203923.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6750
Introduction
In the vast and fascinating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance: Sphagnum fuscum (Schimp.) H.Klinggr., commonly known as Sphagnum. This unassuming yet remarkable plant belongs to the family Sphagnaceae and is a true marvel of nature, playing a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Sphagnum fuscum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but are vital components of many terrestrial and aquatic environments. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.

5f6b53_29384208227a454bbbd0e5d392eda12d~mv2.jpeg from: https://www.wodnepodroze.com/single-post/Torfowiec-brunatny-Sphagnum-fuscum
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
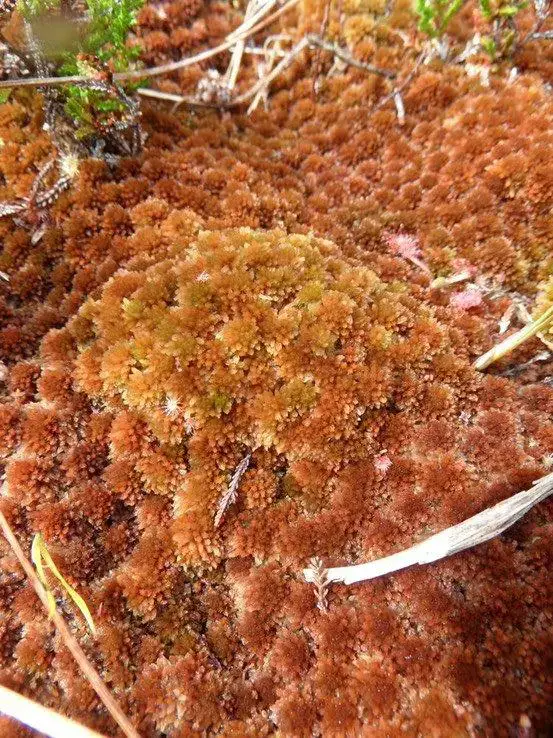
Sphagnum fuscum is a tufted moss that forms dense, compact cushions or mats. Its stems are typically reddish-brown to dark brown in color, and the leaves are ovate-lanceolate

