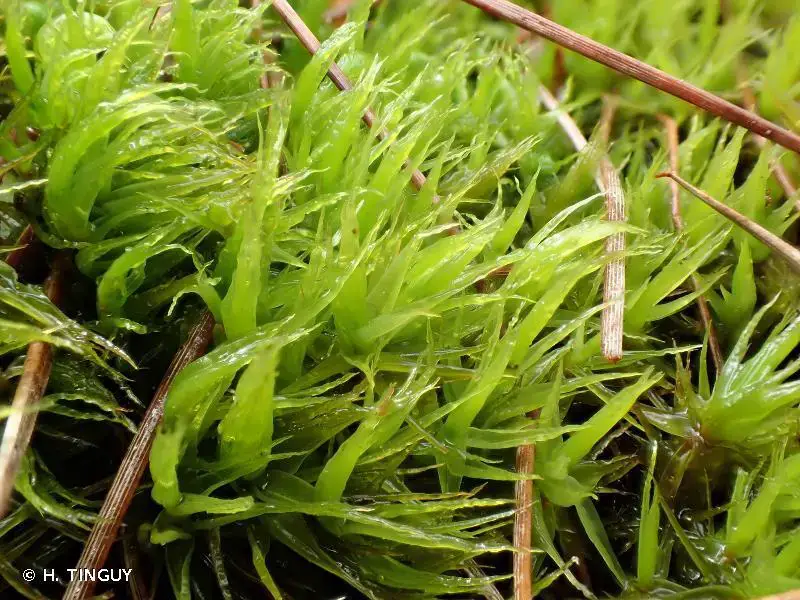
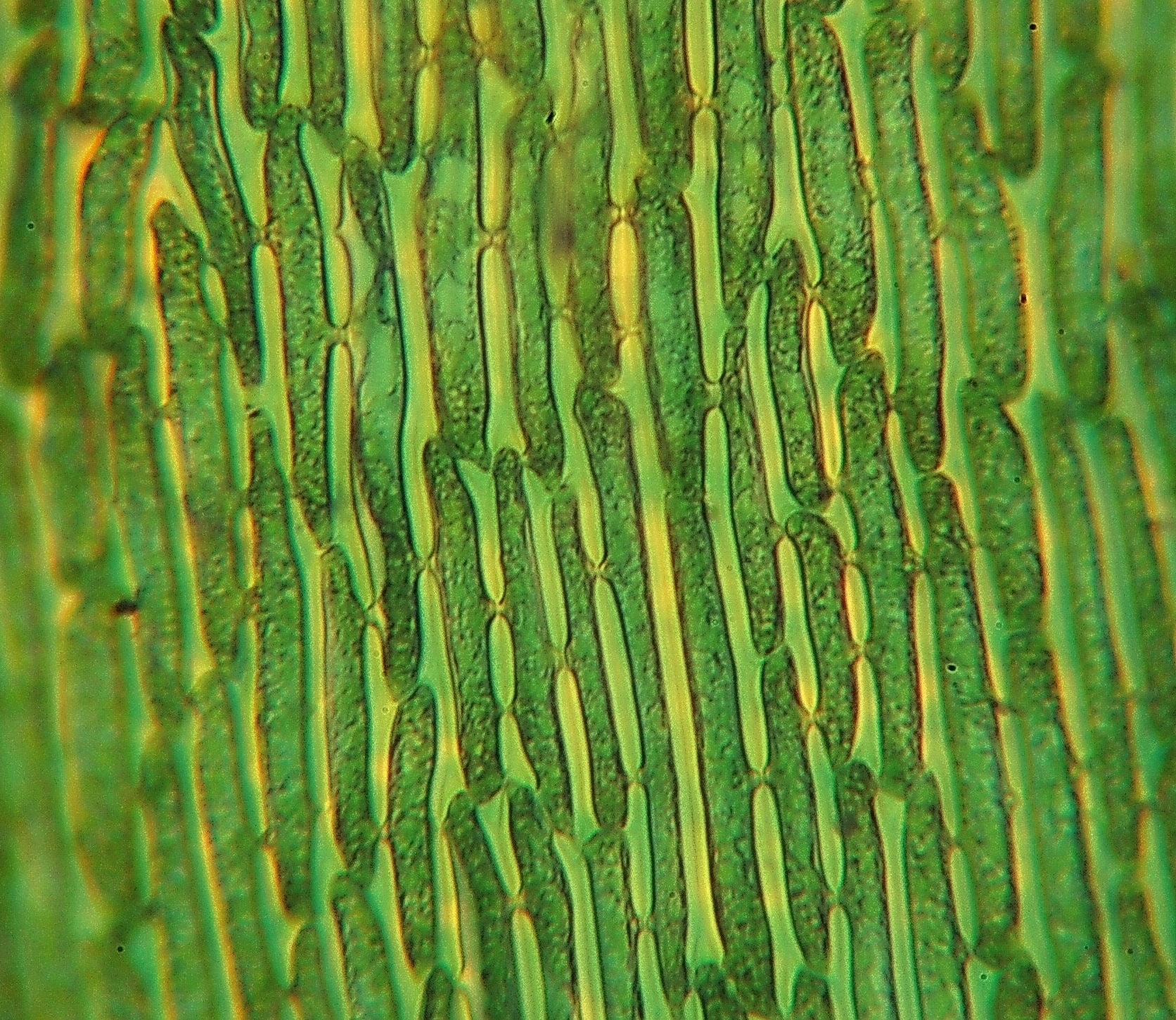
Dicranum bonjeanii is a acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the upright gametophytes. Its leaves are

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2675482
lanceolate (lance-shaped) and falcate (curved like a sickle), with a distinctive
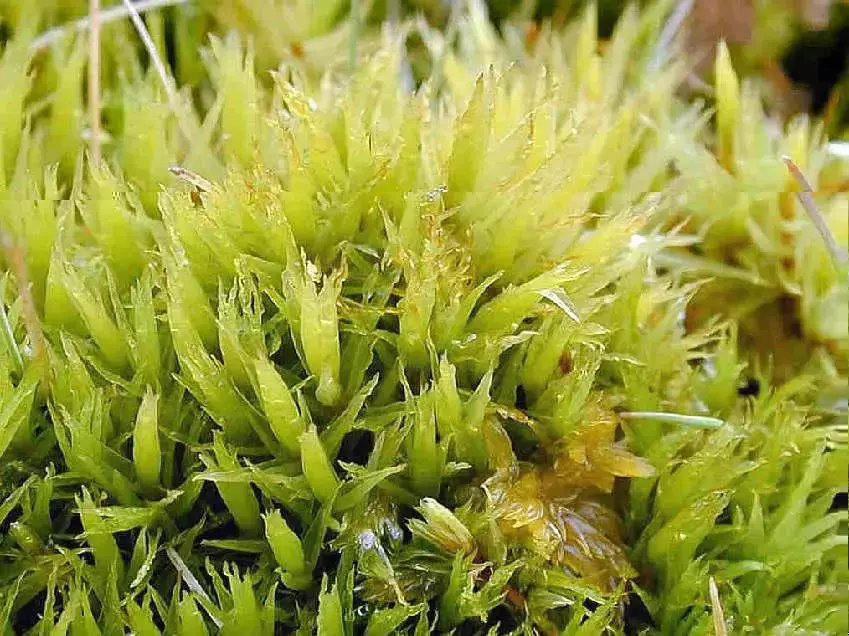

Dicranum_bonjeanii_2.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Dicranum_bonjeanii.html
costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf tip, forming a hair-point. This unique feature aids in identifying the species.
The gametophyte (the leafy, green part of the moss) forms dense cushions or tufts, ranging in color from yellowish-green to brownish-green. The sporophytes, when present, consist of a seta (stalk) supporting a capsule covered by a calyptra (a cap-like structure).
