
B060-02_0.jpg from: http://taibif.tw/zh/namecode/200598
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Gollania varians (Mitt.) Broth. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Hypnaceae family. Also known simply as Gollania, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive wonder and unravel its secrets.

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xQY8asSw-wI
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Gollania varians, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
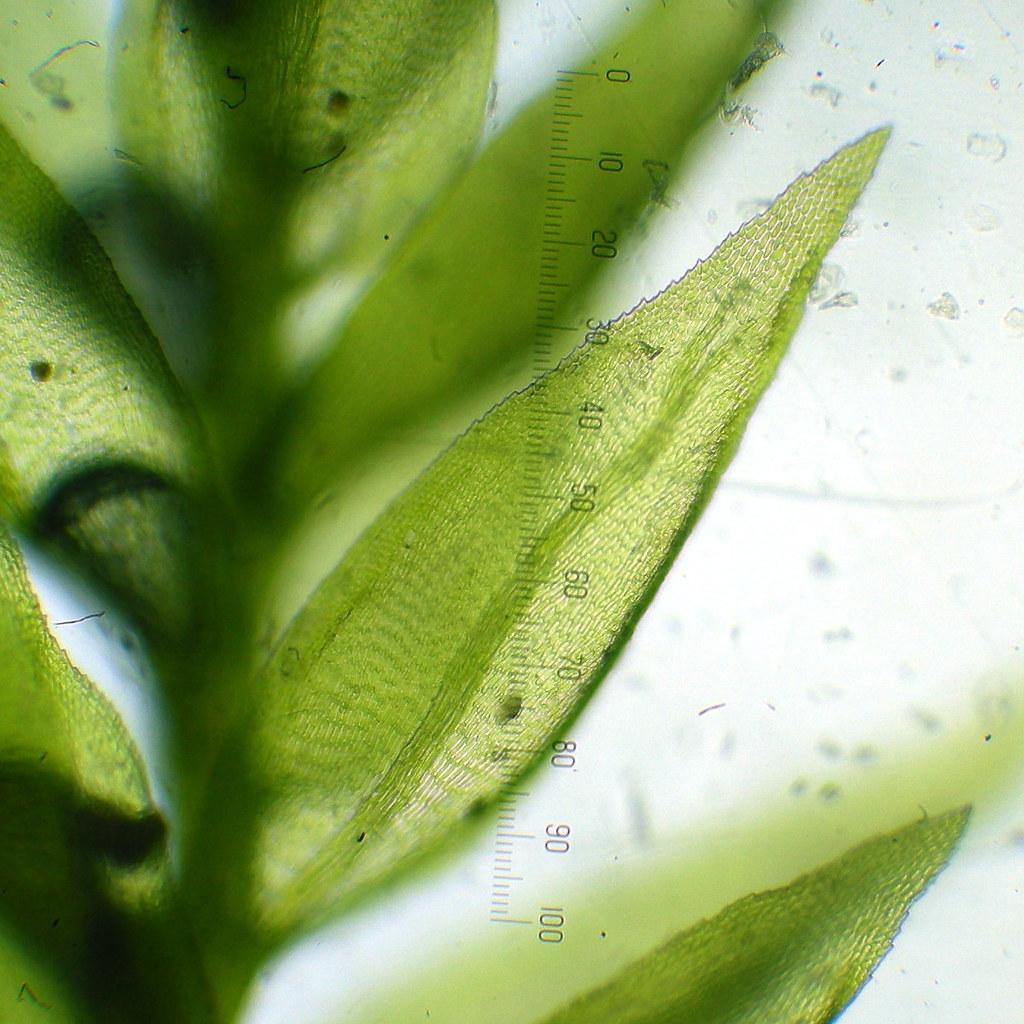
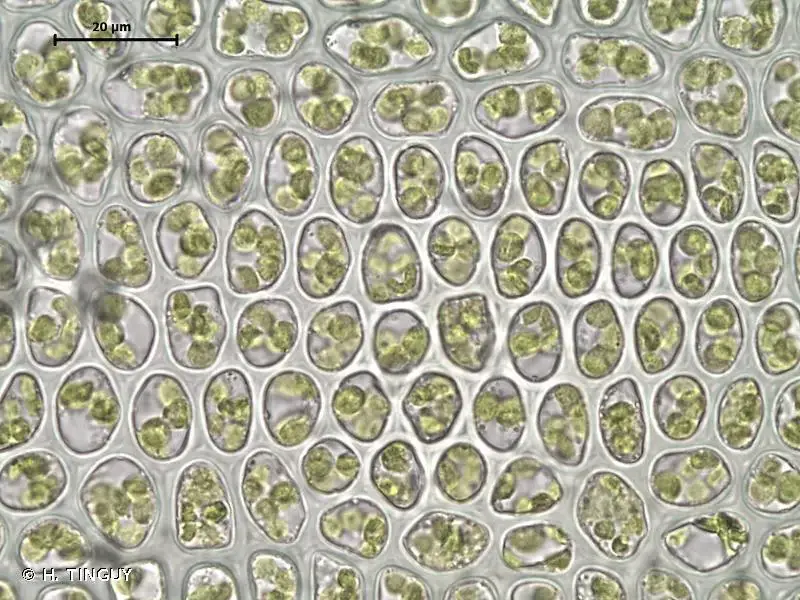
Gollania varians is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that form a feathery appearance. The leaves are typically 1-2 mm long and have a distinctive midrib running along their length.
One of the most striking features of Gollania varians is its vibrant golden-green color, which can vary depending on the moisture levels and environmental conditions. This moss is dioicous, meaning that male and female reproductive structures are found on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
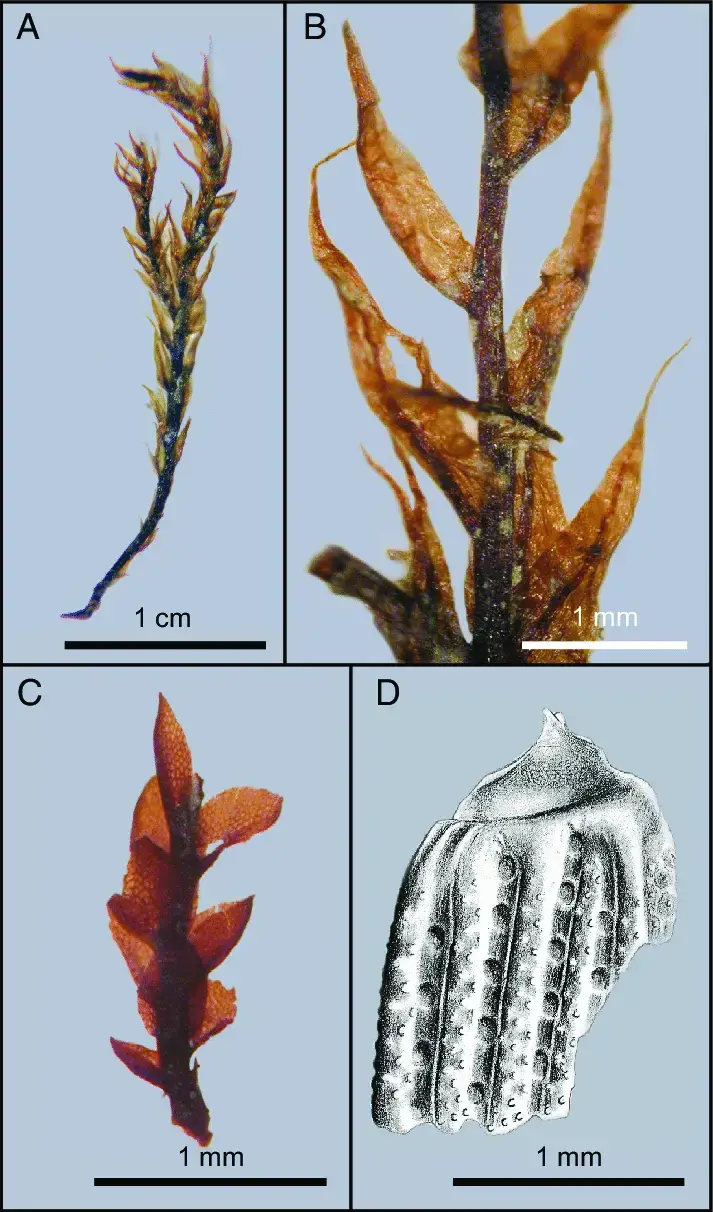
Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
Gollania varians is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock crevices to stream banks and damp soil.
This moss prefers cool, humid environments and is often found in areas with high moisture levels, such as near waterfalls, seeps, or in the spray zones of streams. It can also be found growing on decaying logs, tree bases, and moist, shaded soil.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Gollania varians plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates, such as tardigrades and springtails.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Gollania varians is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives and resumes its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Gollania varians played a crucial role in maintaining the moisture levels and stability of stream banks. The moss’s dense mats helped prevent soil erosion and provided a suitable microhabitat for various aquatic invertebrates.
Another interesting example comes from Japan, where Gollania varians is commonly found growing on the trunks of ancient cedar trees in the Yakushima Forest, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This moss contributes to the rich biodiversity of the forest and serves as an indicator of the area’s pristine environmental conditions.
Technical Table

