Lophozia-turbinata-Raddi-Steph-a-portion-de-tige-feuillee-longueur-des-feuilles.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lophozia-turbinata-Raddi-Steph-a-portion-de-tige-feuillee-longueur-des-feuilles_fig3_283449794
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia turbinata (Raddi) Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Jungermanniaceae family. Also known simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.

61b4fb2b563df.jpg from: https://botanique24.fr/fr/portfolio-97426-hepatiques
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Lophozia turbinata, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.

16319528763_6270591a36_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/stephenbuchan/16319528763
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
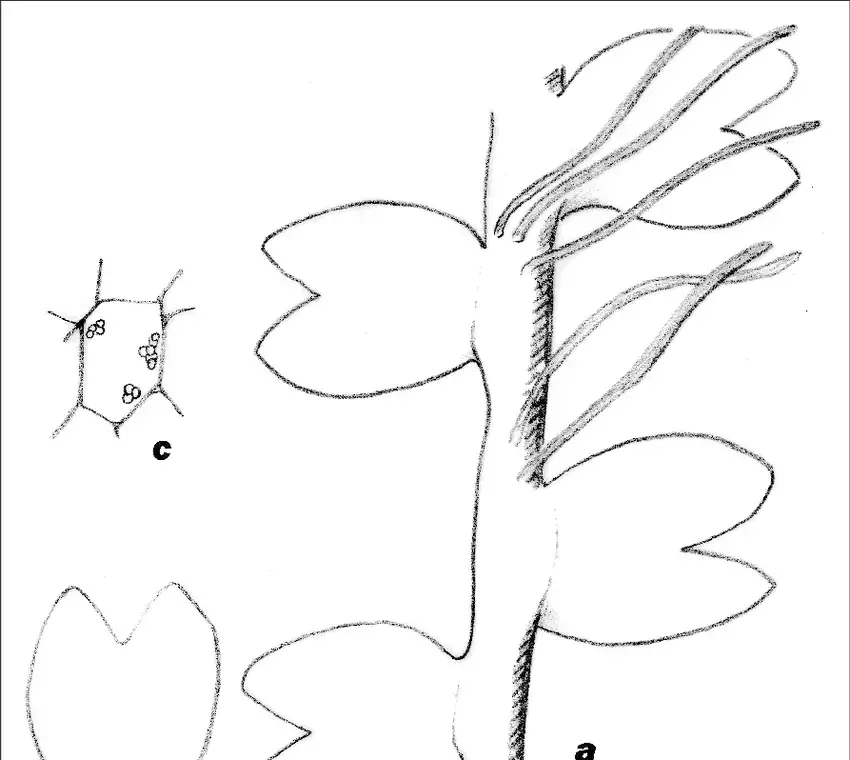
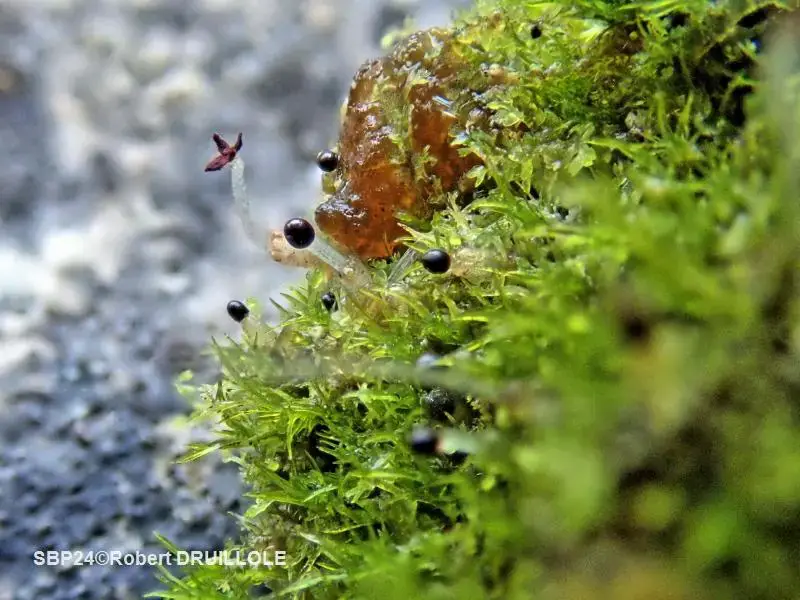
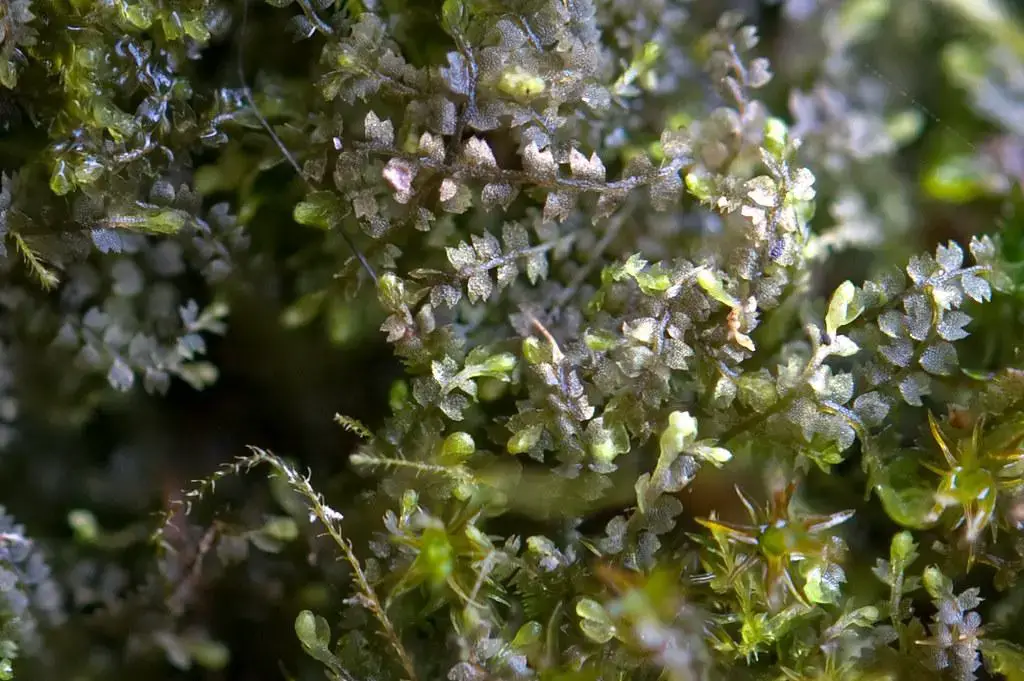
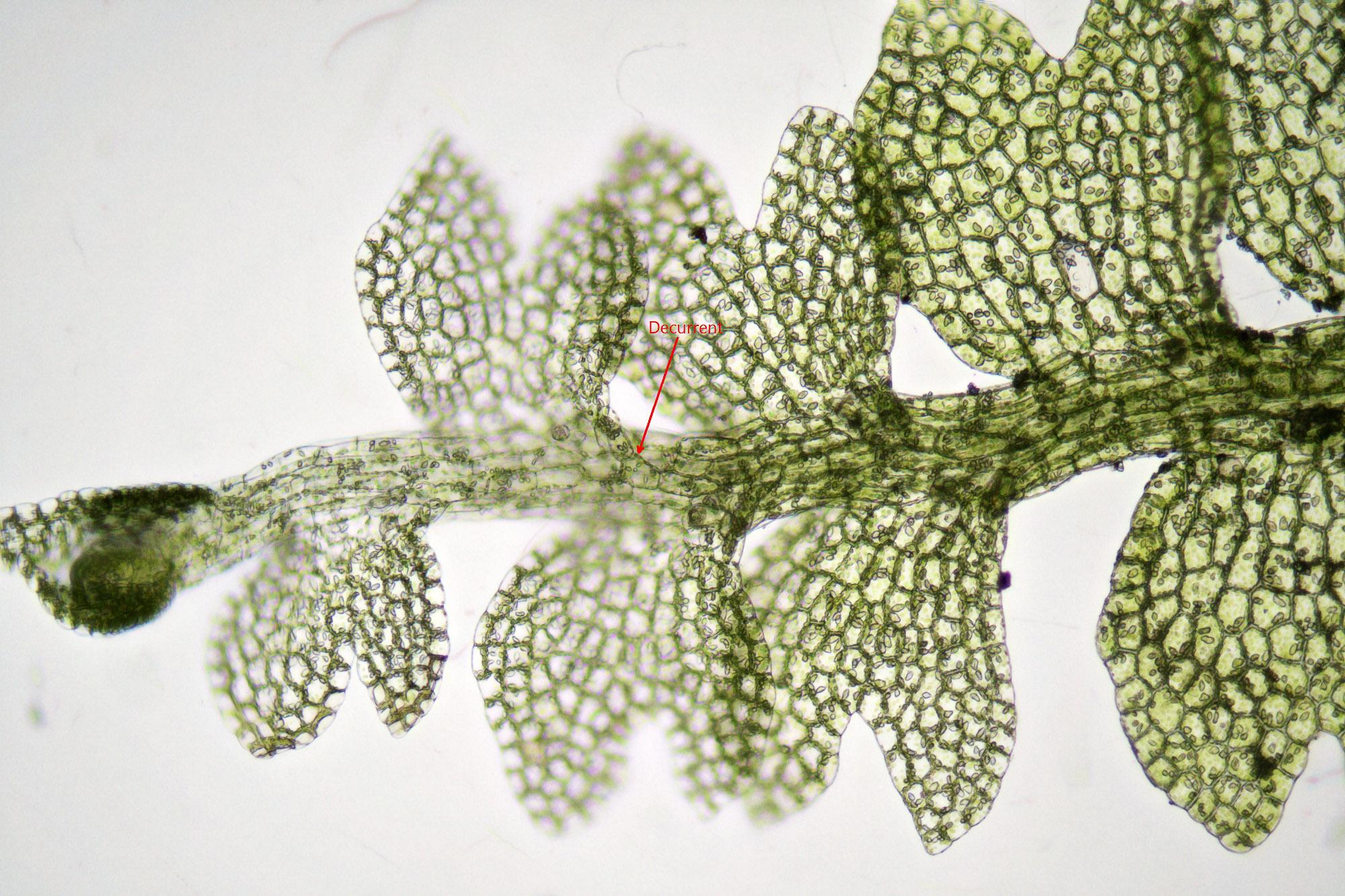
Lophozia turbinata is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green tufts or mats. Its stems are creeping and irregularly branched, with leaves that are deeply bilobed and arranged in a spiral pattern. The leaves are distinctive, with their lobes often curved or twisted, giving the plant a unique and intricate appearance.
