
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Meteoriopsis-reclinata-MuellHal-MFleisch-A-Plant-B-Portion-of-branch-C-G_fig1_348089946
Exploring the Fascinating World of Ctenidiadelphus plumularia Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Ctenidiadelphus plumularia (Müll.Hal.) M.Fleisch., a moss in the Hypnaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating bryophyte, from its morphology to its ecological importance. Get ready to discover the hidden wonders of Ctenidiadelphus!
Background
Ctenidiadelphus plumularia is a species of moss classified in the Hypnaceae family, which is part of the Bryopsida class in the plant division
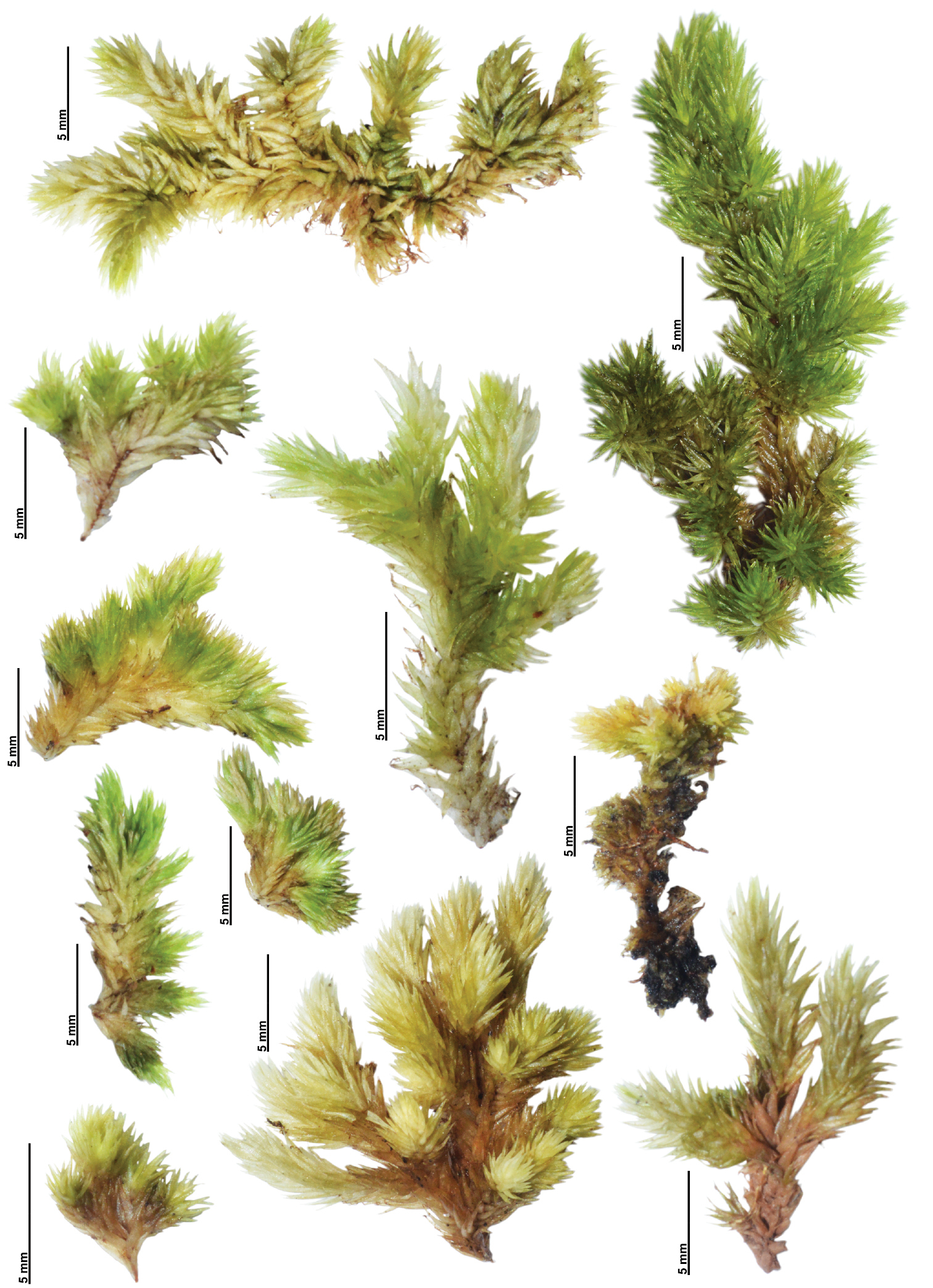

image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/18/
Bryophyta. Mosses are non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids that absorb water and nutrients directly.
