Examples-of-cultured-N-pachyderma-s-specimens-showing-new-calcified-chambers-in_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Examples-of-cultured-N-pachyderma-s-secondary-electron-images-applying-the-scanning_fig2_348241557
Introduction
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the
Plagiochila-parvivittata-Inoue-var-siangensis-Singh-Deo-DKSingh-1-A-portion-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-parvivittata-Inoue-var-siangensis-Singh-Deo-DKSingh-1-A-portion-of_fig2_299423615
Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell, a member of the Plagiochilaceae family, commonly known as Plagiochila. This unassuming moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate world of bryophytes.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it exists. Mosses belong to the division Marchantiophyta, which encompasses liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Within this division, the class Jungermanniopsida houses the leafy liverworts, including the Plagiochilaceae family.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions. Its leaves are arranged in two rows along the stem, giving it a distinctive flattened appearance. The leaves themselves are ovate to oblong in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal intricate patterns and structures that aid in identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, found in various regions across the globe. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on decaying logs, tree trunks, and damp soil in forests and woodlands. Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/404945-Plagiochila-strombifolia
is particularly abundant in temperate and tropical regions, where it plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their diminutive size, mosses like Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell are essential components of their respective habitats. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare surfaces and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, these mosses contribute to soil formation, water retention, and nutrient cycling, making them invaluable allies in maintaining healthy ecosystems.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture returns. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate rainforest, researchers found that Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell played a crucial role in maintaining the diversity of understory plant communities. The moss acted as a nursery for seedlings, providing a moist and nutrient-rich environment for their growth and development.
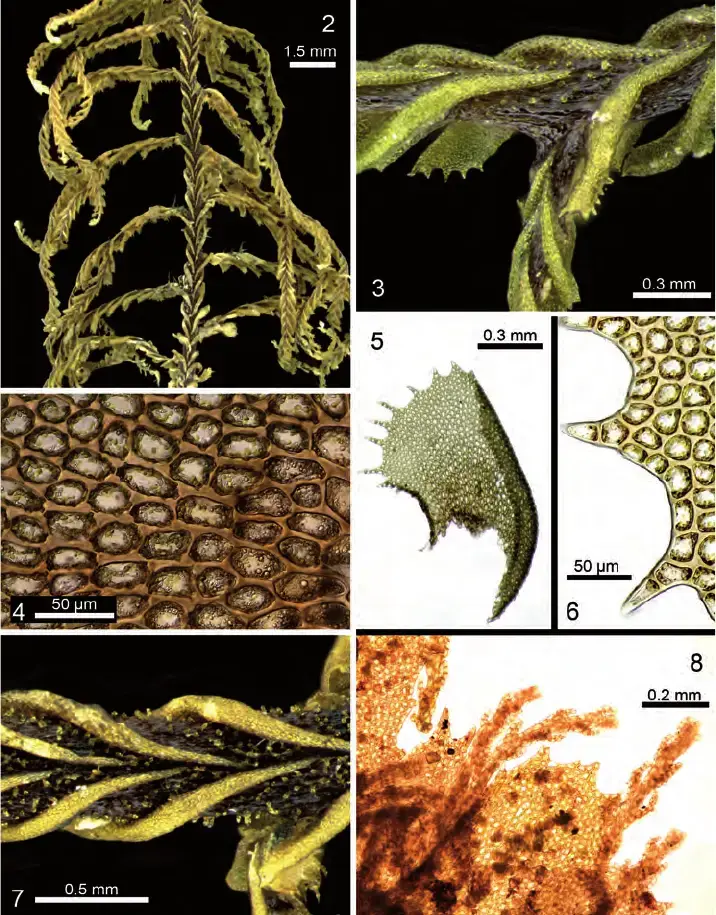

plagiochila%2Bsecci%25C3%25B3n%2Babietinae.png from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/hepaticas-foliosa-plagiochila-genero.html
Technical Table
33-Perichaena-pachyderma-AH-45562-28-30-Sporocarps-gregarious-to-solitary-31.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/33-Perichaena-pachyderma-AH-45562-28-30-Sporocarps-gregarious-to-solitary-31_fig1_302475285
Spores-and-elaters-of-Plagiochila-alternans-P-asplenioides-and-P-ovata-A-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Spores-and-elaters-of-Plagiochila-alternans-P-asplenioides-and-P-ovata-A-C_fig1_256669306
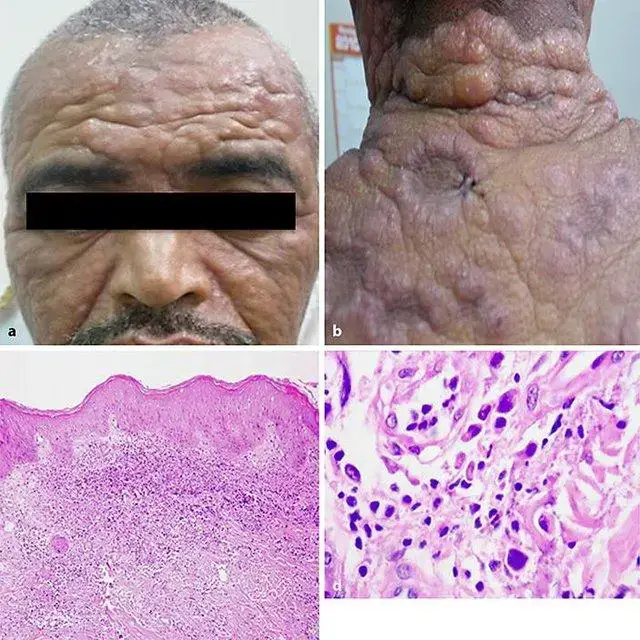
a-Pachydermic-infiltration-of-the-forehead-of-the-patient-with-myeloid-leukemia-cutis-b_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Pachyderma-on-the-right-arm-b-Three-weeks-after-treatment-with-oral-steroids-c-CD4_fig1_319633331
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Plagiochilaceae |
| Genus | Plagiochila |
| Species | capensis |
| Variety | pachyderma |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows along the stem |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to oblong |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
Conclusion
The Plagiochila capensis var. pachyderma S.W.Arnell moss may be small, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is profound. From facilitating plant growth to contributing to nutrient cycling, this unassuming bryophyte plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of life on our planet, perhaps we can find inspiration in the resilience and adaptability of these often-overlooked organisms. After all, who knows what other wonders the world of mosses has yet to reveal?
