
western-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-moss-AYMXR7.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/western-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-moss-image9796598.html
Introducing the Intriguing Symphyodon Moss
Mosses may be small, but they play a big role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly fascinating species is Symphyodon erinaceus (Mitt.) A.Jaeger, also known simply as Symphyodon moss. This unique moss belongs to the Symphyodontaceae family and has some remarkable characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at this tiny but mighty plant!
Background on Bryophytes
Before diving into the details of Symphyodon moss, it’s helpful to understand a bit about mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta

49873322643_c0a9ec871e.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/21657471@N04/49873322643/
. They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having simple structures that serve similar functions. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats across the globe.
Morphology and Identification
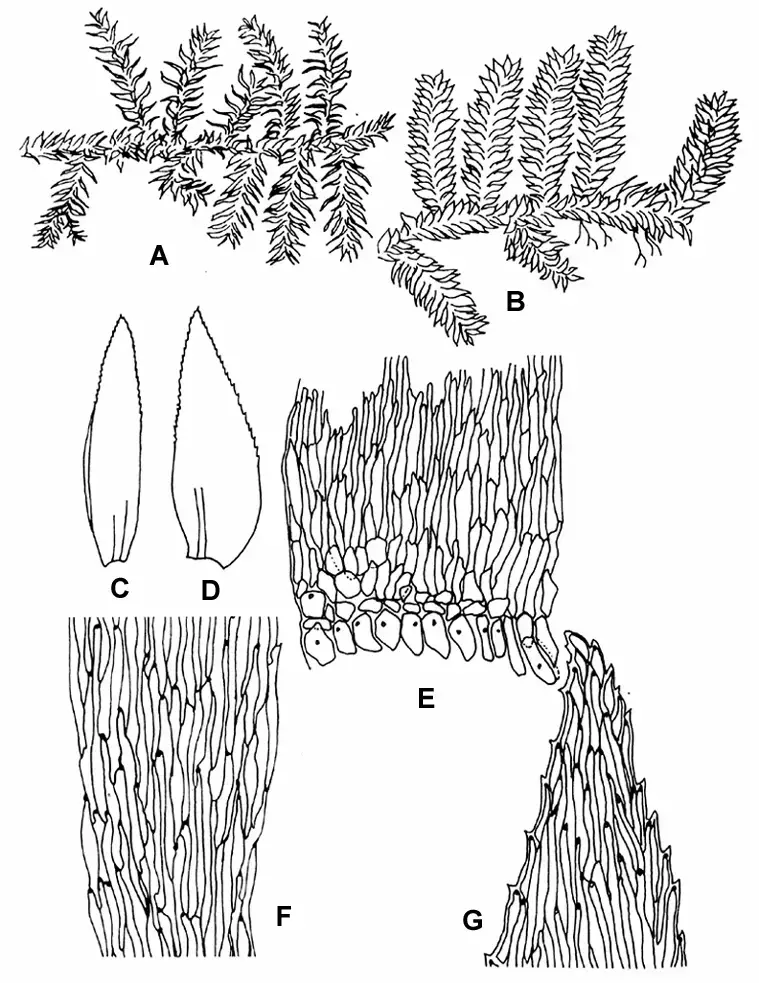
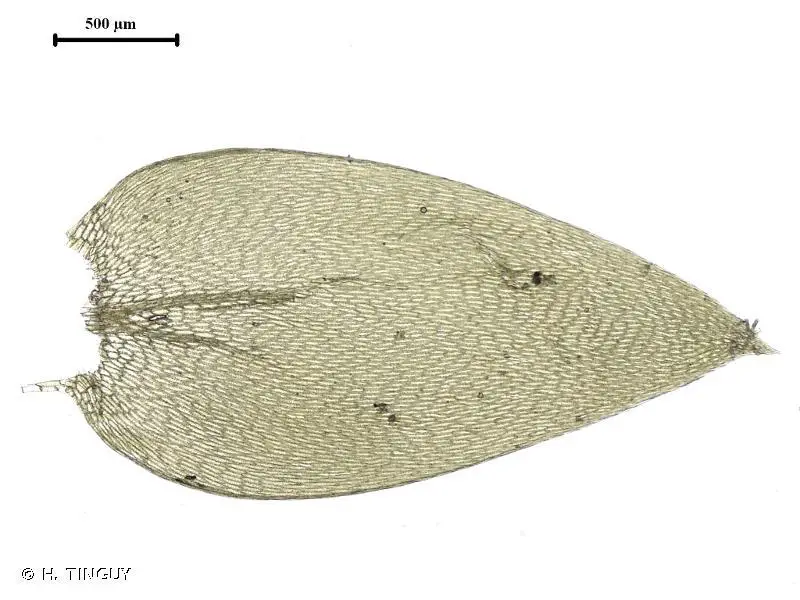
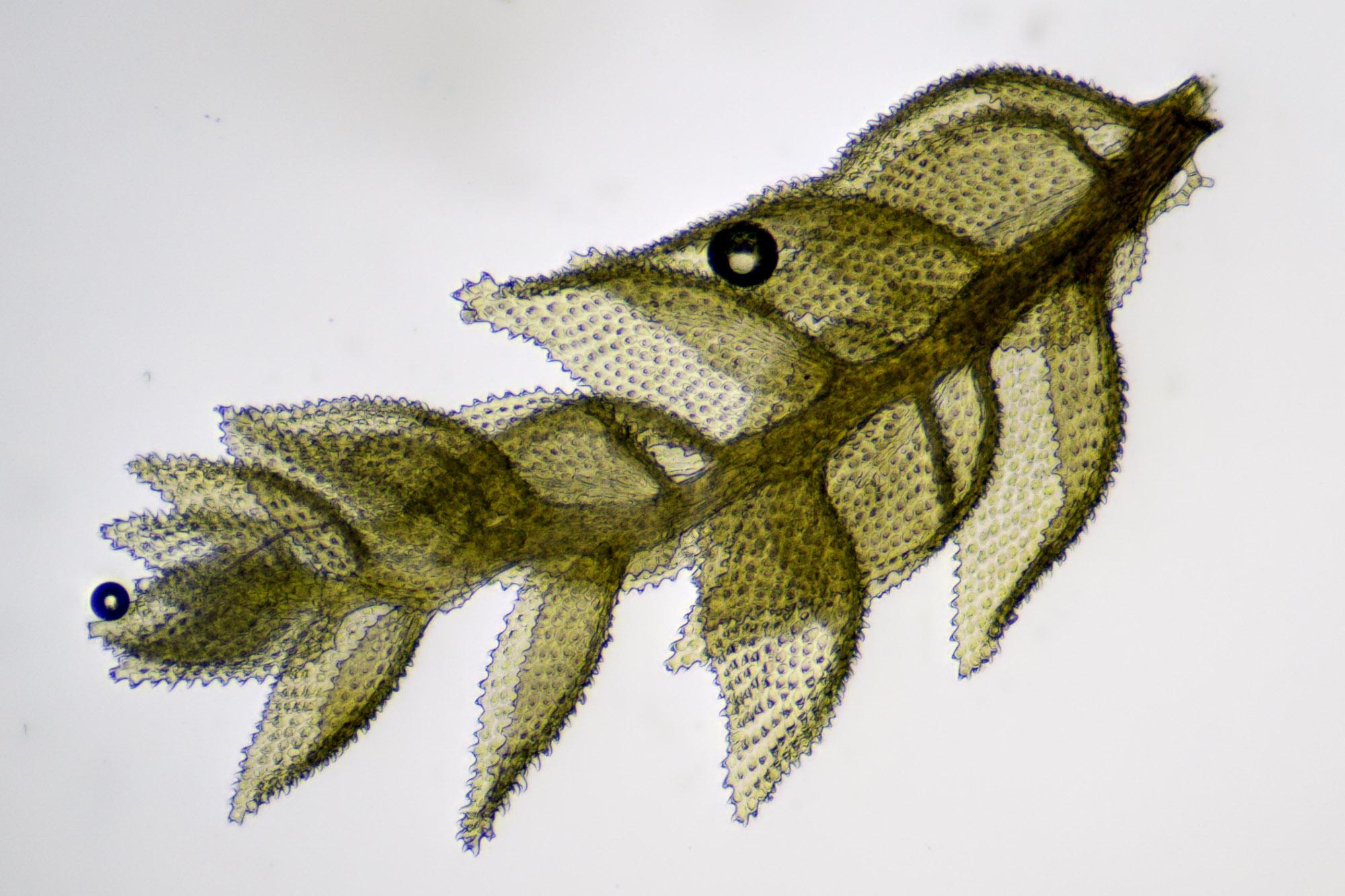
Symphyodon erinaceus is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning it has a branching, creeping growth form. The stems are pinnately branched and can grow up to

european-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-a-green-moss-in-the-forest-summer-image-cute-funny-animal-with-snipes-W7FM6R.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/european-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-a-green-moss-in-the-forest-summer-image-cute-funny-animal-with-snipes-image262803263.html
10 cm long. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, 1-2 mm long, and have a distinctly serrated margin that resembles hedgehog spines (hence the species name “erinaceus,” meaning hedgehog).
The leaf cells are elongated and thick-walled.

