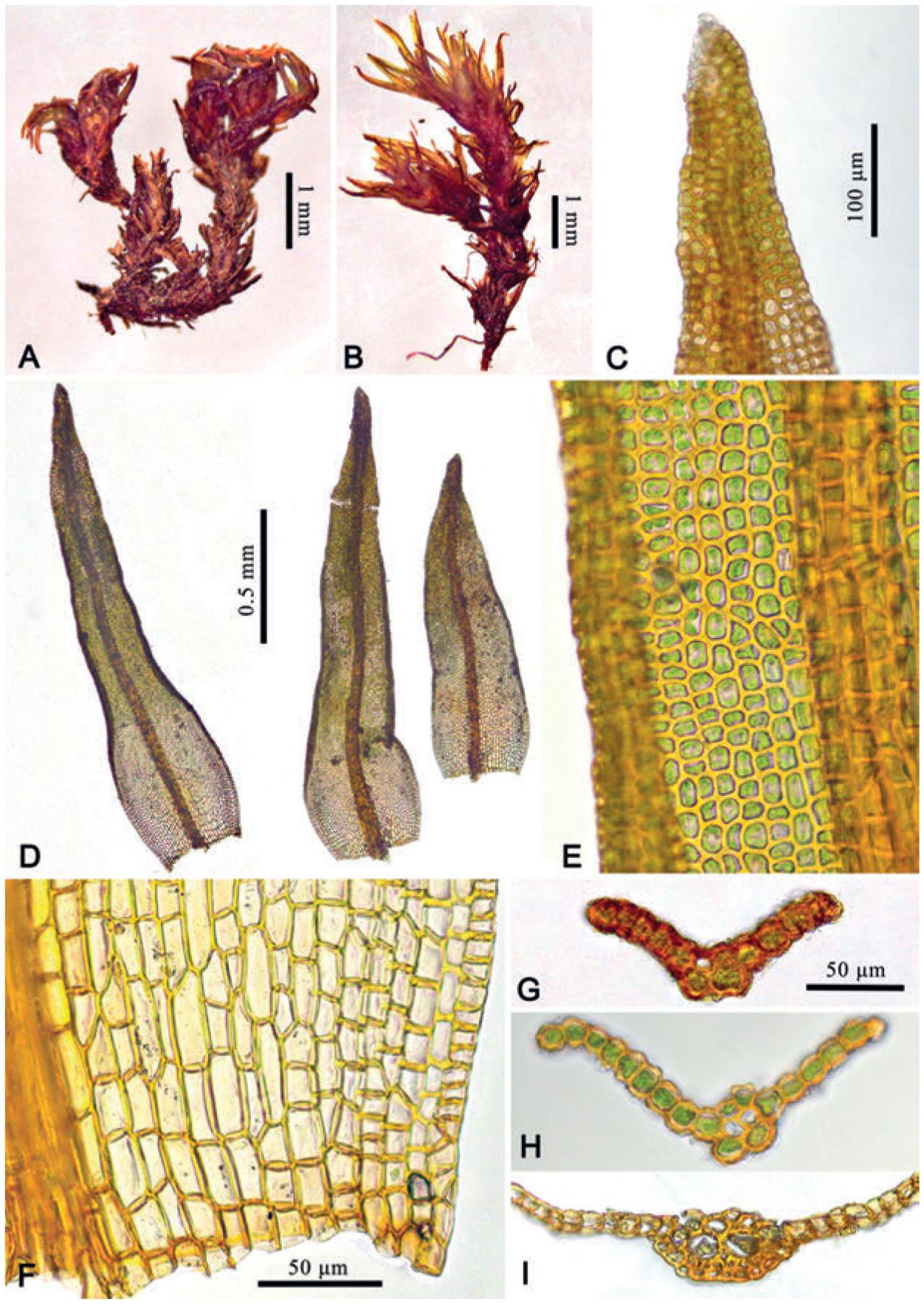
f01_798.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Herzogia/volume-29/issue-2/heia.29.2.2016.798/Didymodon-rufidulus-New-to-Mongolia/10.13158/heia.29.2.2016.798.full
Introduction
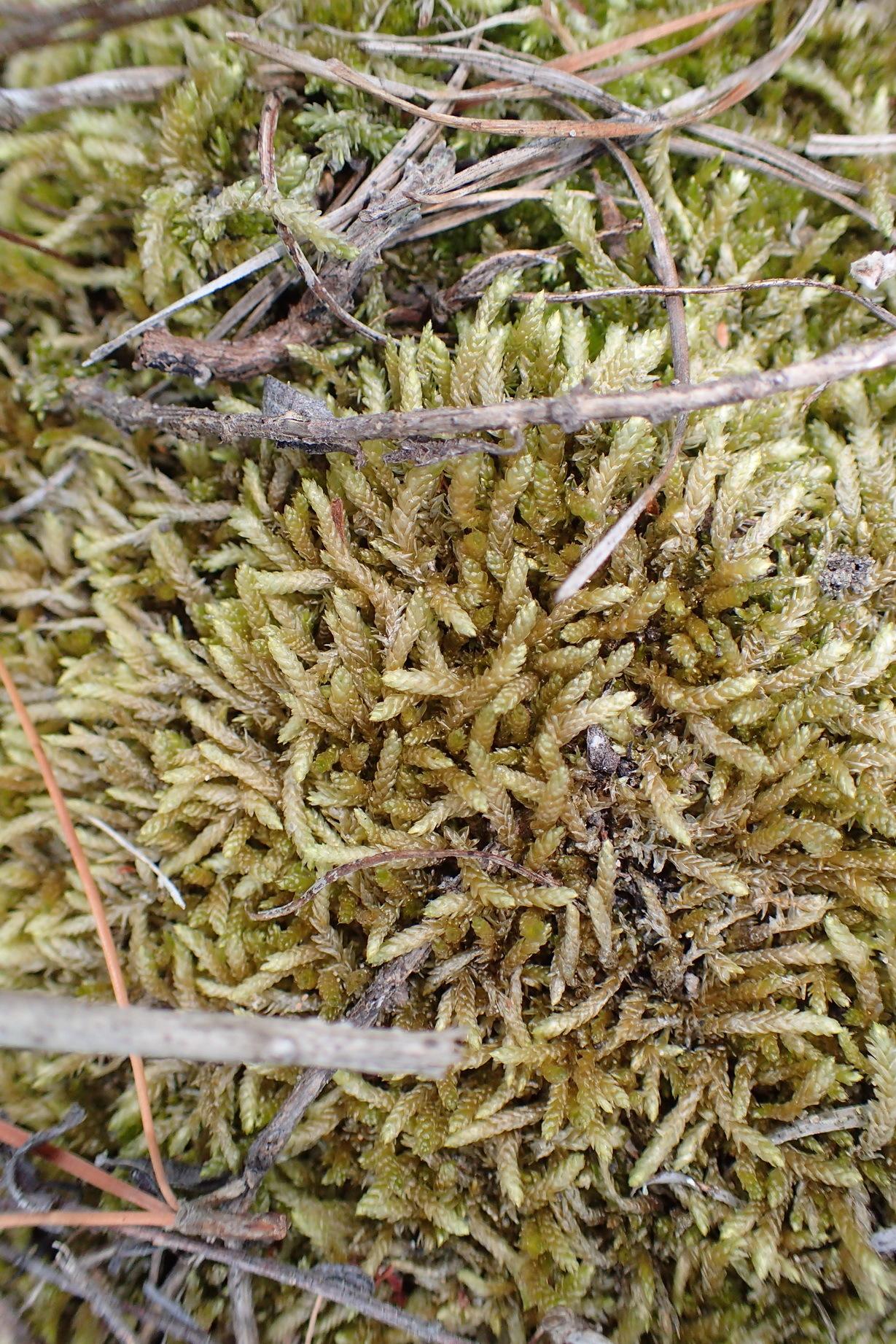
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Didymodon rufidulus (Müll.Hal.) Broth., a captivating member of the Pottiaceae

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
family, also known as Didymodon. This unassuming yet remarkable moss has captured the hearts of bryologists and nature lovers alike, and we’re about to uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, or mosses, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that have been around for millions of years. These resilient organisms play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers, soil stabilizers, and even indicators of environmental health.

