Fissidens-lagenarius-Mitt-A-OPL-note-the-transparent-OPL-lamellae-protruding-beyond.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-lagenarius-Mitt-A-OPL-note-the-transparent-OPL-lamellae-protruding-beyond_fig9_359625226
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Fissidentaceae family. Often referred to simply as Fissidens, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.

5562898.jpg from: https://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5562898
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Fissidens lagenarius Mitt., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. As pioneers of terrestrial life, they have adapted to thrive in diverse habitats, from moist forests to arid deserts.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
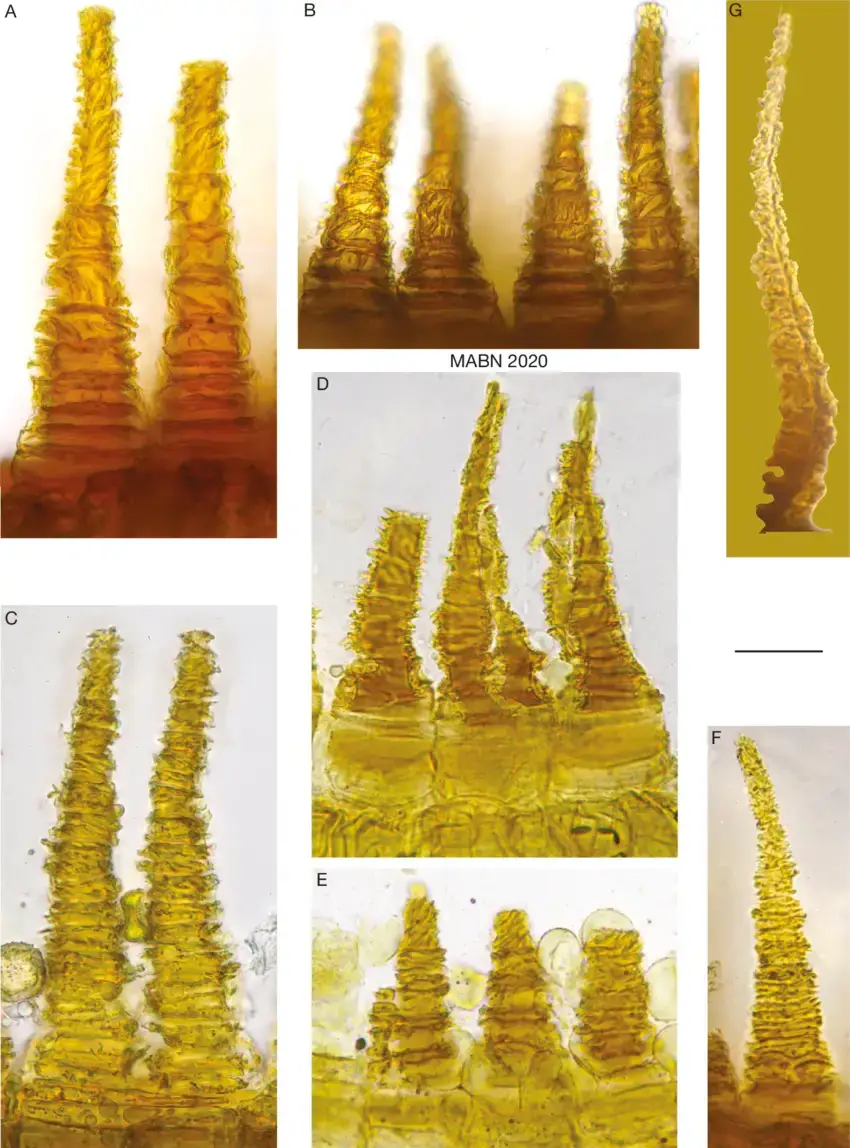
Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green tufts or mats. Its leaves are arranged in two distinct rows, giving it a distinctive, flattened appearance. Each leaf is composed of a single layer of cells, with a characteristic lingulate (tongue-shaped) form and a costa (midrib) that extends nearly to the leaf apex.
One of the most remarkable features of Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. is its ability to produce specialized structures called gemmae. These tiny, bud-like propagules are found on the leaf tips and can detach to form new individuals, allowing for efficient vegetative reproduction.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas like stream banks, rock crevices, and rotting logs, to more exposed environments like soil banks and disturbed areas.
This moss’s ability to colonize diverse habitats is a testament to its adaptability and resilience. It can withstand periods of desiccation and quickly rehydrate when moisture becomes available, making it a successful pioneer species in many ecosystems.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

IMG_4746.JPG from: https://www.aquaticquotient.com/forum/showthread.php/25486-Terrestrial-fissidens-moss-)
Despite its diminutive size, Fissidens lagenarius Mitt.

moss_fissidens_species_15-11-10_1.jpg from: https://www.aphotoflora.com/moss_fissidens_species.html
plays crucial ecological roles in the environments it inhabits. As a primary producer, it contributes to the cycling of nutrients and the formation of soil. Its dense mats can also provide microhabitats for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. is its ability to regulate water loss through specialized structures called hyaline hair points. These hair-like projections on the leaf tips help the moss retain moisture, allowing it to survive in drier conditions.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. played a vital role in the recovery of disturbed areas after logging activities. Its ability to rapidly colonize and stabilize soil surfaces made it a valuable pioneer species, facilitating the establishment of other plant communities.
Technical Table

IMG_8942_1600x.jpg from: https://aquaticmotiv.com/products/fissidens-nobilis-moss-mat-fissidens-nobilis

Fissidens-bryoides-21-800×533.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-fissidens-bryoides/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Fissidentales |
| Family | Fissidentaceae |
| Genus | Fissidens |
| Species | Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Distichous (two rows) |
| Leaf Shape | Lingulate (tongue-shaped) |
| Gemmae Production | Present on leaf tips |
Conclusion
The Fissidens lagenarius Mitt. moss, a member of the Fissidentaceae family, is a remarkable species that deserves our appreciation and admiration. Its unique morphology, adaptations, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
As we continue to explore and understand the intricate world of bryophytes, the

fissidens-fontanus-phoenix-moss~2.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.de/Fissidens-fontanus-Phoenix-Moss-Pad-7-x-4-cm-Dennerle
Fissidens lagenarius Mitt.

fissidens-fontanus-phoenix-moss-4_2048x2048.jpg from: https://shrimperyandaquatics.com/collections/plants-moss/products/fissiden-moss

fissiden-1024×768.jpg from: https://www.acestory.com.my/ace-story-aquatic/aquatic-plant/moss/fissidens-moss-large-2-x-2-aquatic-moss-aquarium
serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush, green mat of moss, you’ll pause and wonder if it might be the unassuming yet extraordinary

4c6af7cb7099ff9c1435c4f4593bf5c1.jpg from: https://shrimplovers.com.au/product/us-fissidens-phoenix-moss-fissidens-fontanus
Fissidens lagenarius Mitt..