european-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-a-green-moss-in-the-forest-summer-image-cute-funny-animal-with-snipes-W7FM73.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/european-hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus-on-a-green-moss-in-the-forest-summer-image-cute-funny-animal-with-snipes-image262803271.html
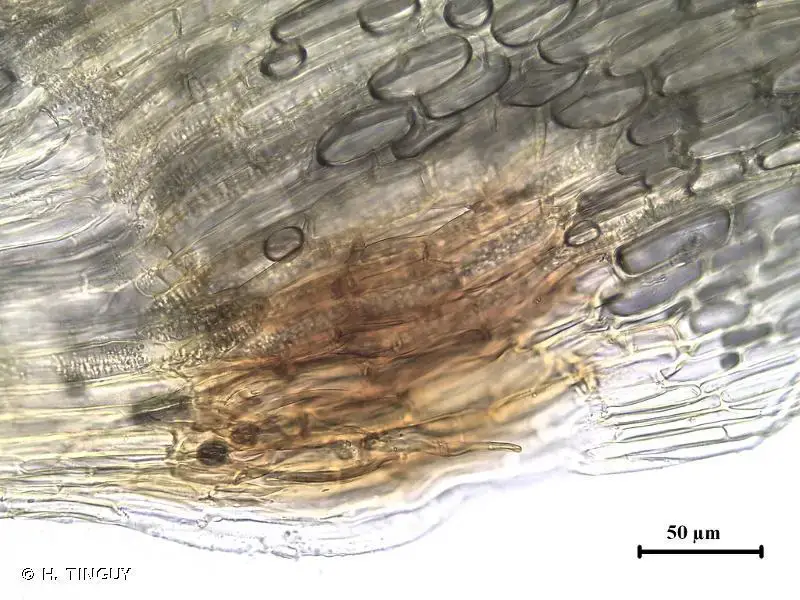
Sporophytes (spore-producing structures) are relatively rare but distinctive, with a long seta (stalk) and cylindrical capsule. Symphyodon can be tricky to identify in the field due to its small size and similarity to other mosses, but its unique leaf margins are a key feature.
Global Distribution and Habitat

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u_0EAsxYOSY
Symphyodon moss has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. It typically grows as an epiphyte on tree trunks and branches in moist, shady forests at elevations from
Symphyodon-erraticus-Mitt-Jaeg-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet-plant-667-C-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Symphyodon-erraticus-Mitt-Jaeg-A-dry-plant-667-B-wet-plant-667-C-D_fig2_242597571
sea level to 2,500 meters.
Symphyodon is often associated with other epiphytic bryophytes and can form dense mats on its substrate. While widespread, it is not usually a dominant component of the ecosystems where it occurs.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Symphyodon plays several important ecological roles:
- Moisture retention: The mat-like growth traps and holds moisture, helping to regulate humidity in the immediate environment.
- Nutrient cycling: Mosses absorb nutrients from rainwater and trap organic debris, later releasing these nutrients as the moss dies and decays.
- Microhabitat creation: The complex structure provides shelter and habitat for various micro-organisms and invertebrates.
Symphyodon has several adaptations that allow it to thrive as an epiphyte in tropical forests:
- Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of drying out and rehydrate quickly when moisture is available again.
16039829971857UnRWou9LJyaJ5SW from: https://science.mnhn.fr/institution/mnhn/collection/pc/item/pc0093625
- Leaf morphology: The thick cell walls and small, overlapping leaves help to prevent water loss.
- Asexual reproduction: In addition to spores, Symphyodon can reproduce vegetatively via fragments, allowing it to colonize new substrates easily.
229012.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434135/tab/taxo
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Symphyodontaceae |
| Growth form | Pleurocarpous (branching) |
| Stem length | Up to 10 cm |
| Leaf shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf length | 1-2 mm |
| Leaf margin | Serrated |
| Habitat | Epiphytic in tropical forests |
| Elevation range | Sea level to 2,500 m |
| Distribution | Pantropical |
Conclusion
Symphyodon erinaceus is a small but fascinating moss with a unique morphology and widespread tropical distribution. Its ecological roles in moisture retention, nutrient cycling, and microhabitat creation make it a valuable component of the ecosystems where it occurs, even if it often goes unnoticed.

248819.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5969
Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the tree trunks and branches – you might just spot a patch of Symphyodon! What other secrets do you think this mighty moss holds?

2017-04-29-14-16-55.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/thuidium-assimile/