A-E-Taxithelium-vernieri-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Taxithelium-ramivagum-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_fig8_232683560
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Taxithelium mundulum (Sull.) E.B.Bartram. Belonging to the Sematophyllaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as Taxithelium
A-Poorly-developed-alar-cells-in-T-planissimum-400-B-Poorly-developed-alar-cells_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232683560_A_Re-Circumscription_of_the_Moss_Genus_Taxithelium_Pylaisiadelphaceae_with_a_Taxonomic_Revision_of_Subgenus_Vernieri
. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant and explore its intricate world.
A-D-Taxithelium-homalophyllum-A-B-Variation-in-leaf-shape-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Taxithelium-homalophyllum-A-B-Variation-in-leaf-shape-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_fig10_261697502
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Taxithelium mundulum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Taxithelium mundulum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, ovate-lanceolate leaves that are typically 1-2 mm long. These leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, creating a feathery appearance. The moss can form dense, weft-like mats or cushions, often with a vibrant green hue.
One of the distinguishing features of Taxithelium mundulum is its double costa, or midrib, which extends beyond the leaf apex. This characteristic, along with its leaf shape and arrangement, aids in its identification among other moss species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Taxithelium mundulum is widely distributed across various regions, including North America, Central America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist forests and shaded rock outcrops to decaying logs and tree bark.
A-E-Taxithelium-kaernbachii-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-E-Taxithelium-kaernbachii-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_fig2_232683560
This moss species is particularly well-adapted to humid environments, often found in areas with high moisture levels, such as near streams, waterfalls, or in cloud forests. Its ability to colonize a variety of substrates, including soil, rocks, and decaying wood, contributes to its widespread distribution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Taxithelium mundulum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, supporting biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Taxithelium mundulum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
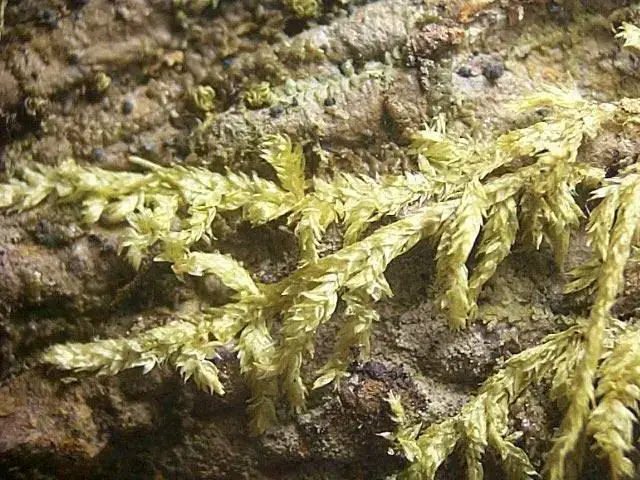
Anomodontopsis-rugelii-Muell-Hal-Ignatov-Fedosov-A-Habit-B-Branch-leaves-C_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Racopilum-magnirete-EBBartram-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-shoot-C-Lateral-leaves-D_fig9_356611709
In the Pacific Northwest region of North America, Taxithelium mundulum is a common sight in old-growth forests, where it carpets the trunks of ancient trees and decaying logs. Its presence is often an indicator of a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem, making it a valuable species for conservation efforts.

dd3489abe80c070f257d40f5dc5735b8.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.co.uk/pin/533958099550369620/
Similarly, in the cloud forests of Costa Rica, Taxithelium mundulum plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of these unique ecosystems. Its ability to capture and retain moisture from the ever-present mist contributes to the overall humidity levels, supporting the diverse array of plant and animal life found in these environments.
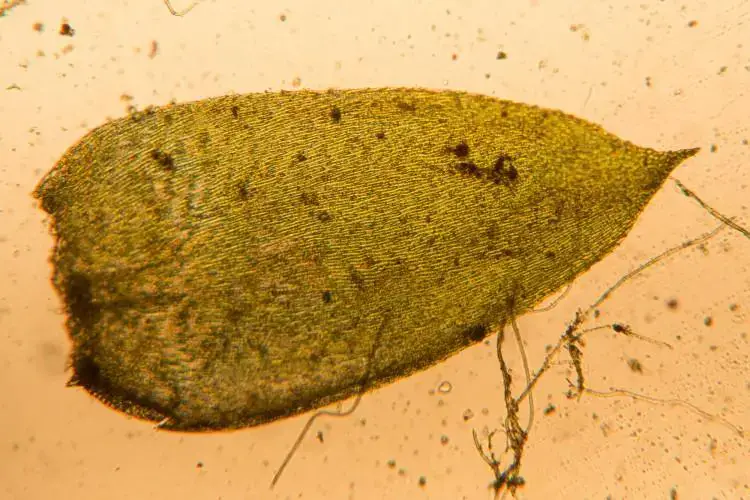

Taxiphyllum-deplanatum-2-750×500.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-taxiphyllum-deplanatum/
Technical Table

4fc7d0321444427dea03d2ab48fc4f19–regno-animale-family-names.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/handcolored-botanical-illustration-mosses-genus-phascum-several-species-shown-common-names-phascum-moss–533958099550365801/
f01_07.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/systematic-botany/volume-36/issue-1/036364411X553081/A-Re-Circumscription-of-the-Moss-Genus-Taxithelium-Pylaisiadelphaceae-with/10.1600/036364411X553081.full

Taxithelium%2BPLANUM%2BC.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/musgos-hypnales-taxithelium-planum.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Taxithelium mundulum (Sull.) E.B.Bartram |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm long |
| Costa | Double costa, extending beyond leaf apex |
| Habitat | Moist forests, shaded rock outcrops, decaying logs, tree bark |
| Distribution | North America, Central America, South America, Europe, Asia, Oceania |
Conclusion
Taxithelium mundulum, a unassuming yet remarkable moss species, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its ability to thrive in various habitats, contribute to ecosystem processes, and adapt to challenging conditions makes it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, Taxithelium mundulum stands as a reminder of the intricate beauty and ecological significance that can be found in even the smallest of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the microscopic wonders around us, what other hidden gems might we be missing, and how can we cultivate a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us?