One of the key identifying features of Lophozia turbinata is its turbinate (top-shaped) perianth, which encloses the reproductive structures. This characteristic, along with its deeply bilobed leaves, helps distinguish it from other members of the Jungermanniaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Lophozia turbinata is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist and shaded areas, rotting logs, and the bases of trees. This moss is often found in coniferous and mixed forests, as well as in bogs and other wetland environments.

2021-06-27-15-28-11.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/mesoptychia-turbinata/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Lophozia turbinata plays an essential role in its ecosystems. Like other bryophytes, it contributes to soil formation, moisture retention, and nutrient cycling. Additionally, it provides a microhabitat for various invertebrates and serves as a food source for some organisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia turbinata is its ability to survive in harsh conditions. It can withstand periods of desiccation and quickly rehydrate when moisture becomes available. This resilience allows the moss to thrive in environments where water availability may be limited or unpredictable.
Marchantia-papillata-subsp-grossibarba-A-Thalli-B-Appendage-of-ventral-scales-C_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348252050_Marchantia_papillata_Raddi_subsp_grossibarba_Steph_Bischl_Marchantiaceae_Marchantiophyta_new_to_Japan
Case Studies/Examples
Lophozia turbinata has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological significance and evolutionary history. For instance, researchers have investigated its role in facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas, highlighting its importance in ecosystem recovery.
Additionally, the moss has been used as a bioindicator, providing insights into environmental conditions and pollution levels due to its sensitivity to certain pollutants and changes in its surroundings.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Jungermanniaceae |
| Genus | Lophozia |
| Species | turbinata (Raddi) Steph. |
| Common Name | Lophozia |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply bilobed |
| Perianth | Turbinate (top-shaped) |
Conclusion
The Lophozia turbinata (Raddi) Steph. moss, a member of the Jungermanniaceae family, is a remarkable and intriguing plant that deserves our attention and appreciation. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can our understanding of these often-overlooked plants contribute to the preservation and restoration of ecosystems worldwide?