Gollania-ruginosa01L.jpg from: https://digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Gollania ruginosa/Gollania_ruginosa.html

29102375665_0e87db4790_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/kochibii/29102375665

392444.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5248
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
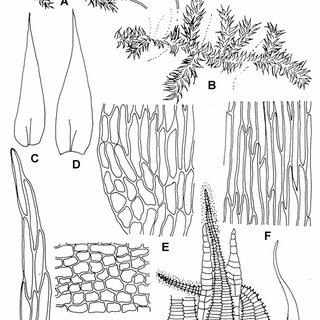 Campylium-gollanii-C-Muell-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet-plant-667-C-D-leaves_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Symphyodon-orientalis-Mitt-Broth-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet-plant-667-C-leaf_fig1_242597571 |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Hypnaceae |
| Genus | Gollania |
| Species | varians
 d35b1b807187da97958d2d008a037da8.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8731 |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm long |
| Color | Golden-green |
| Habitat | Moist forests, rock crevices, stream banks, damp soil |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |
Conclusion
The Gollania varians (Mitt.) Broth.

ab81e564b824bf8c71147ee9c2778e90.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/34412/articles
moss, a member of the Hypnaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, vibrant colors, and remarkable adaptations have captivated moss enthusiasts worldwide. From its ecological roles in maintaining soil moisture and providing habitats for invertebrates to its ability to survive desiccation, this moss is a testament to the resilience and beauty of bryophytes.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve the delicate ecosystems that support these extraordinary organisms?
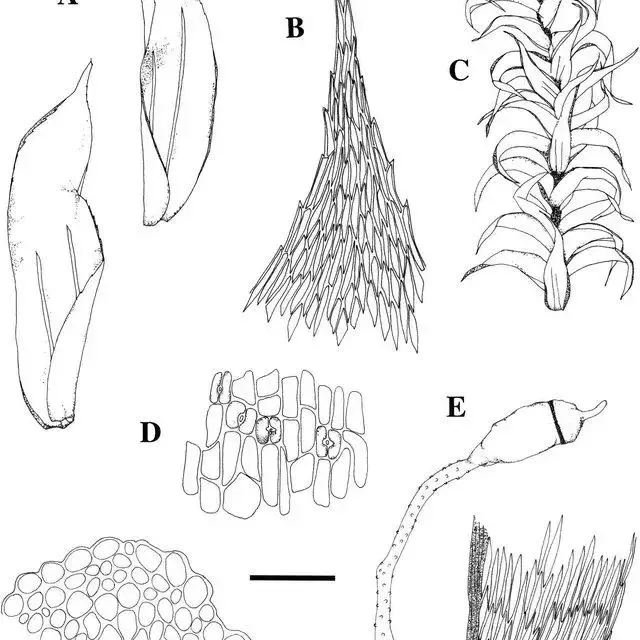
Lepidopilidium-devexum-Mitt-Broth-A-Lateral-leaves-B-Lateral-leaf-apex-C_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280989042_Taxonomic_Revision_of_the_Moss_Genus_Lepidopilidium_Pilotrichaceae