cryptogamie-bryologie2006v27f2a7.jpg from: https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/fr/periodiques/bryologie/27/2/trematodon-ambiguus-hedw-hornsch-bryopsida-spanish-pyrenees
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Trematodon ambiguus (Hedw.) Hornsch. moss stands out as a fascinating representative of the Bruchiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Trematodon, this unassuming yet remarkable moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this intriguing bryophyte.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Trematodon ambiguus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260868733_Discovery_of_a_natural_hybrid_between_Bruchia_vogesiaca_Schwagr_and_Trematodon_ambiguus_Hedw_Hornsch_Musci_Bruchiaceae
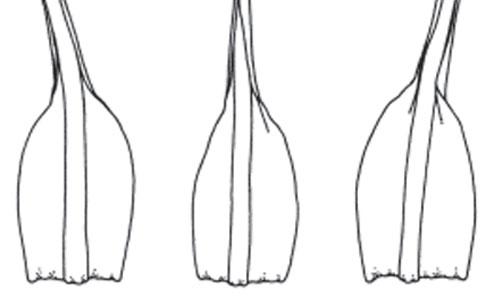
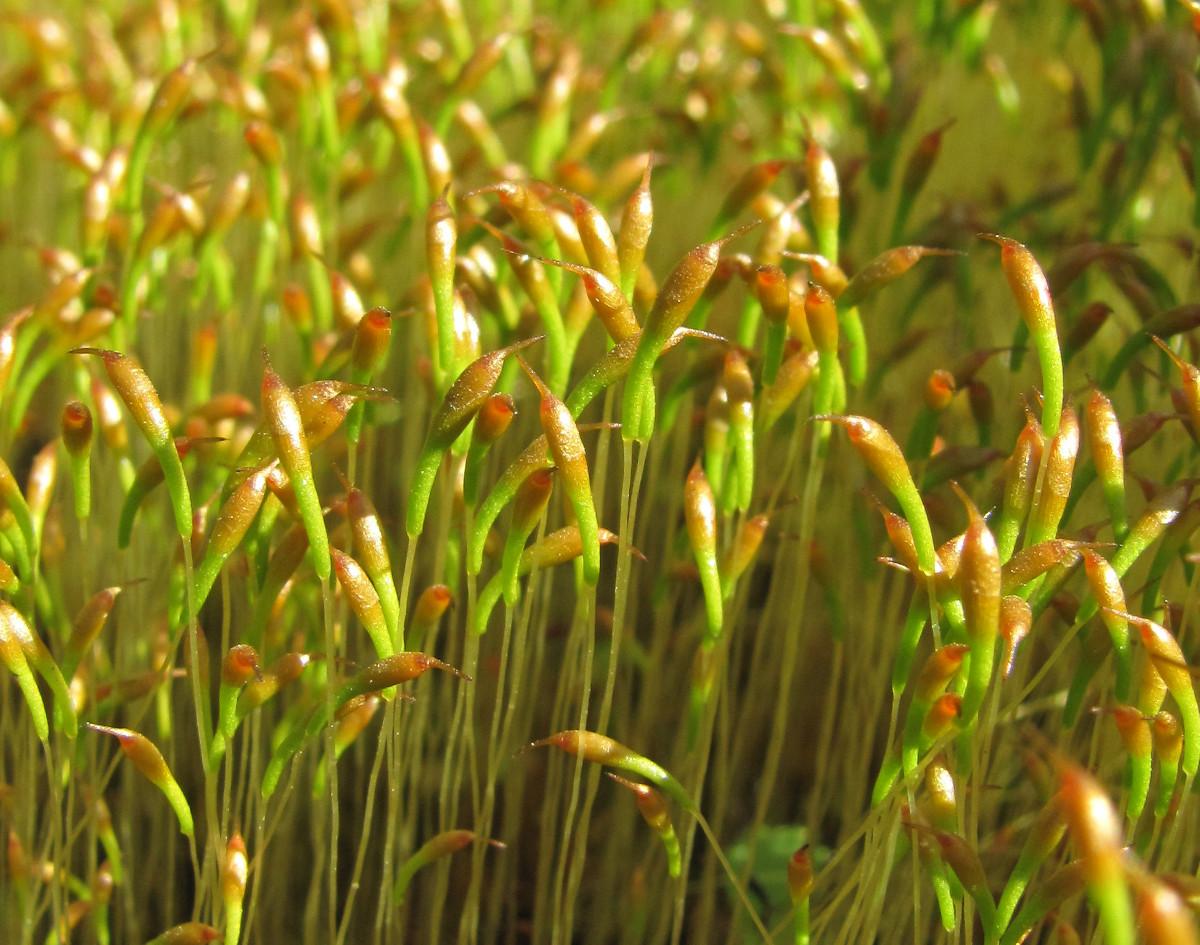
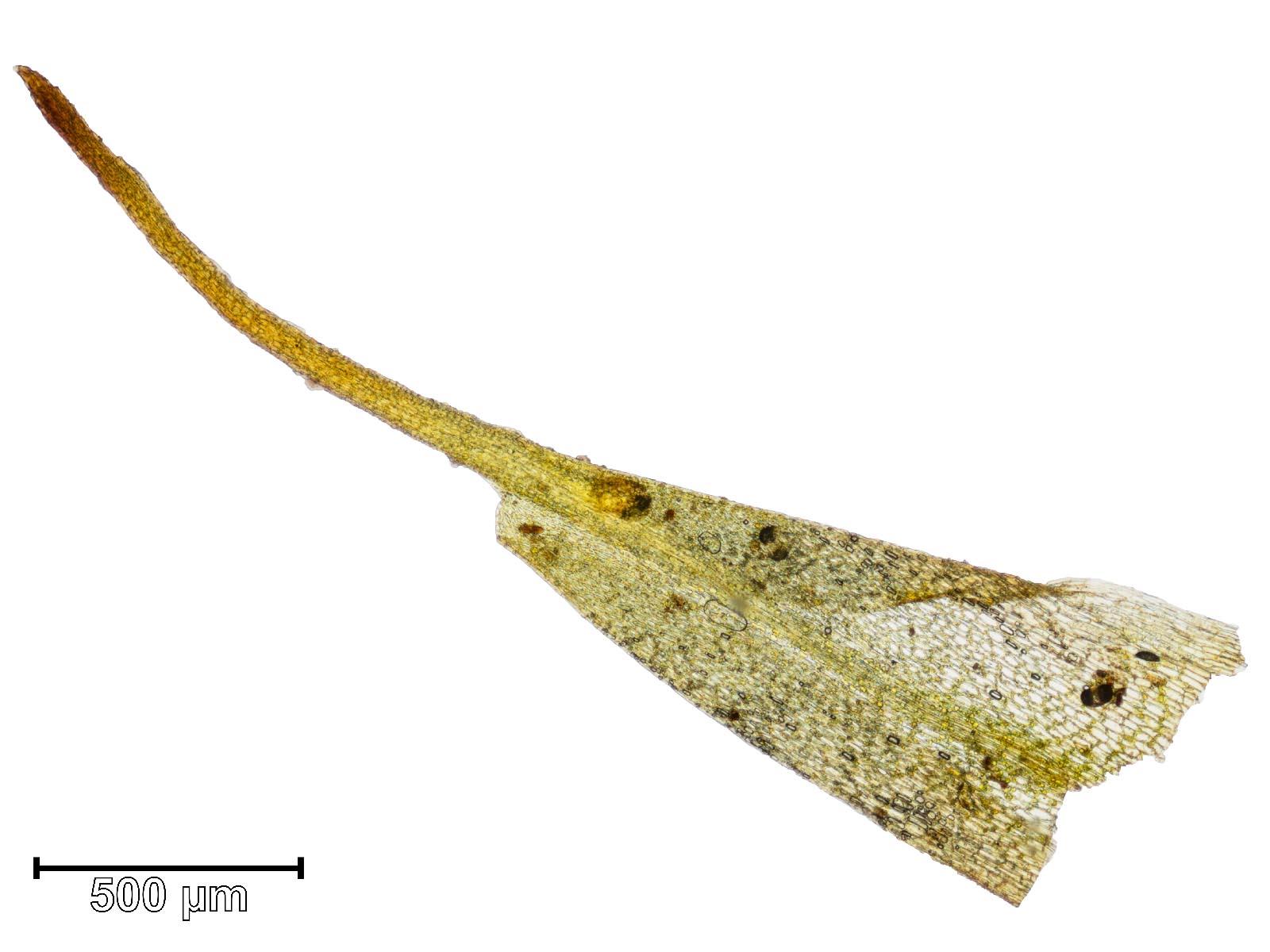
Trematodon ambiguus is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense tufts or cushions. Its slender stems are typically less than an inch tall, adorned with delicate, lanceolate leaves that are spirally arranged. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its apiculate leaf tips, which appear slightly pointed or mucronate.
