
large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/298311
Exploring the Fascinating World of Lepidozia subtransversa Steph. Moss
Lepidozia subtransversa Steph. is a captivating species of moss belonging to the Lepidoziaceae family. Commonly known as Lepidozia, this tiny but mighty plant plays important ecological roles and boasts unique adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the intriguing world of Lepidozia subtransversa Steph. and discover what makes it so special.
Background on Lepidozia Mosses
Lepidozia is a genus of leafy liverworts in the Marchantiophyta division and Jungermanniopsida class. There are over 400 Lepidozia species found worldwide, typically in damp, shaded habitats like forests and wetlands. These small, delicate plants lack true roots and instead absorb water and nutrients through their leaves and stems.
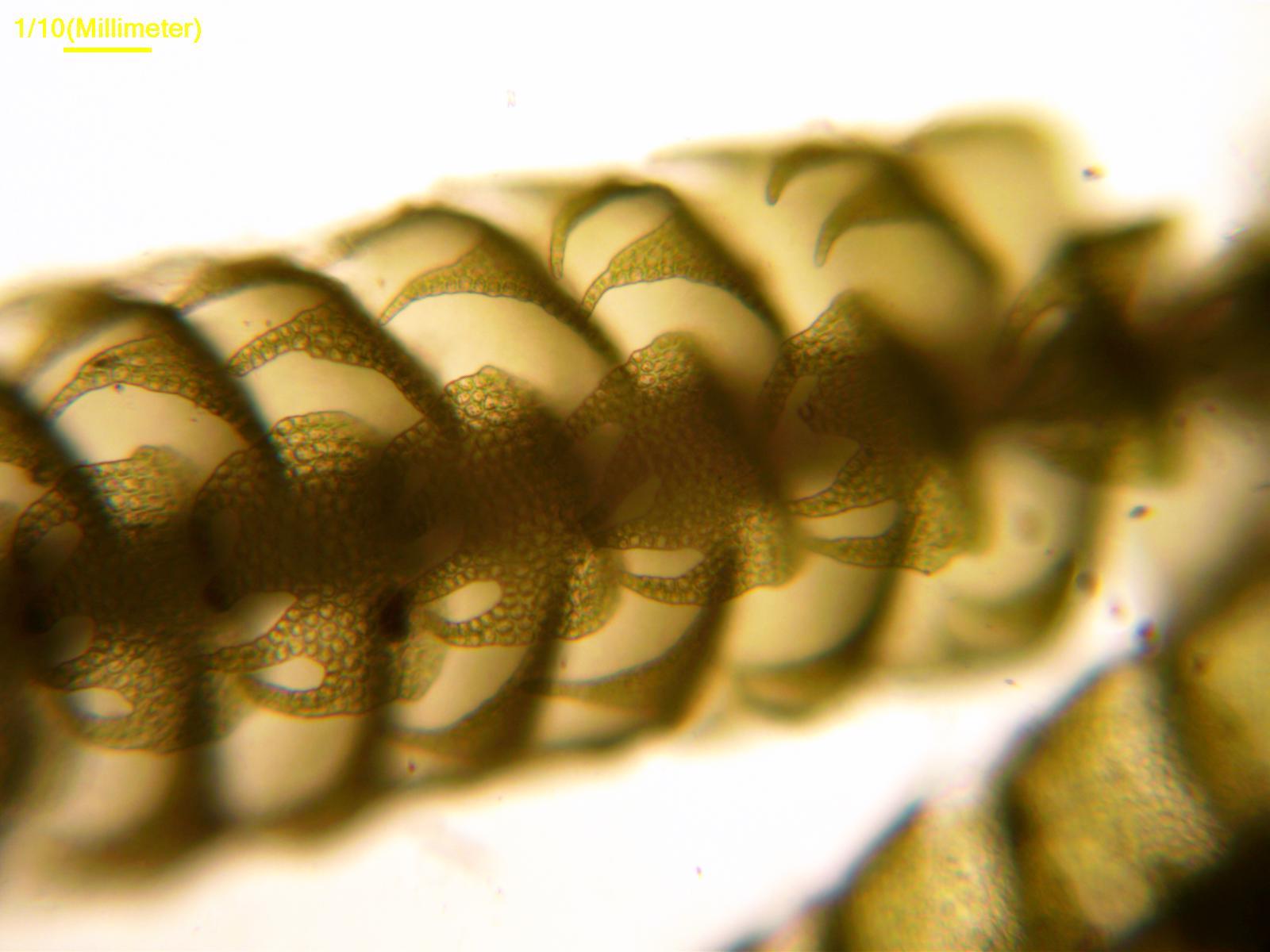
Lepidozia2.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/01/lepidozia-cupressina-at-taffs-well.html
Morphology and Identification of Lepidozia subtransversa Steph.
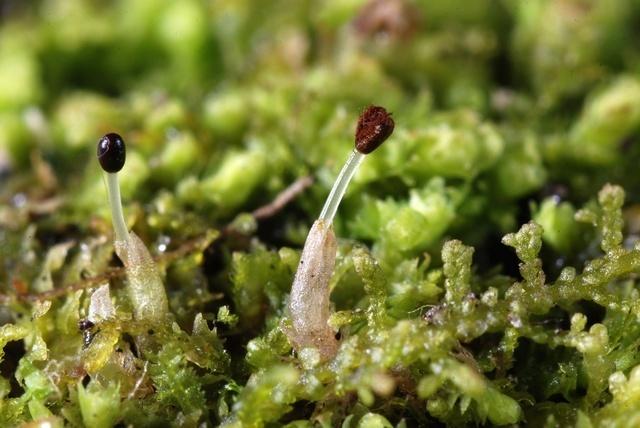
Lepidozia subtransversa Steph. is characterized by its creeping, branched stems that form dense mats. The leaves are deeply divided into narrow lobes, giving them a distinctive hand-like appearance under magnification. Lepidozia subtransversa produces tiny, spherical capsules on short stalks to disperse its spores.
Proper identification requires examining the number and shape of leaf lobes, underleaves, and specialized oil bodies in the leaf cells. A microscope is essential for seeing these minute diagnostic features.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This species is found across Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It grows on damp soil, rocks, logs, and tree bases in forests, ravines, and along streams. Lepidozia subtransversa thrives in humid, shaded microclimates and is sensitive to disturbances that alter these conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
As a pioneer species, Lepidozia subtransversa helps initiate soil formation on bare substrates by trapping organic matter and weathering surfaces. It provides shelter and moisture for invertebrates and microorganisms.
Lepidozia subtransversa exhibits desiccation tolerance, enabling it to survive periods of dryness by entering a metabolically inactive state. The dense mats help retain moisture and buffer temperature fluctuations in its microhabitat. Asexual reproduction via fragmentation allows rapid colonization of disturbed sites.
| Trait | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Small size | Thrives in limited space |
| Divided leaves | Increases surface area |
| Dense mats | Retains moisture, regulates temperature |
| Desiccation tolerance | Survives dry periods |
| Asexual reproduction | Rapid colonization |
Conclusion
Lepidozia subtransversa Steph. may be small, but it plays an outsized role in its ecosystems. From pioneering soil formation to providing microhabitats, this mighty moss is a fascinating example of how even the tiniest organisms can have a big impact.
Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot a patch of Lepidozia subtransversa making its mark on the world. What other small wonders are waiting to be discovered?