
206158.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4415/tab/fiche

235025.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5574
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one unassuming yet remarkable moss species stands out – the Desmatodon latifolius (Hedw.) Brid., a member of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Desmatodon, this diminutive plant has captured the hearts and curiosity of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this unsung hero of the bryological kingdom.
Background
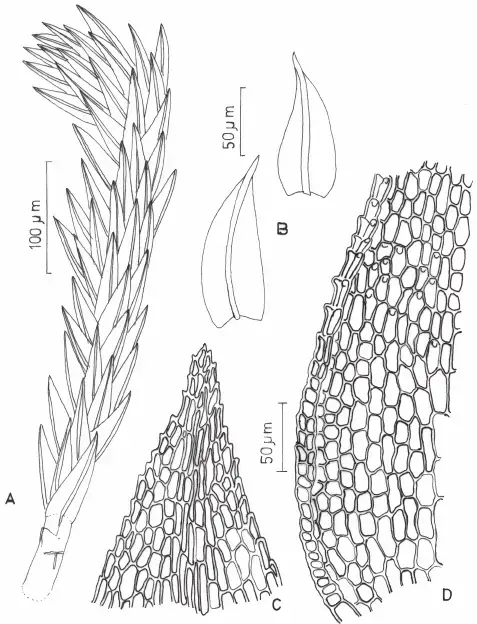
Philonotis-fontana-Hedw-Brid-A-Habit-of-gametophyte-B-leaves-C-apical-cells-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Philonotis-fontana-Hedw-Brid-A-Habit-of-gametophyte-B-leaves-C-apical-cells-of_fig1_250021680
Before we explore the intricacies of Desmatodon latifolius, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, comprising mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most resilient plant lineages on Earth. These ancient organisms have played a pivotal role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems, paving the way for more complex plant life to flourish.
Main Content

post-25-1168071522.jpg from: https://forum.mikroscopia.com/topic/5377-racomitrium-lanuginosum-hedw-brid/
Morphology and Identification
Desmatodon latifolius is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive hyaline hair-point at the apex. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the costa (midrib) is excurrent, extending beyond the leaf blade. This moss produces erect, cylindrical capsules on short setae (stalks), which are often immersed within the gametophyte.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Desmatodon latifolius is a cosmopolitan species, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from dry and exposed areas to more sheltered environments. You can find this resilient moss growing on soil, rocks, walls, and even tree bark, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive stature, Desmatodon latifolius plays a crucial role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a vital microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, providing shelter, food, and breeding grounds.

8687616850_253817536d_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/belinda712/8687616850/
One of the remarkable adaptations of Desmatodon latifolius is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself when moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the arid regions of the southwestern United States, Desmatodon latifolius was found to be a key component of the biological soil crust community. These crusts play a vital role in preventing soil erosion and promoting the establishment of vascular plants in these harsh environments.
Another fascinating example comes from the urban landscapes of Europe, where Desmatodon latifolius has been observed growing on historic buildings and monuments. Its ability to colonize these man-made structures highlights its adaptability and resilience, even in the face of human disturbance.
Technical Table
336011.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/4775
216725.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5581
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Desmatodon
 235029.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5574/tab/fiche |
| Species | latifolius |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Hyaline hair-point |
| Leaf Margins | Often recurved |
| Costa | Excurrent (extending beyond leaf blade) |
| Capsules | Erect, cylindrical, on short setae |

194109.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/435628
Conclusion
The Desmatodon latifolius (Hedw.) Brid. moss, a member of the Pottiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unassuming appearance belies its remarkable resilience, adaptability, and ecological significance. From stabilizing soils to providing microhabitats for countless organisms, this humble moss plays a vital role in the intricate web of life.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the bryological world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: In a world where size often dictates our perception of importance, what other unsung heroes might we be overlooking, and what valuable lessons can they teach us about the intricate balance of our ecosystems?
Limnoscelis21DB.jpg from: https://de-academic.com/dic.nsf/dewiki/326388