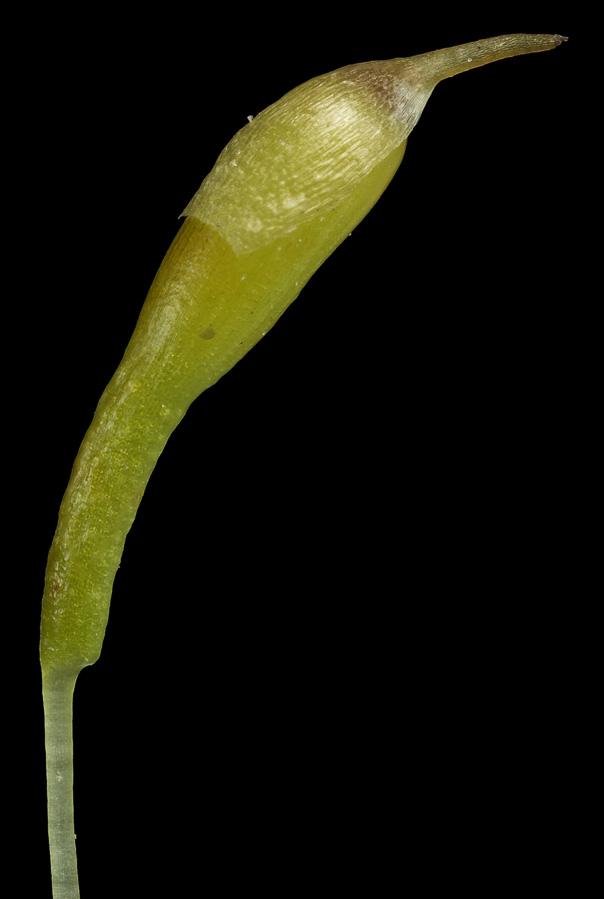
The sporophytes of Trematodon ambiguus are equally fascinating. The seta (stalk) supporting the capsule is often curved or bent, giving the moss a unique appearance. The

409103_5b704961.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/409103.html
capsules themselves are cylindrical and slightly curved, with a distinctive operculum (lid) that detaches when the spores are ready for dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Trematodon ambiguus is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests to rocky outcrops and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and quarries.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to acidic soils and can often be found growing on decaying wood, rotting logs, or humus-rich substrates. Its ability to colonize such diverse environments is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.

NFA-Bryos-Trematodon-ambiguus-00955.jpg from: https://northernforestatlas.org/atlas-image-category/trematodon-ambiguus/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Trematodon ambiguus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, these mosses provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to biodiversity.

trematodon_ambiguus4.jpg from: https://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/sammalet/rutakaulasammal.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Trematodon ambiguus is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its remarkable resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found Trematodon ambiguus to be a valuable indicator species for assessing the health of old-growth forests. Its presence was closely linked to the availability of decaying wood and the overall complexity of the forest ecosystem.
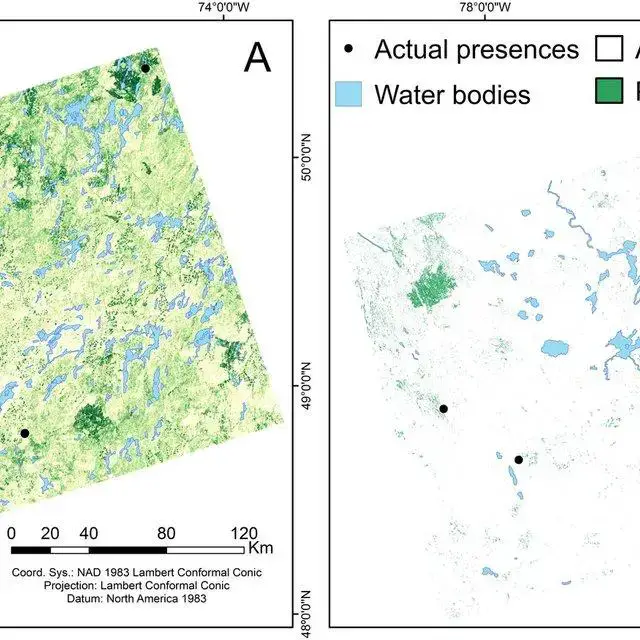
Example-of-A-continuous-and-B-binary-predictive-mapping-of-the-moss-Trematodon_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Example-of-A-continuous-and-B-binary-predictive-mapping-of-the-moss-Trematodon_fig2_357638148

Comparison-of-sporophyte-morphology-of-Trematodon-ambiguus-Bruchia-vogesiaca-and-their_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Single-plants-of-Trematodon-ambiguus-left-Bruchia-vogesiaca-right-and-their-hybrid_fig2_260868733
Another interesting example comes from the United Kingdom, where Trematodon ambiguus has been observed growing on the mortar of old brick walls and buildings. This highlights the moss’s ability to colonize human-made structures, adapting to unique microhabitats.