52270783062_4f46a71ff1_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/davejglaves/52270783062/
in shape, with a distinctive cucullate (hood-like) apex. One of the most striking features of this moss is its ability to absorb and retain large amounts of water, thanks to its specialized
KKgL8dfspffzzRYeWMy5TKYk4VjA-VozzN0Om6qNfEPPGwHkCqr5AcAnXXYi0Qd7C0nMYbnjTBp6IhItaDYJ-Q=s600 from: https://www.projectnoah.org/spottings/160296010
hyaline cells and capillary spaces.
Global Distribution and Habitat
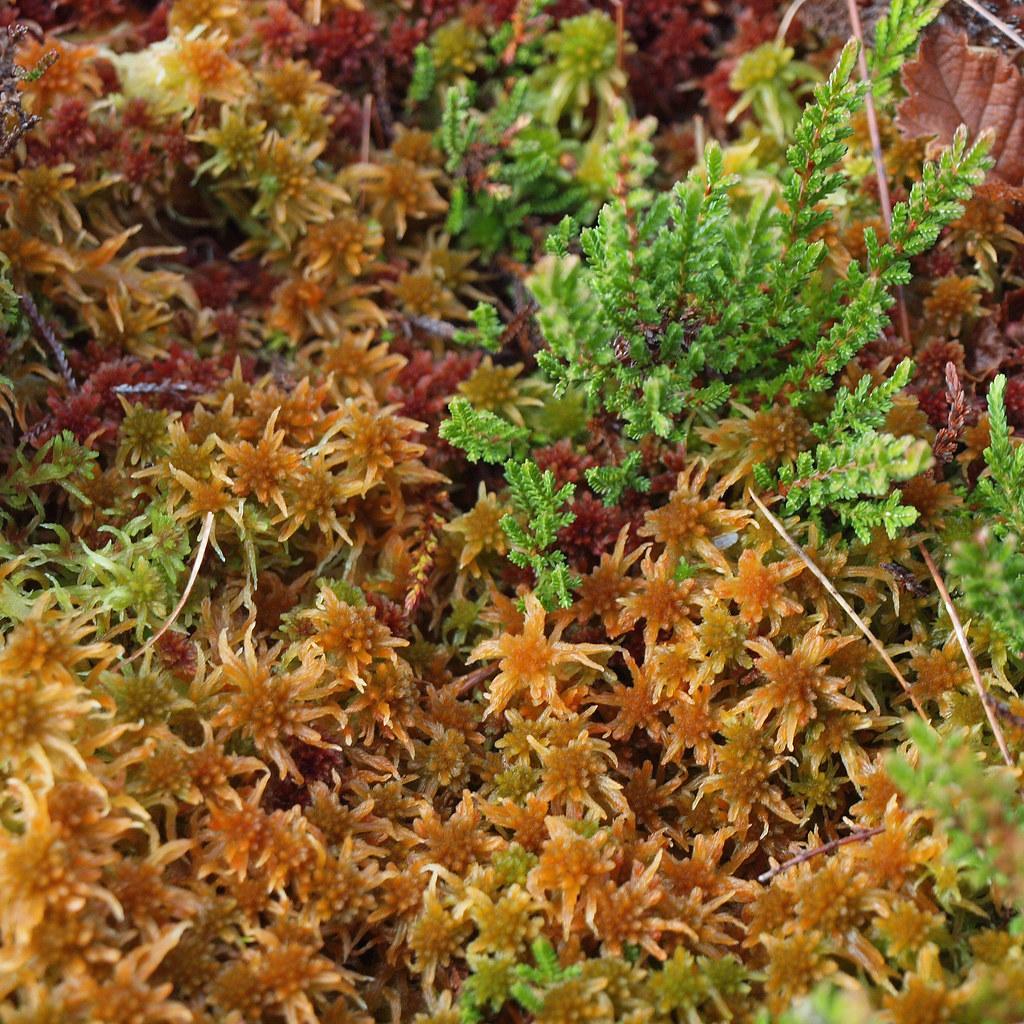
Sphagnum fuscum is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in a variety of habitats, including bogs, fens, swamps, and wet tundra. It is particularly abundant in boreal and subarctic regions, where it plays a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of peatlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Sphagnum