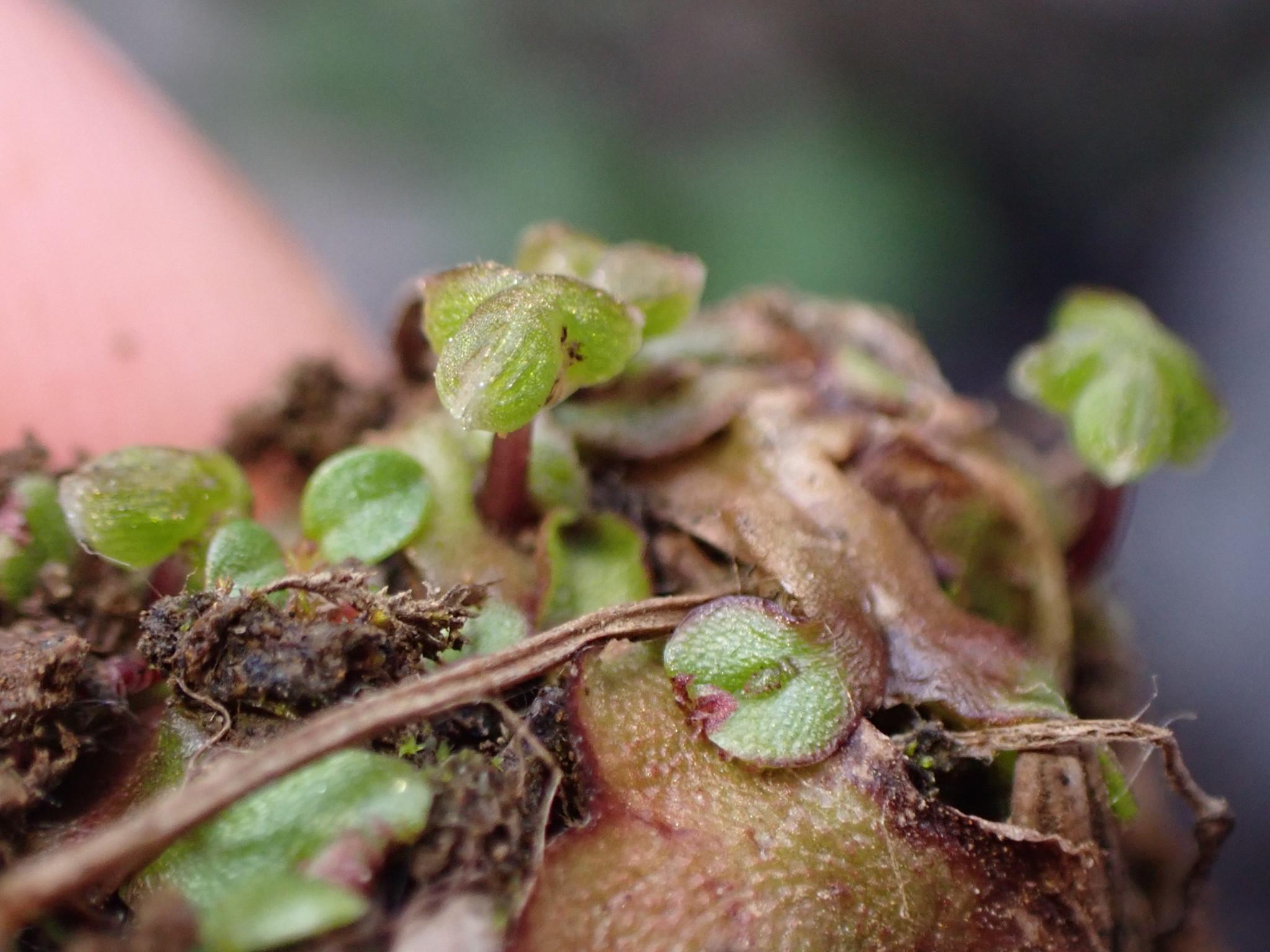

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2688622
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Scapania himalayica Müll.Frib. moss stands out as a remarkable representative of the Scapaniaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating moss, commonly referred to as Scapania, has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Scapania himalayica belongs to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida, which encompasses a diverse array of liverworts and mosses. These bryophytes play crucial roles in various ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling, soil formation, and providing microhabitats for other organisms.
Main Content
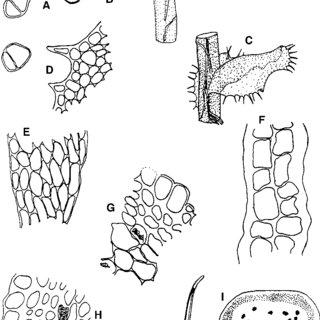
Scapania-orientalis-Muell-Frib-A-Gemmae-B-Leaf-on-stem-antical-aspect-C-Same_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scapania-orientalis-Muell-Frib-A-E-Leaves-All-drawn-from-Poelt-H190-JE-Scale_fig3_297484269
Morphology and Identification
Scapania himalayica is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form. Its gametophyte (the dominant, haploid phase) consists of a prostrate, irregularly branched thallus that adheres closely to the substrate. The thallus is typically greenish-brown to reddish-brown in color, with a distinct midrib running along its length.
One of the key identifying features of Scapania himalayica is the presence of underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the thallus. These underleaves are bifid (divided into two lobes) and decurrent (extending down the stem), providing a unique characteristic for identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Scapania himalayica is widely distributed across various regions, including Asia, Europe, and North America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as coniferous forests, rocky outcrops, and stream banks. This moss prefers acidic substrates and is often found growing on decaying logs, humus-rich soil, or among other bryophyte communities.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes, Scapania himalayica plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants and organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Scapania himalayica is its ability to desiccate and revive when moisture becomes available. This trait, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive in harsh environments and quickly resume its metabolic activities upon rehydration.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Himalayan region, researchers observed Scapania himalayica growing in abundance on moist, shaded rock surfaces. The moss formed dense mats, creating a unique microhabitat for various invertebrates, including springtails and mites. This highlights the ecological importance of this species in supporting biodiversity.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Scapaniaceae |
| Genus | Scapania |
| Species | himalayica |
| Growth Form | Thallose liverwort |
| Thallus Color | Greenish-brown to reddish-brown |
| Underleaves | Bifid, decurrent |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Asia, Europe, North America |
Conclusion
The Scapania himalayica Müll.Frib. moss, a member of the Scapaniaceae family, is a remarkable bryophyte that showcases the diversity and ecological significance of these often overlooked organisms. From its unique morphological features to its adaptations and roles within ecosystems, this moss continues to captivate enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us, leaving us with a thought-provoking question: What other wonders await discovery in the realm of these unassuming yet extraordinary plants?