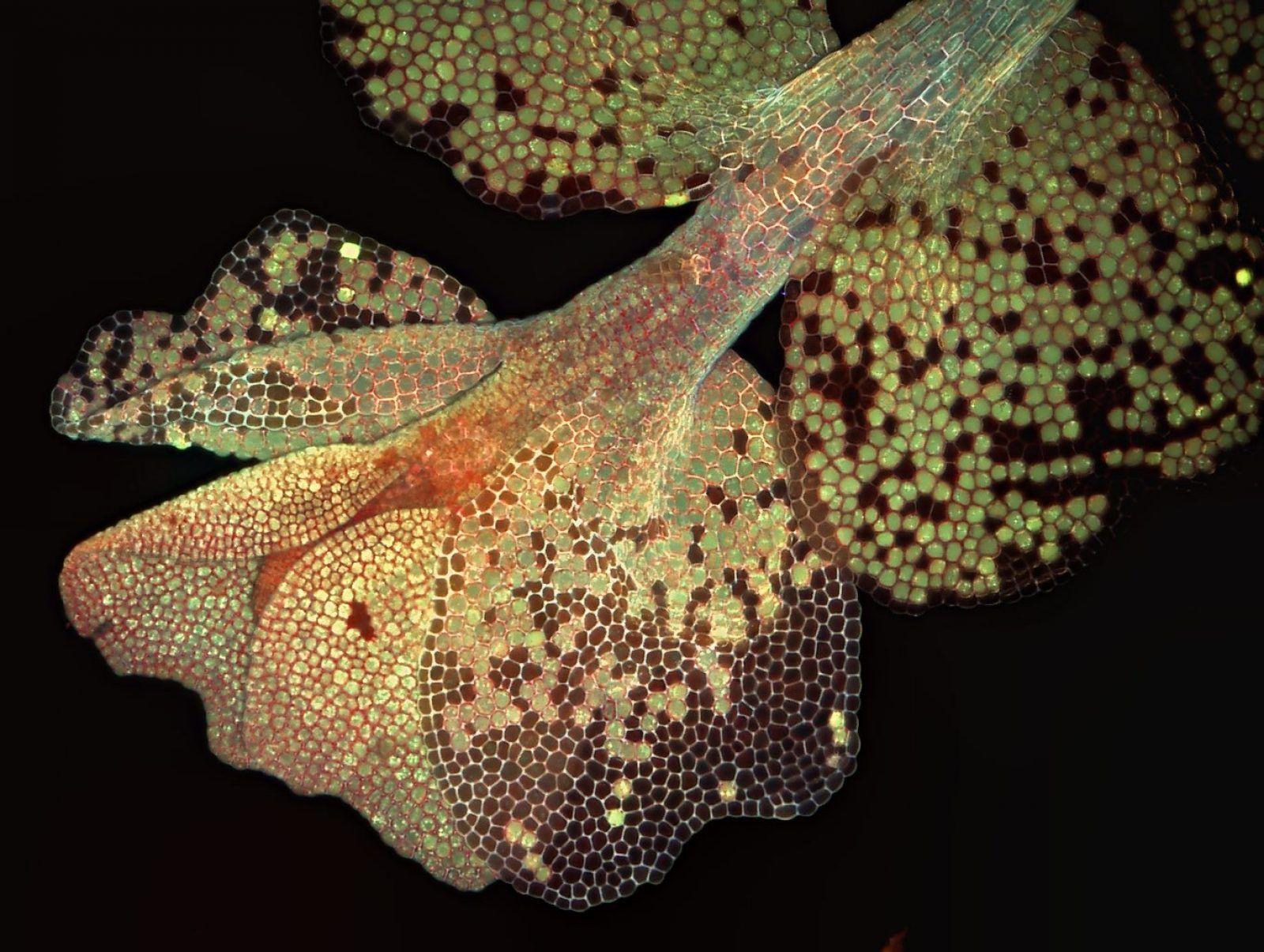
0e3a8c4bbf8c40ef51cbf86d136b9878.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/413275703312310555/
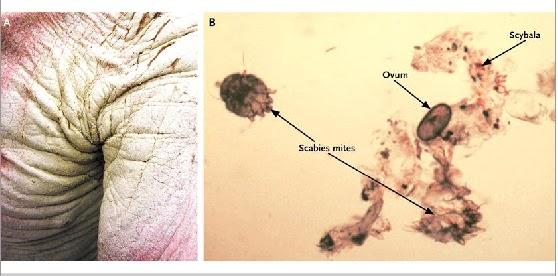