mosses, including Sphagnum fuscum, are often referred to as “ecosystem engineers” due to their ability to modify their environment and create unique habitats. These mosses are highly adapted to acidic and nutrient-poor conditions, and their decomposition process is slow, leading to the accumulation of peat.
Peatlands formed by Sphagnum species are not only important carbon sinks but also provide valuable ecosystem services, such as water regulation, nutrient cycling, and habitat for a diverse array of plant and animal species. Additionally, Sphagnum mosses have been used in various applications, including horticulture, medicine, and even as a wound dressing during World War I.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of the ecological significance of Sphagnum fuscum can be found in the Mer Bleue Bog near Ottawa, Canada. This vast peatland is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, and Sphagnum fuscum plays a crucial role in maintaining the unique ecosystem. Researchers have studied the moss’s ability to regulate water levels, create microhabitats, and support a wide range of organisms, including rare and endangered species.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Sphagnopsida |
| Order | Sphagnales
 Sphagnum-fuscum-1008.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sphagnum-fuscum/ |
| Family | Sphagnaceae |
| Genus | Sphagnum |
| Species | Sphagnum fuscum (Schimp.) H.Klinggr. |
| Growth Form | Tufted, compact cushions or mats |
| Stem Color | Reddish-brown to dark brown |
Leaf Shape
 29279356461_21e9b6628a_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/95549735@N08/29279356461/ |
Ovate-lanceolate, cucullate apex |
| Water Absorption | Highly efficient due to hyaline cells and capillary spaces |
Conclusion
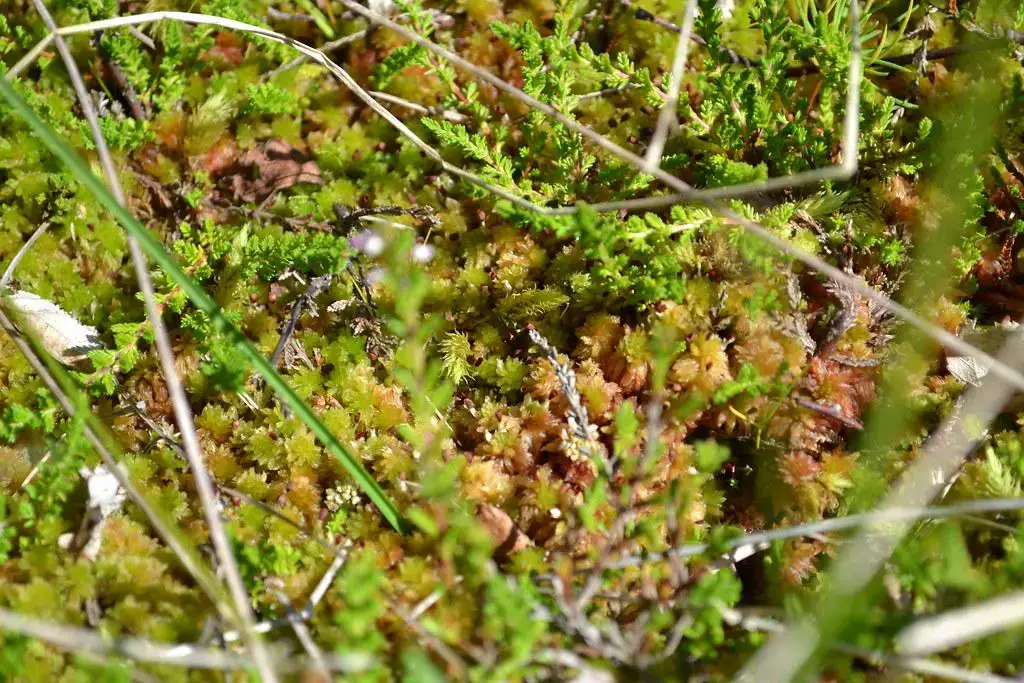

8790052093_182d0e2ca7_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/95549735@N08/8790052093/