Technical Table

trematodon_ambiguus_blatt.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/dicranaceae/index.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta
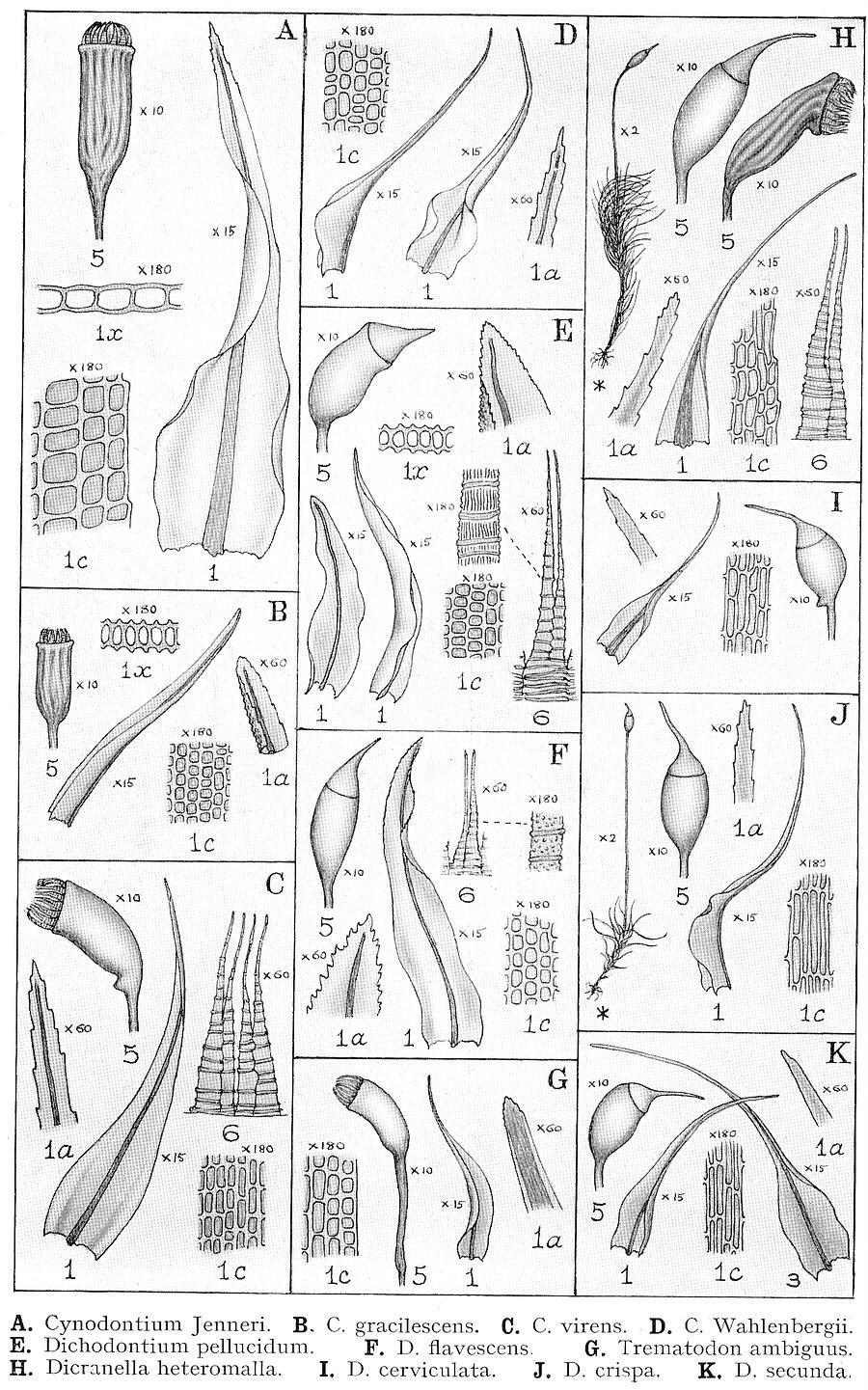 dix10.jpg from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/britms/www/dicranac.htm |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Dicranales |
| Family | Bruchiaceae |
| Genus | Trematodon |
| Species | ambiguus |
| Common Name | Trematodon moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, tufted or cushion-like |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with apiculate tips |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical, slightly curved |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, decaying wood, rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Widespread across Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America |
Conclusion

Trematodon-longicollis-449×300.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-trematodon-longicollis/
The Trematodon ambiguus (Hedw.) Hornsch. moss, a member of the Bruchiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological adaptations make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?