3210-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=18679
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
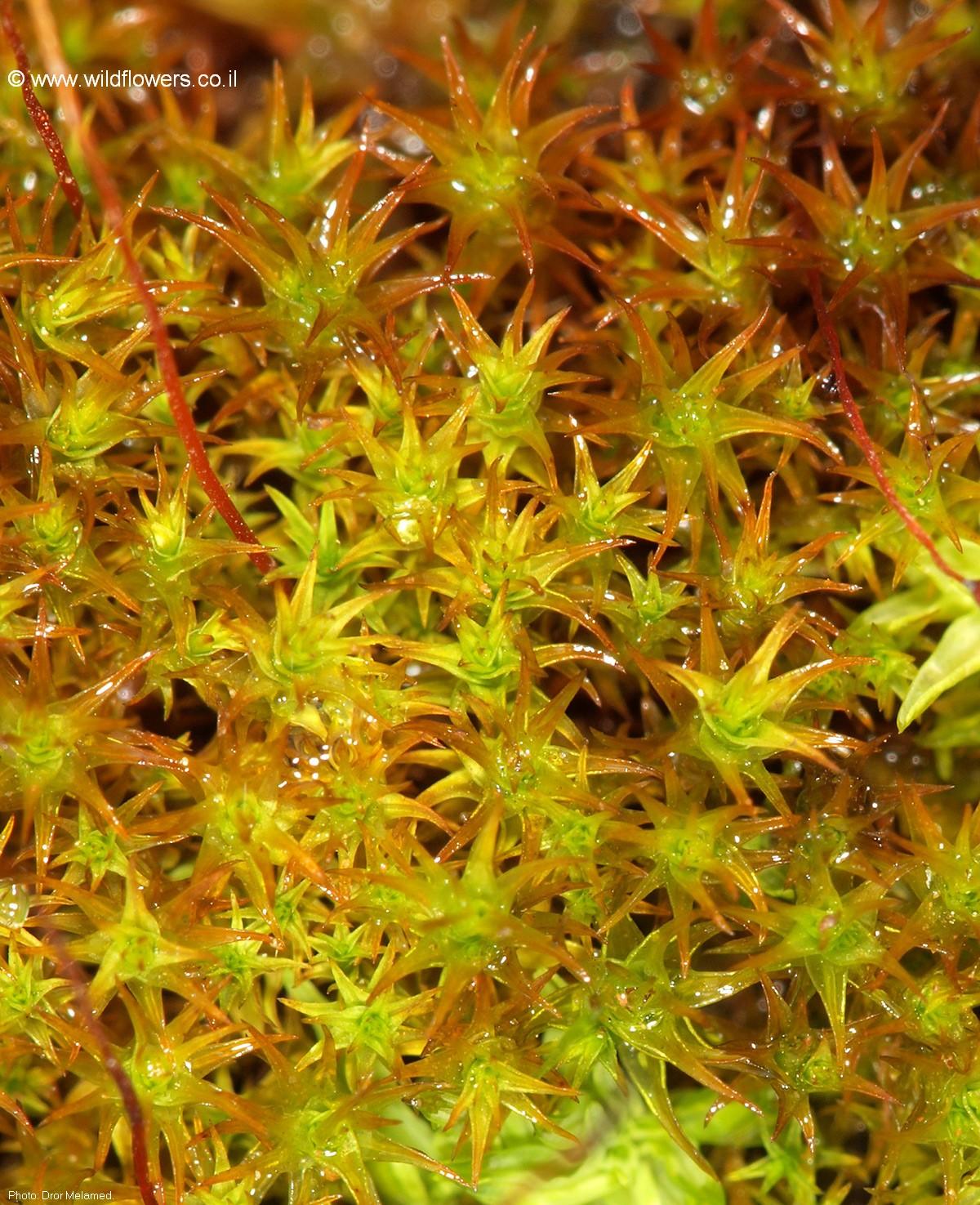
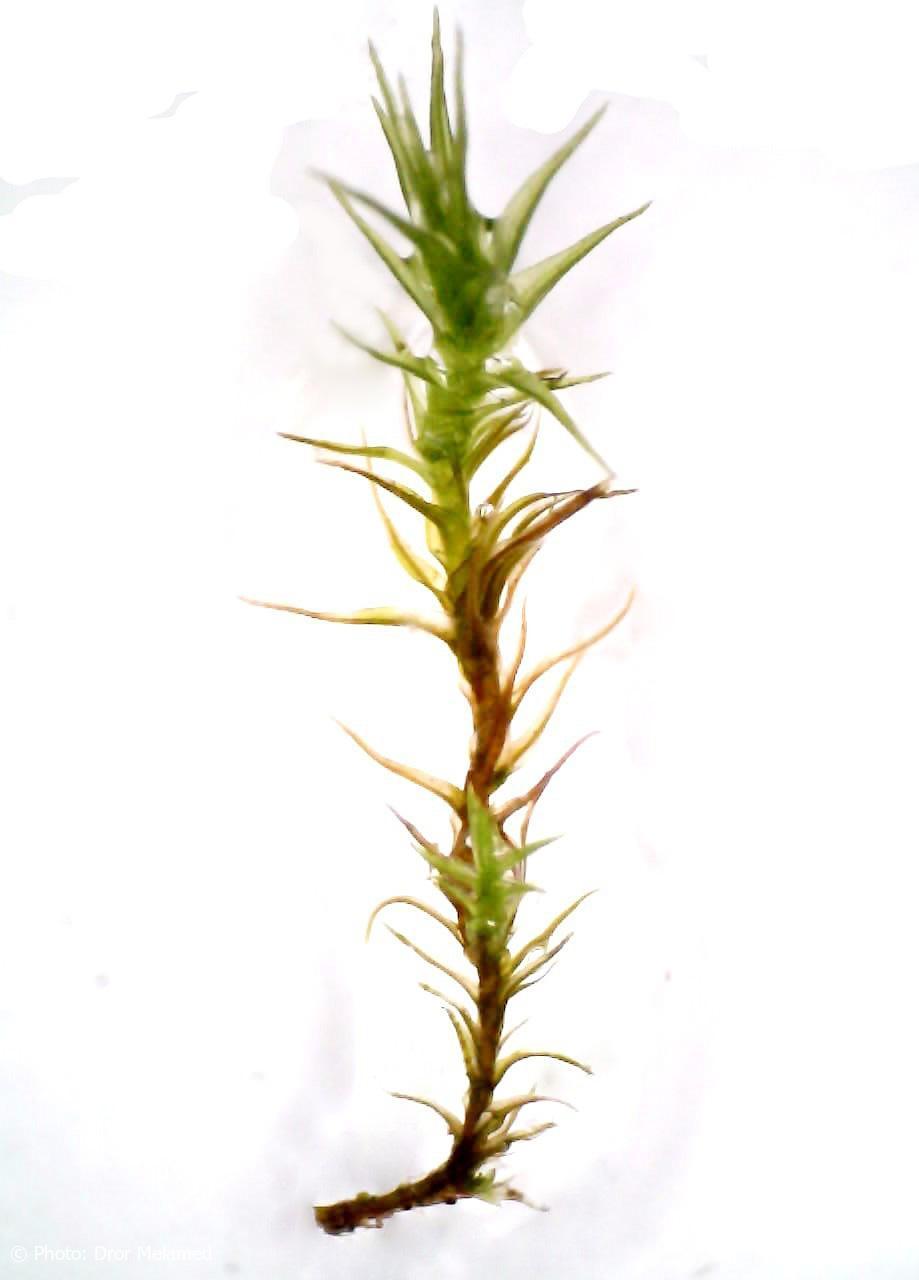
Didymodon rufidulus is a true chameleon in the moss world. Its appearance can vary greatly depending on its environment, but there are a few key characteristics that set it apart. This moss forms dense, reddish-brown tufts or cushions, with stems that can reach up to 2 cm in height. The leaves are

2020-11-02-16-28-40-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/didymodon-rigidulus/
lanceolate (lance-shaped) and crisped when dry, giving it a distinctive, almost curly appearance.