Sphagnum fuscum, a humble yet extraordinary moss species, plays a vital role in shaping and sustaining various ecosystems worldwide. From its unique morphology and water-absorbing capabilities to its role in peatland formation and carbon sequestration, this moss is a true testament to the incredible diversity and importance of bryophytes.
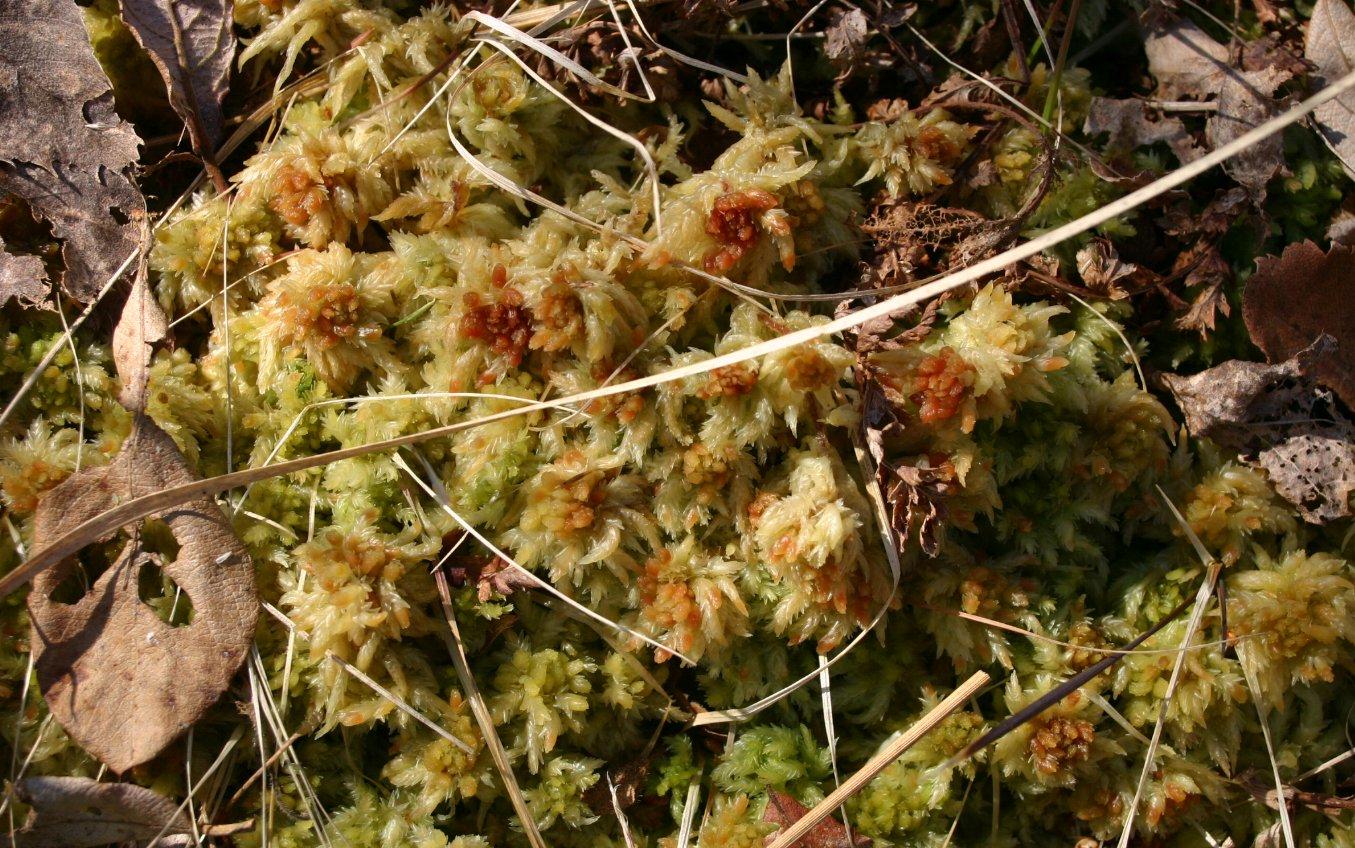

Sphagnum-fuscum.JPG from: https://de-academic.com/dic.nsf/dewiki/2284527
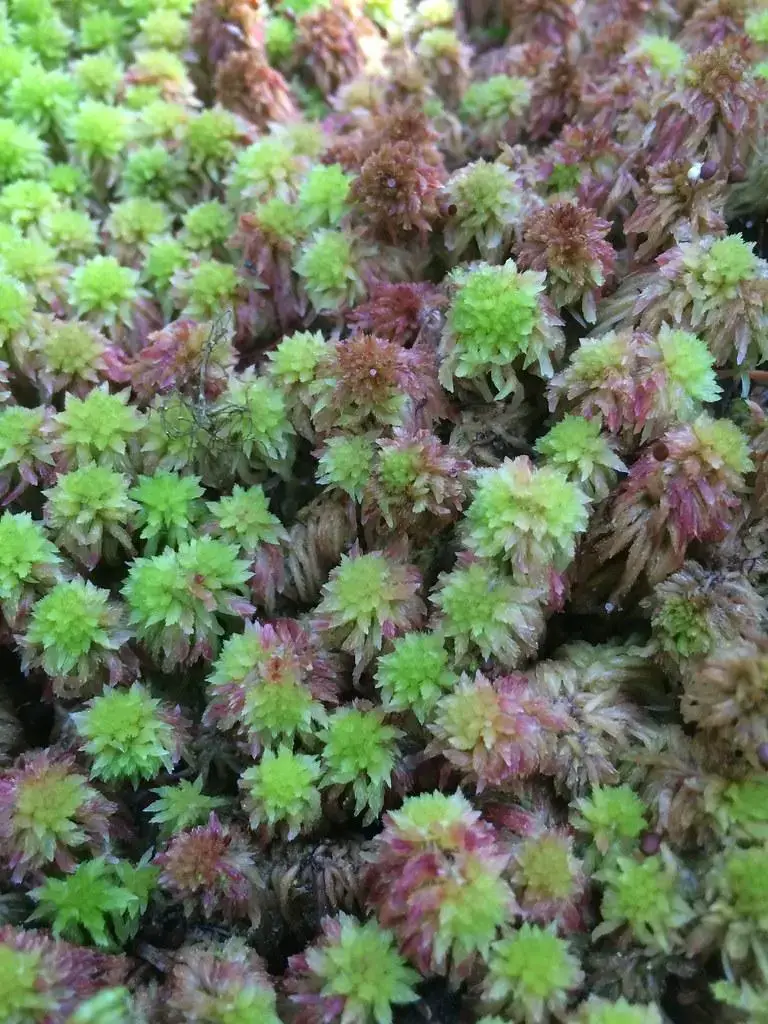

51986804471_fe6fb20351_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/195292270@N06/51986804471
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet invaluable ecosystems, ensuring that the intricate web of life remains intact for generations to come?
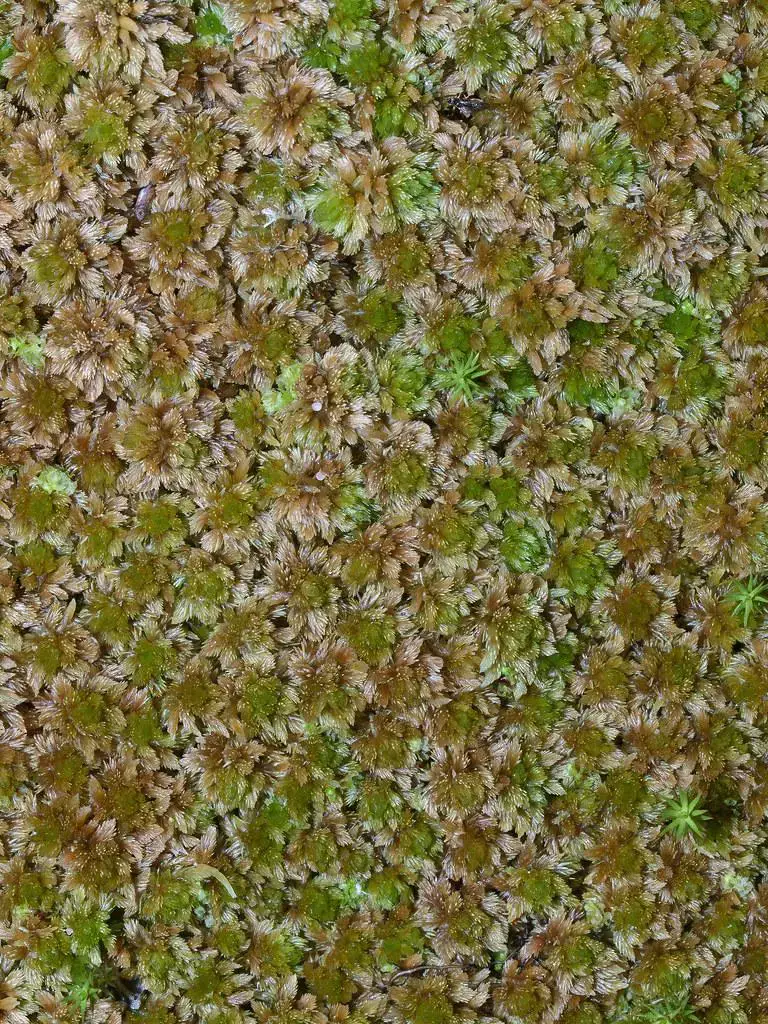

4953876097_09b1b3dbfd_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/dougcwaylett/4953876097/