Morphology and Identification
C. plumularia forms dense, feathery mats. Its stems are pinnately branched, meaning the branches are arranged on opposite sides of the stem like a feather. The phyllids are ovate-lanceolate in shape, gradually tapering to a fine point. They have a single costa (midrib) that extends 3/4 the length of the phyllid.
The alar cells, found at the base corners of the phyllids, are quadrate to short-rectangular
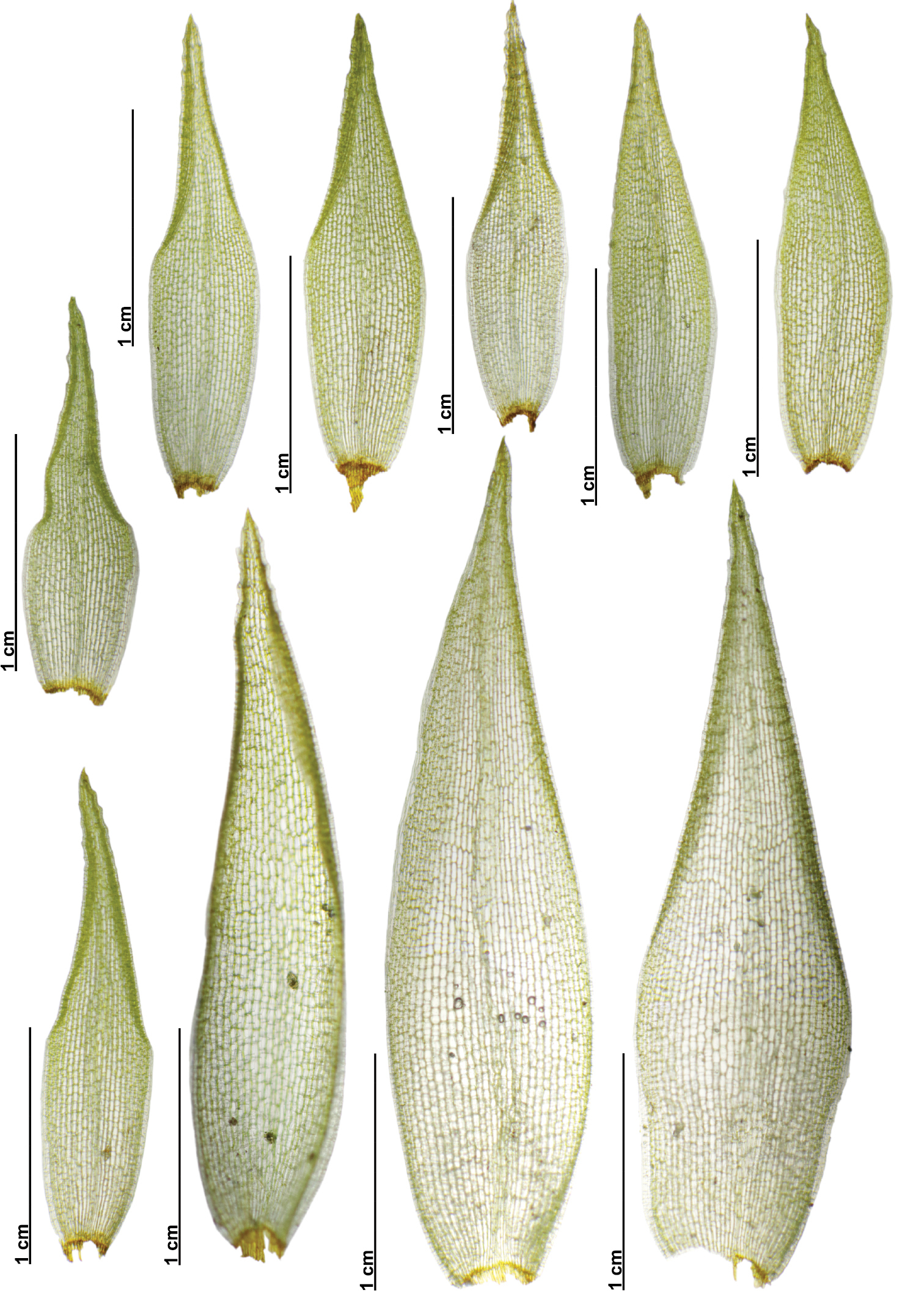

image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/19/
and thick-walled. Identifying C. plumularia requires examining these microscopic leaf cell characteristics.