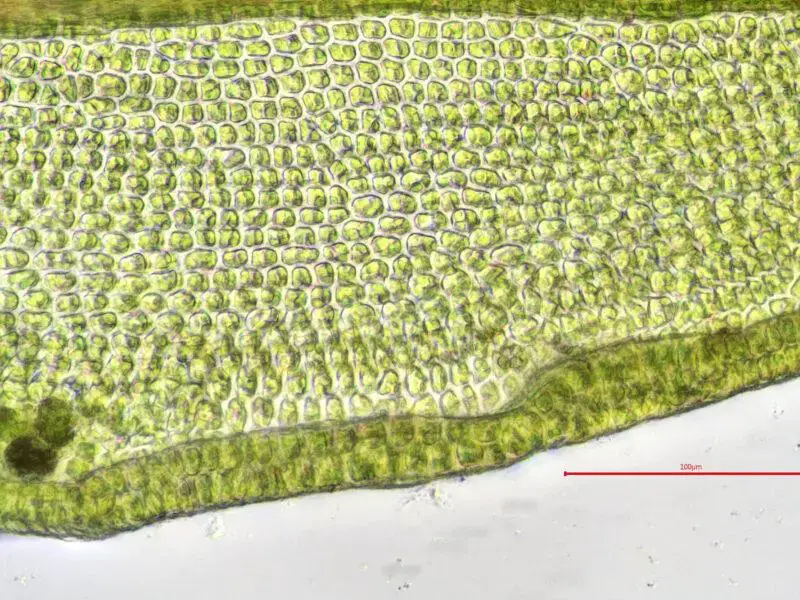
One of the most fascinating features of Didymodon rufidulus is its peristome, the intricate fringe of teeth surrounding the opening of the capsule (spore-bearing structure). This peristome is

3397-l-1.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=21800
twisted and papillose (covered in tiny bumps), making it a valuable identification tool for bryologists.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Didymodon rufidulus is a true globetrotter, found on almost every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from dry and exposed areas to shaded rock crevices and even disturbed urban environments. This moss is a true survivor, able to withstand harsh conditions and colonize new territories with ease.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Didymodon rufidulus plays a significant role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize soil and create favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its ability to absorb and retain moisture makes it an important contributor to water regulation in arid environments.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Didymodon rufidulus is its ability to desiccate (dry out completely) and then revive when water becomes available again. This incredible feat is made possible by specialized cellular structures and mechanisms that protect the moss during periods of drought.
Case Studies/Examples
To illustrate the resilience and adaptability of Didymodon rufidulus, let’s take a look at a fascinating case study. In the heart of New York City, this moss has been found thriving on the concrete walls of buildings and even in the cracks of sidewalks. Its ability to colonize these urban environments is a testament to its remarkable tolerance for pollution and disturbance.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Didymodon |
| Species | rufidulus |
| Growth Form | Dense tufts or cushions |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, crisped when dry |
| Peristome | Twisted, papillose |
| Habitat | Dry and exposed areas, rock crevices, urban environments |
| Distribution | Widespread, found on most continents except Antarctica |
Conclusion
Didymodon rufidulus is a true marvel of the moss world, showcasing incredible adaptations, ecological significance, and a remarkable ability to thrive in even the harshest environments. As we bid farewell to this fascinating species, we’re left with a thought-provoking question: What other secrets might the humble mosses hold, waiting to be uncovered by curious minds and dedicated enthusiasts?