Global Distribution and Habitat
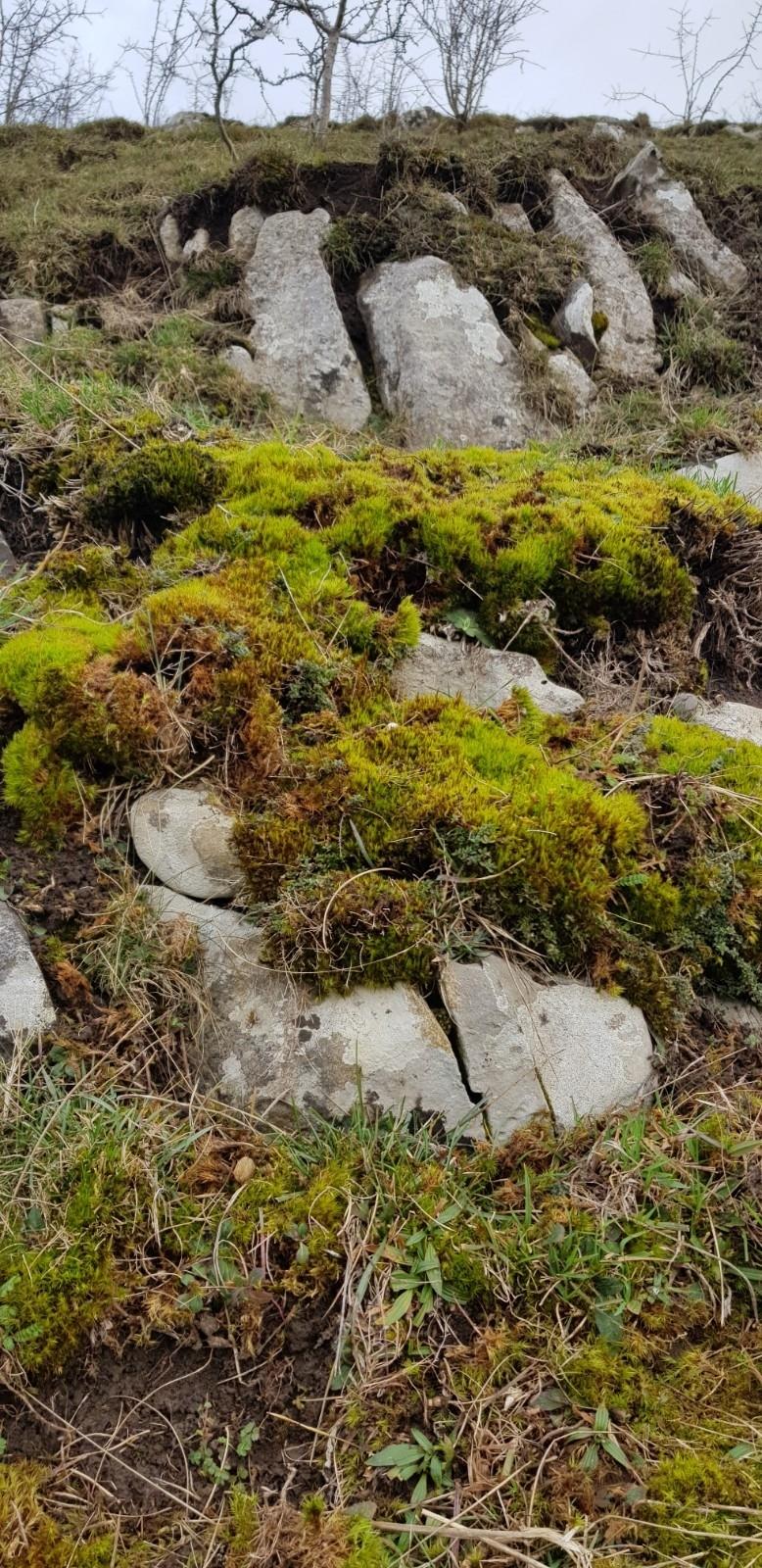
Dicranum bonjeanii is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as coniferous and mixed forests, rocky outcrops, and shaded areas with high moisture levels.
This moss prefers acidic soils and is often found growing on
Dicranum-bonjeanii-leaf-cells-1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranum-bonjeanii/
decaying logs, tree bases, and humus-rich substrates. Its ability to tolerate low light conditions and its preference for moist environments make it a common sight in the understory of forests and shaded areas.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
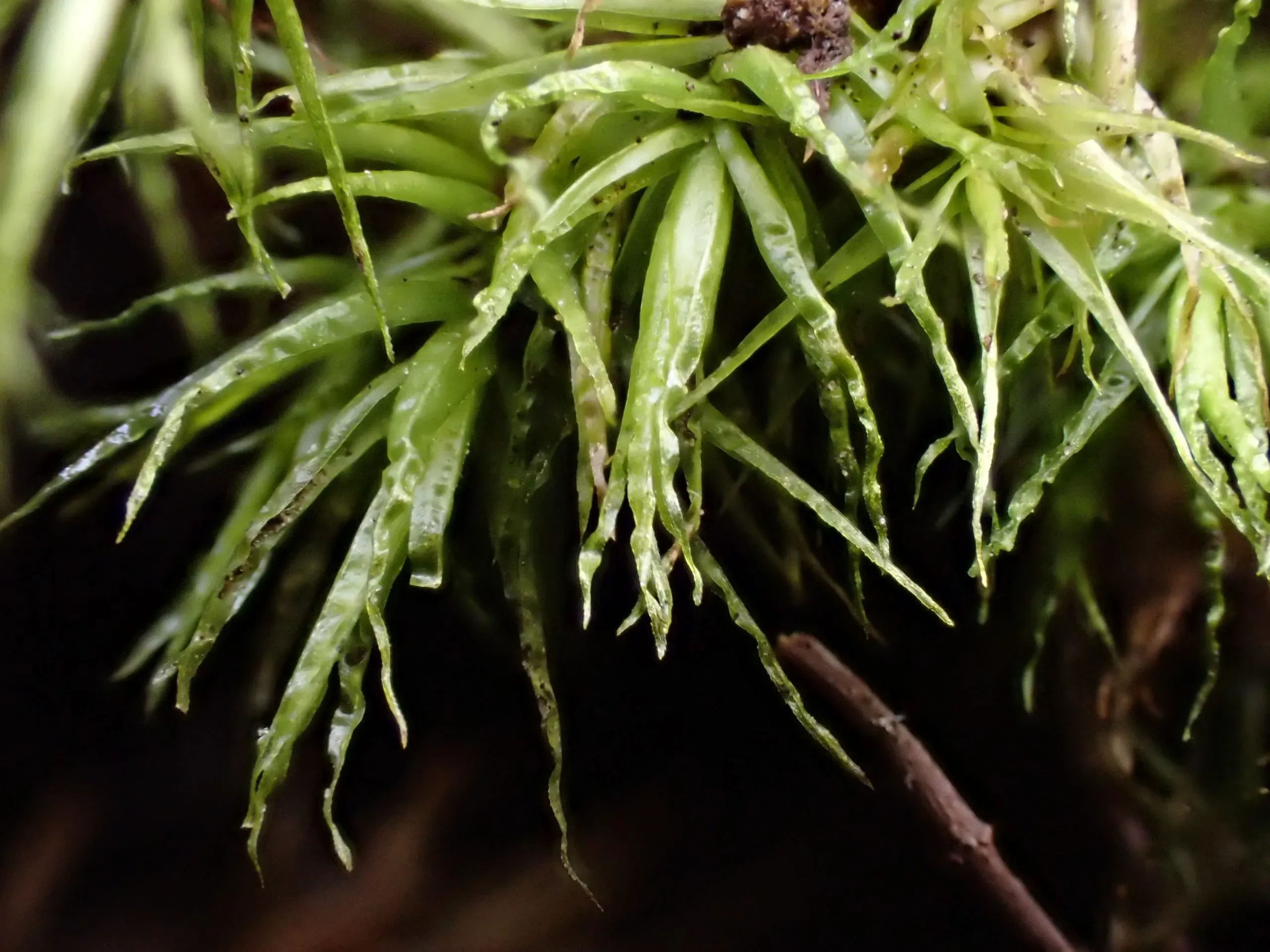

Close-up-of-Dicranum-bonjeanii-scaled.jpg from: https://buxtonfieldclub.org.uk/the-wildlife-places/wildlife-places-in-the-high-peak/cowlow/
Dicranum bonjeanii plays a vital role in forest ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and moisture retention. Its dense cushions provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and other organisms, supporting biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dicranum bonjeanii is its ability to desiccate (dry out) and rehydrate without suffering significant damage. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive periods of drought and resume its metabolic activities when moisture becomes available again.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Dicranum bonjeanii was a dominant species in old-growth forests, indicating its importance in these ecosystems. The moss was observed to provide crucial habitat for various invertebrates, including springtails and mites, which play essential roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling.
Another study in Central Europe highlighted the ability of Dicranum bonjeanii to colonize disturbed areas, such as clear-cut forests or abandoned quarries. Its pioneering nature and tolerance to harsh conditions make it a valuable species for ecosystem restoration and soil stabilization.