ff.bmp from: https://doctorsgates.blogspot.com/2010/11/pachyderma-due-to-scabies.html
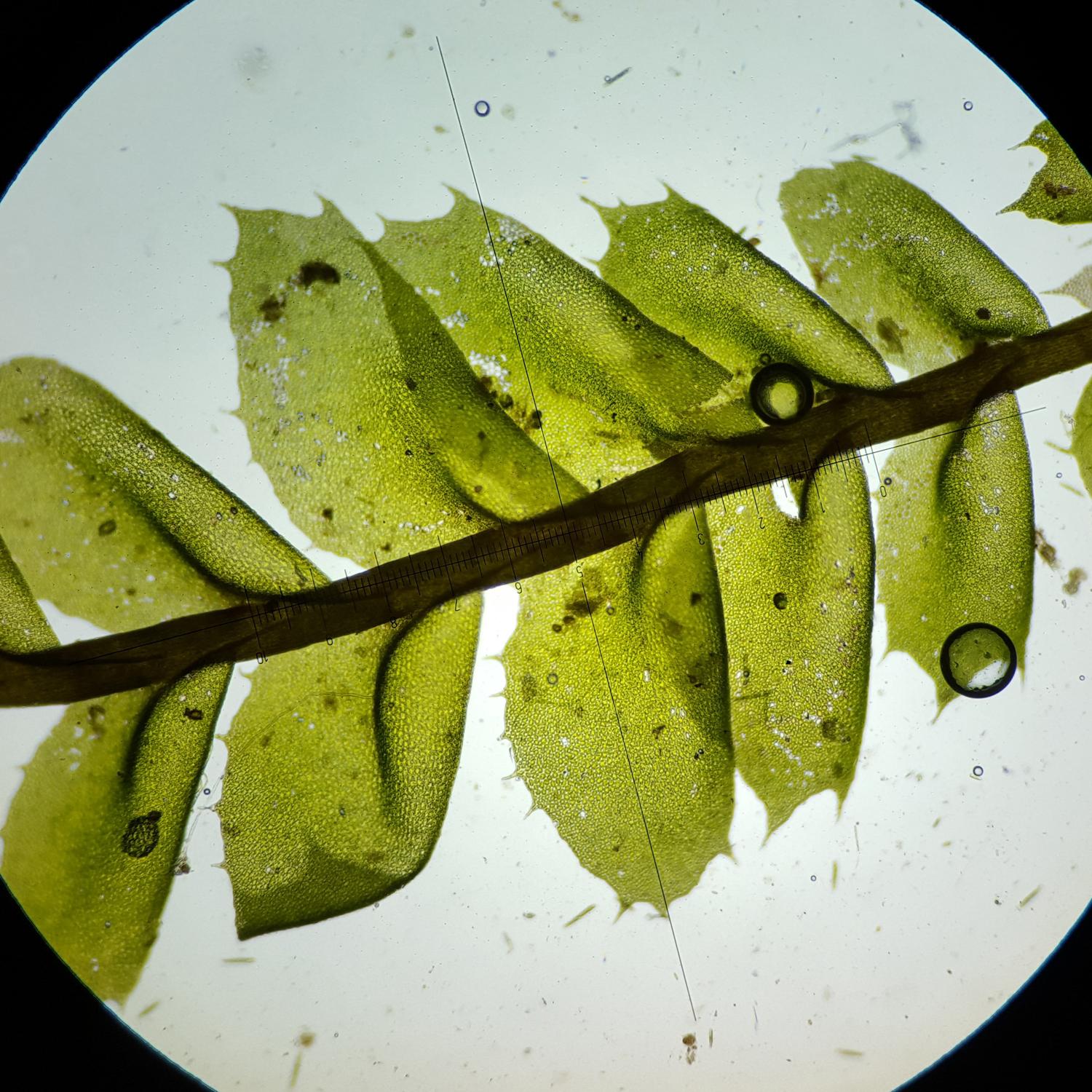

20160222_195517a.jpg from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/02/plagiochila-query-from-cwm-clydach.html