image from: https://bioone.org/journals/cryptogamie-bryologie/volume-35/issue-1/cryb.v35.iss1.2014.47/Studies-on-African-Riccardia-Types-and-Related-Material/10.7872/cryb.v35.iss1.2014.47.full
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Riccardia caespitans (Steph.) E.W.Jones, 1956 moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Aneuraceae family. Also known simply as Riccardia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive marvel and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Riccardia caespitans, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
image from: https://mosswalks.blogspot.com/2012/07/sphagnum-id.html?m=1
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
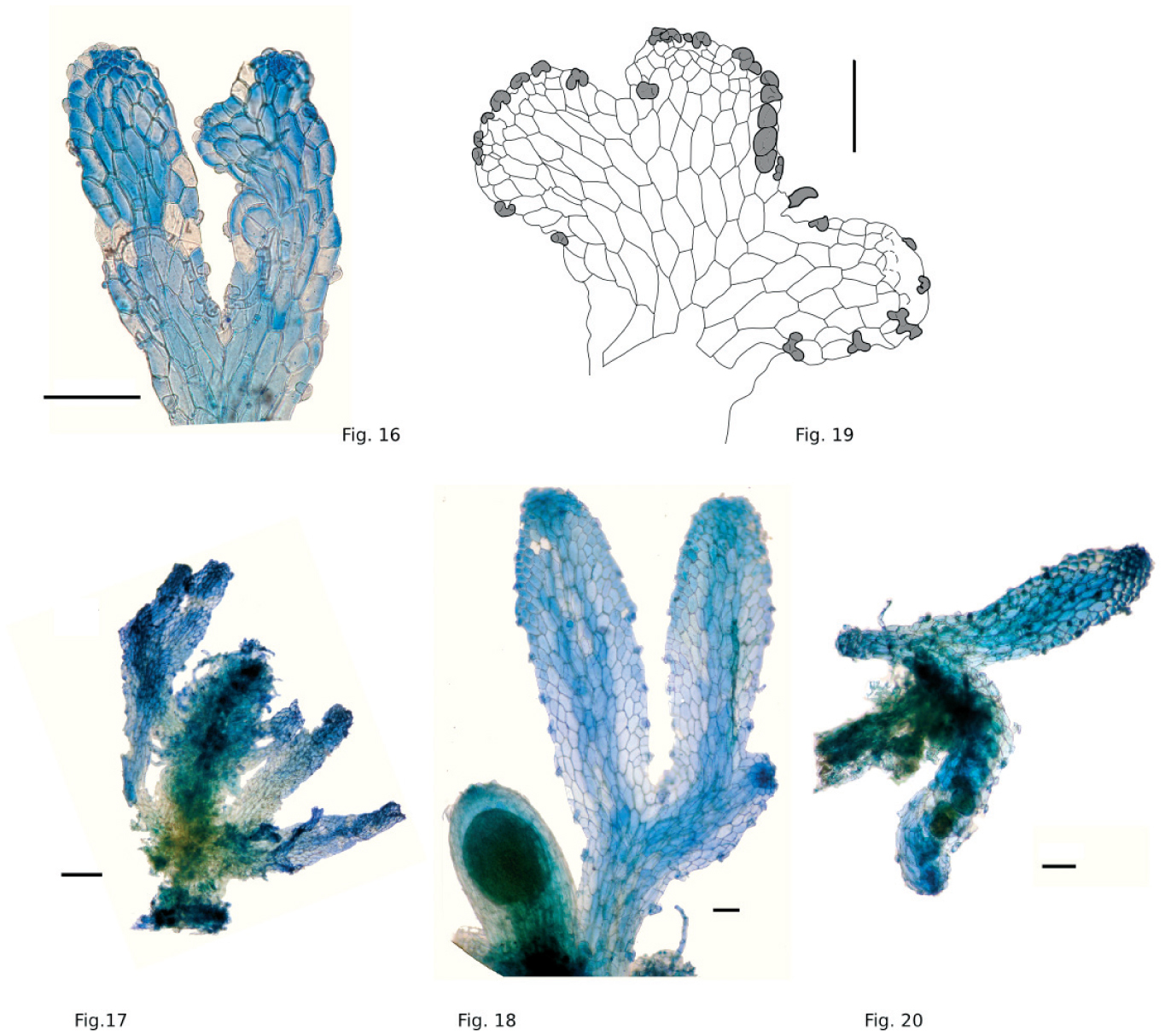
Riccardia caespitans is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form. Its creeping stems are densely branched, forming compact tufts or mats. The plant’s leaves are deeply divided into narrow segments, giving it a delicate, feathery appearance. When viewed under a microscope, the intricate details of its

image from: https://www.reddit.com/r/PlantedTank/comments/dzb0nx/can_somebody_help_me_identify_this_moss_thank_you/
leaf cells and

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Riccardia-graeffei-Steph-Hewson-1-3-Habit-4-A-portion-of-thallus-in-ventral-view_fig1_321824313
reproductive structures become apparent, revealing the intricate beauty of this tiny organism.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Riccardia caespitans is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including
image from: https://tropica.com/en/plants/plantdetails/Riccardiachamedryfolia(003D)/4400
Europe, Asia, North America, and New Zealand. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on damp soil, rotting logs, or rock surfaces in forests, ravines, and stream banks. This moss’s ability to adapt to a wide range of habitats contributes to its successful dispersal and survival.

image from: https://taieol.tw/pages/46308
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Riccardia caespitans plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide a microhabitat for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.

image from: https://sv.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flikbålmossor
One of the remarkable adaptations of Riccardia caespitans is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the plant can curl up and enter a dormant state, conserving moisture and reviving once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest, researchers discovered that Riccardia caespitans played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas and create a suitable microenvironment facilitated the establishment of other plant species, accelerating the overall regeneration process.
Technical Table

image from: https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/262397
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta
 image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Riccardia-angusticosta-Steph-Grolle-A-thalli-B-main-axis-in-cross-section-C_fig2_339096326 |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
Order
_0073.jpg/240px-Riccardia_multifida_(b%2C_144711-475653)_0073.jpg) image from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Riccardia_multifida |
Metzgeriales |
| Family | Aneuraceae |
| Genus | Riccardia |
| Species | caespitans |
| Growth Form | Thallose liverwort |
| Leaf Morphology | Deeply divided into narrow segments |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, New Zealand |