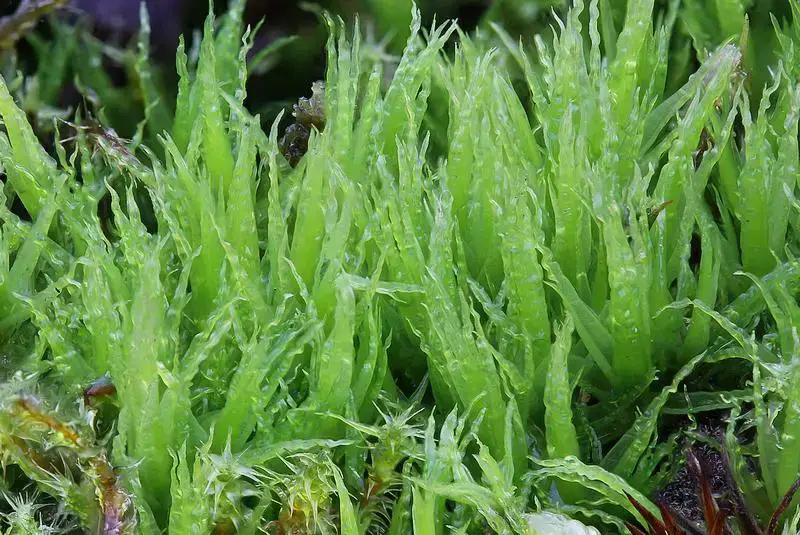

7850203.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/species/17349/
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Dicranales |
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Genus | Dicranum |
| Species | bonjeanii |
Growth Form
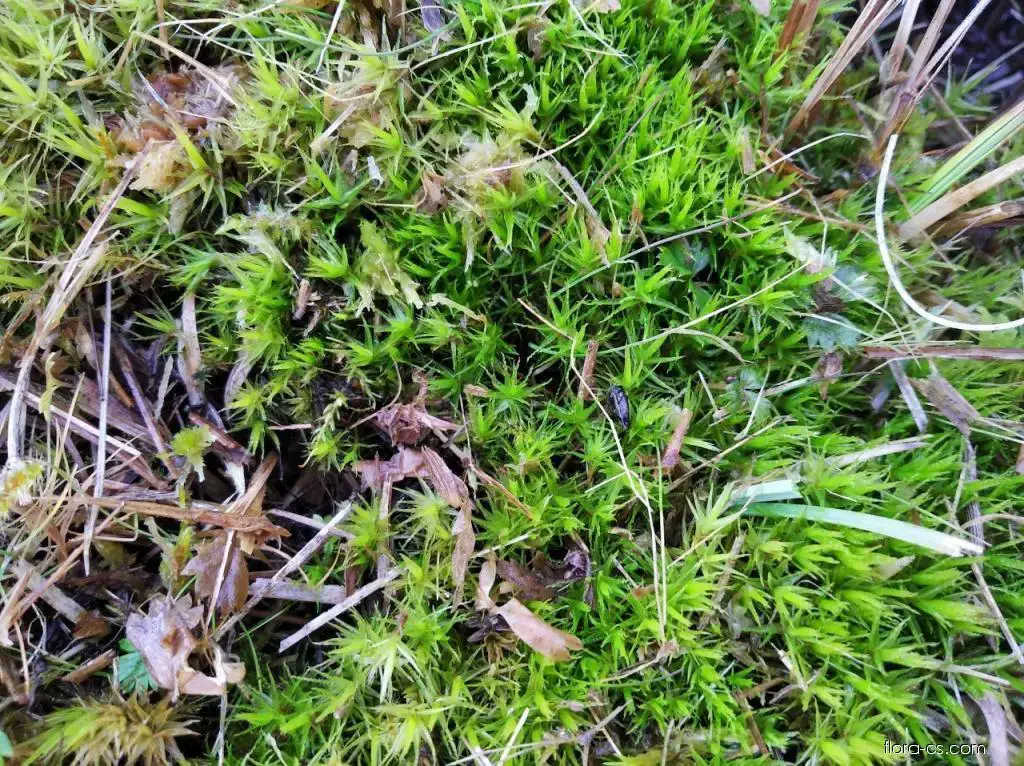 44436-dicranum-bonjeanii-6261-pp-zlamanec-unor-2020.jpg from: https://www.flora-cs.com/forum/vt/cz/17798-dvouhrotec-bahenní-dicranum-bonjeanii/ |
Acrocarpous moss, forming dense cushions or tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, falcate (curved like a sickle) |
| Leaf Tip | Costa (midrib) extending beyond the leaf tip, forming a hair-point |
| Color | Yellowish-green to brownish-green |
| Habitat | Coniferous and mixed forests, rocky outcrops, shaded areas with high moisture |
| Substrate | Acidic soils, decaying logs, tree bases, humus-rich substrates |
Conclusion
The Dicranum bonjeanii De Not. moss, a member of the Dicranaceae family, is a remarkable species that has captured the attention of bryophyte enthusiasts worldwide. Its unique morphological features, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study and appreciation.