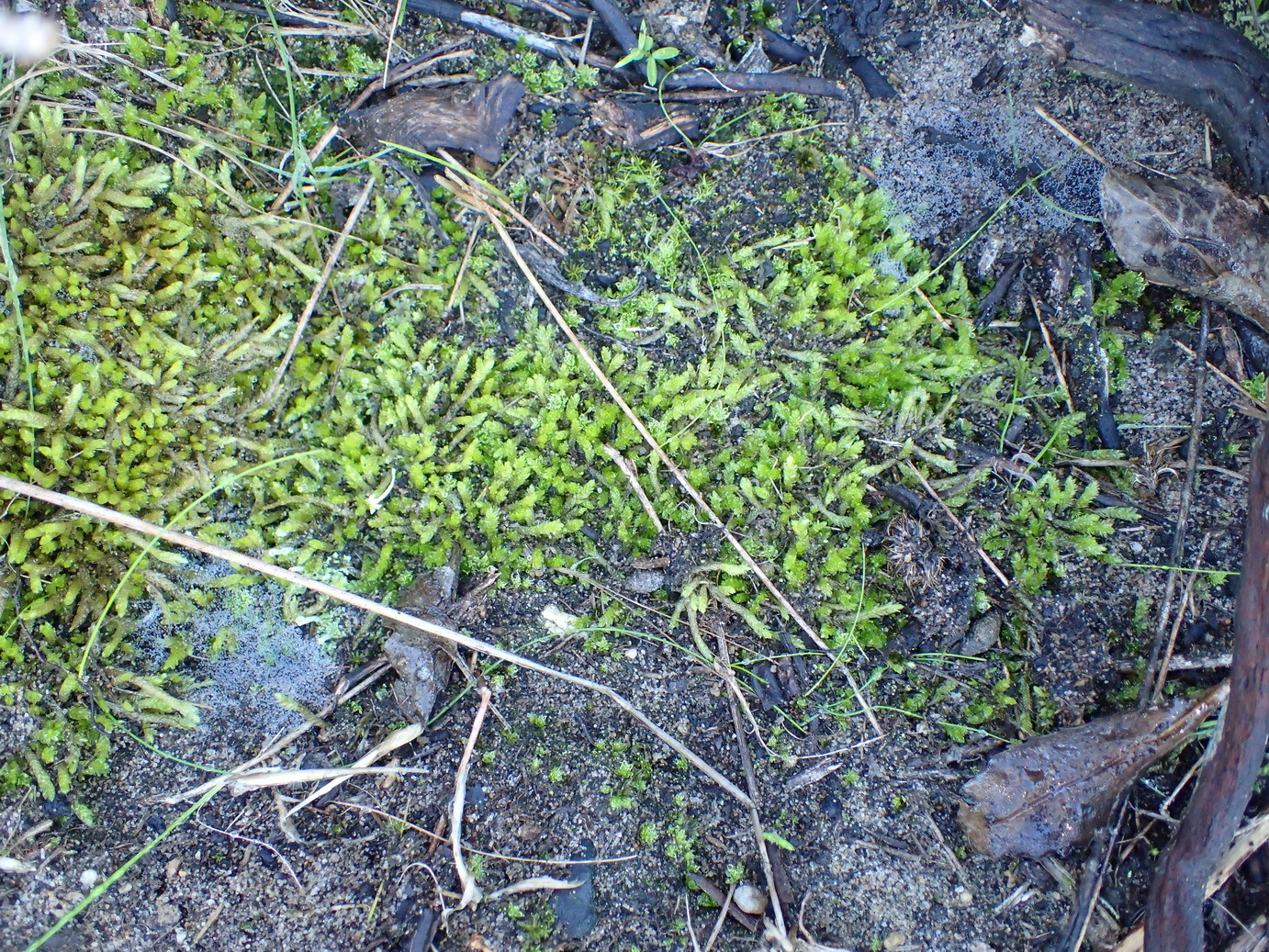

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Global Distribution and Habitat
Ctenidiadelphus plumularia has a wide distribution
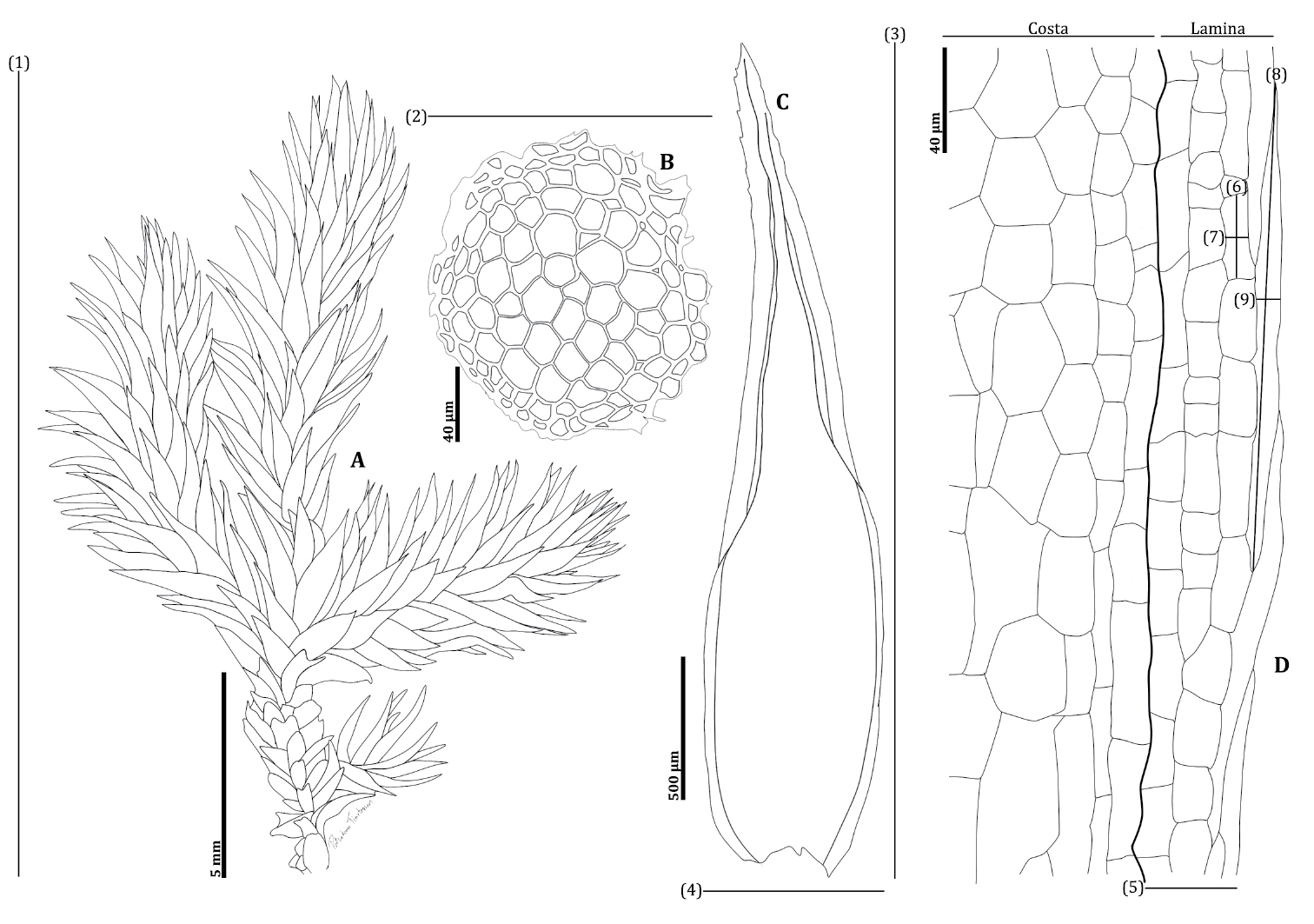
image from: https://phytokeys.pensoft.net/article/98990/zoom/fig/12/
, found in many parts of the world including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It typically grows on tree trunks and branches in humid forests, forming pendant growths. The moss is able to survive in areas with high precipitation by efficiently absorbing and retaining water in its dense mats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, C. plumularia plays important roles in its forest ecosystems:
Moisture retention: Its dense growth traps and holds moisture, helping regulate humidity in the forest understory.
Nutrient cycling: As it grows and dies back, the moss contributes to nutrient cycling by breaking down and releasing nutrients back to the soil.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
Microhabitats: The mats provide shelter and moisture for small invertebrates and other organisms.
image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/47945928@N02/50948153257
Ctenidiadelphus plumularia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its pendant tree habitat:
- Feathery branching

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Taxiphyllum-giraldii-MuellHal-MFleisch-A-Habit-B-Pseudoparaphyllia-C-D-Stem_fig5_354916178

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-m-In-vitro-growth-of-Entodon-macropodus-Hedw-Muell-Hal-a-Germinated-spores-b-c_fig1_269775914

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/9415978
maximizes surface area for water and nutrient absorption
- Thick-walled alar cells may provide structural support
- Slender, pointed phyllids minimize water loss and form a capillary network to distribute water
Conclusion
From its intricate branching patterns to its microscopic leaf cells, Ctenidiadelphus plumularia is a prime example of the amazing adaptations and ecological importance of mosses. Next time you’re in a humid forest, take a closer look at the mossy mats hanging from the trees – you may just spot this fantastic feathery species! What other secrets of the bryophyte world are waiting to be uncovered?