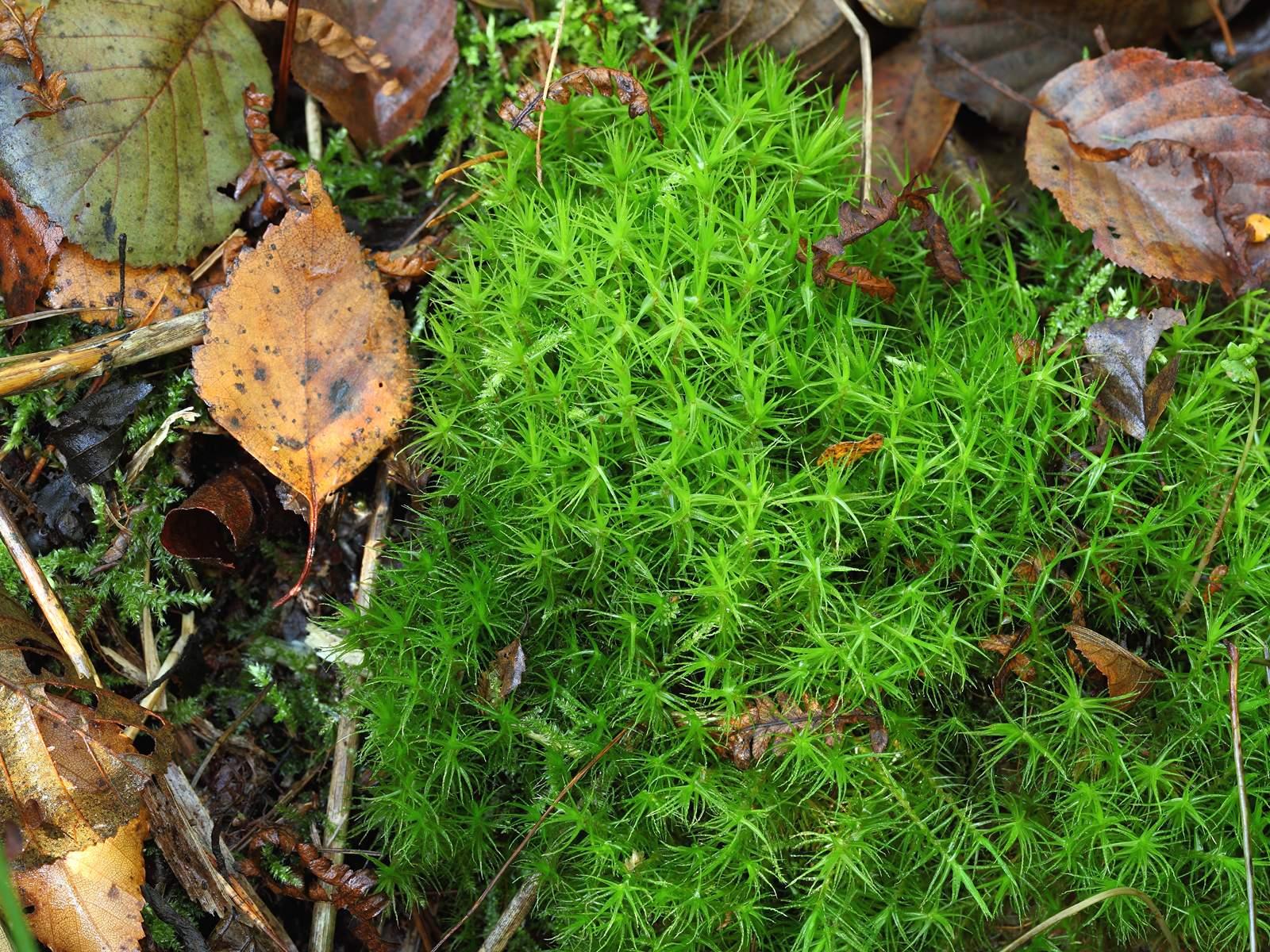

dicranum_bonjeanii.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/dicranaceae/index.html
As we continue to explore and understand the intricate world of bryophytes, species like Dicranum bonjeanii serve as reminders of the incredible diversity and resilience of these ancient land plants. Perhaps the next time you venture into a shaded forest or encounter a moss-covered log, you’ll pause to appreciate the unassuming beauty and significance of this remarkable moss.
Thought-provoking question: How might the study and conservation of species like Dicranum bonjeanii contribute to our understanding of ecosystem dynamics and the preservation of biodiversity?