
5226_177070_.jpg from: https://biodiv-paysdelaloire.fr/espece/198519
Exploring the Fascinating World of Tortula cochlearifolia P.de la Varde Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Tortula cochlearifolia P.de la Varde, a moss in the Pottiaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its unique morphology to its global distribution and ecological importance. Get ready to discover the hidden world of Tortula moss!
Background on Mosses
Before we focus on

Tortula-obtusifolia-3.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-tortula-obtusifolia/
T. cochlearifolia specifically, let’s review some background on mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division

Tortula%2Bmuralis%2B1.jpg from: http://floressilvestresdehormaza.blogspot.com/2017/12/tortula-muralis.html
Bryophyta. Unlike other land plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have rhizoids, simple stem-like and leaf-like structures. Mosses are found on every continent and play important roles in the water and nutrient cycles.

Tortula%2Bmuralis%2B2.jpg from: https://floressilvestresdehormaza.blogspot.com/2017/12/tortula-muralis.html
Morphology and Identification
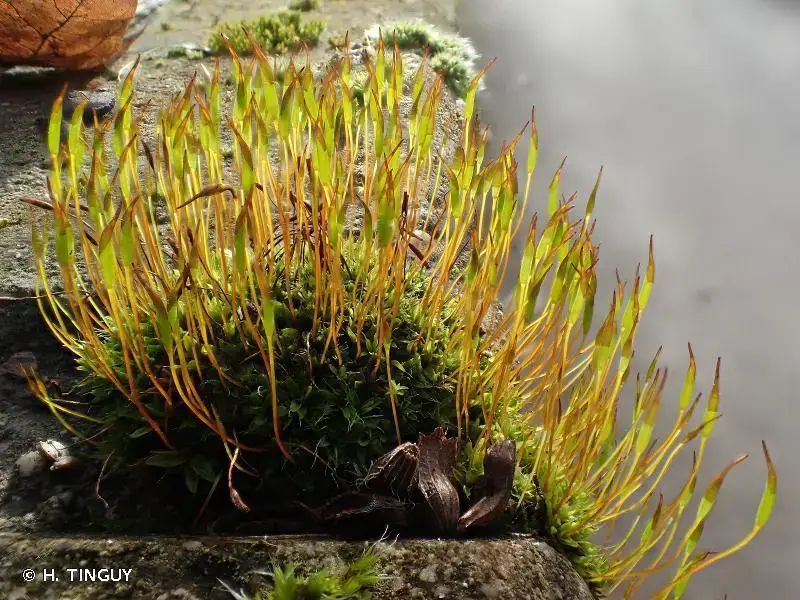
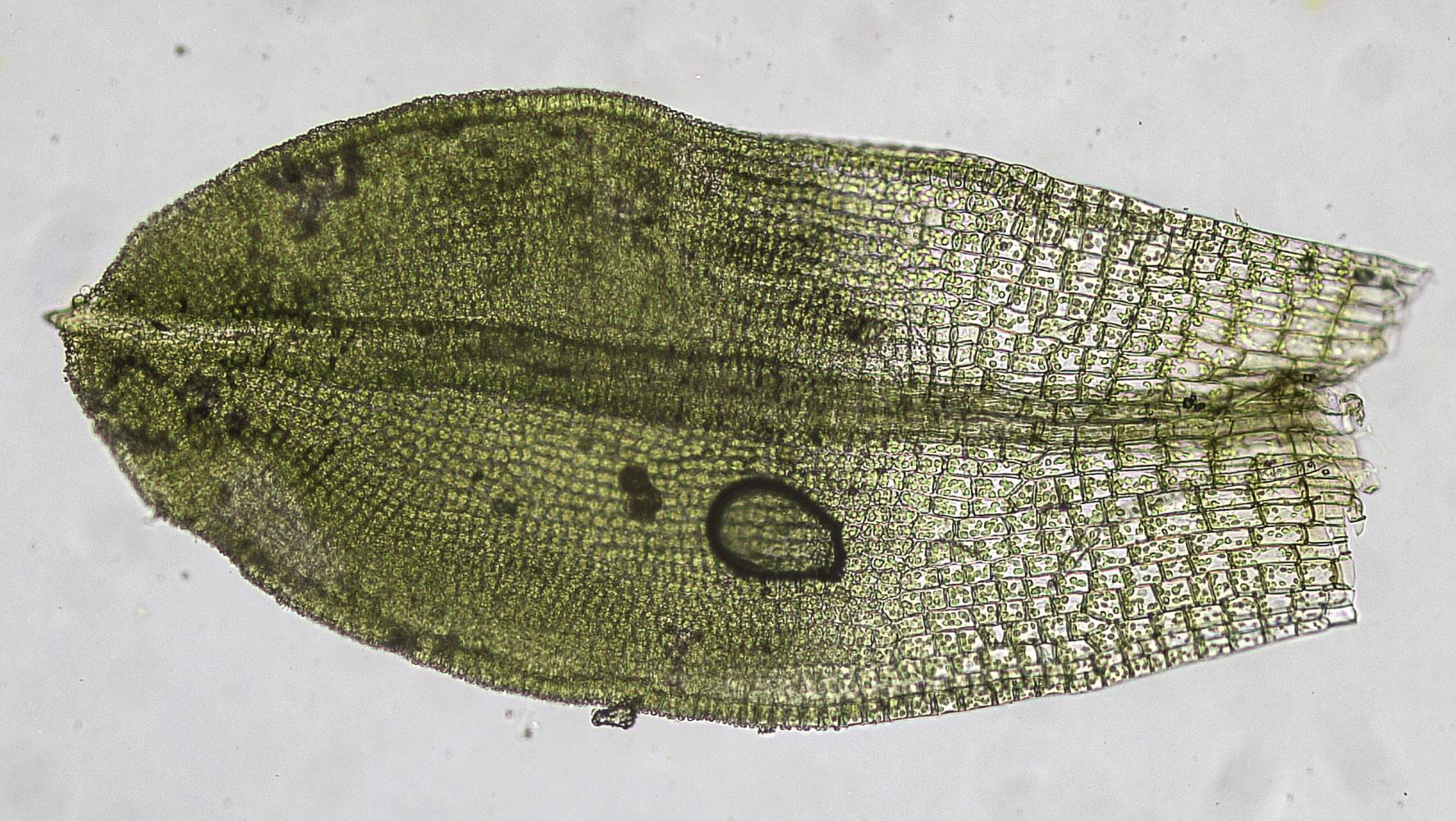
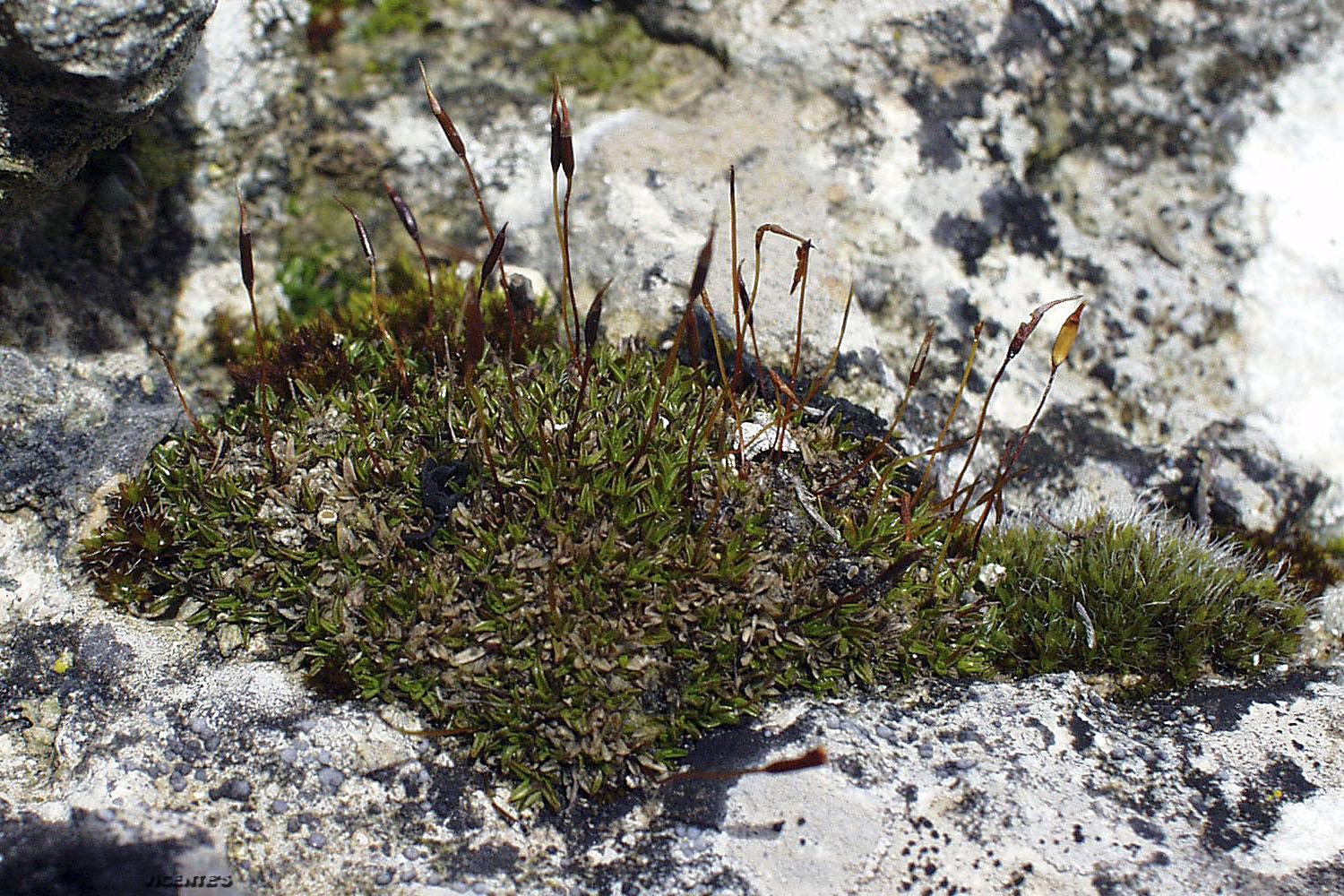
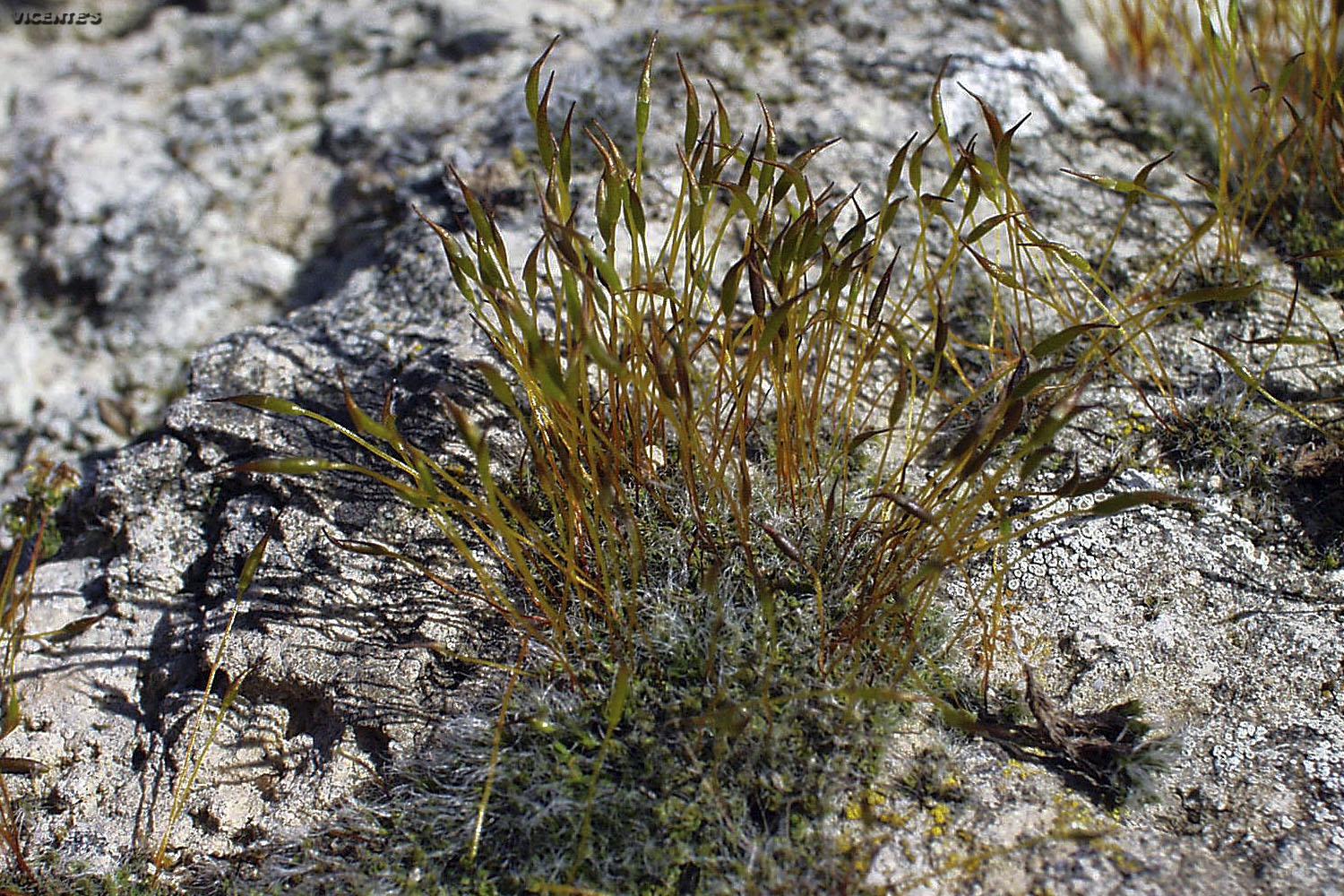
Tortula cochlearifolia is a small moss, typically growing in tufts or cushions. Its leaves are oblong to spoon-shaped (cochleariform), hence its species name. The leaves have a distinct border of elongated cells and a strong midrib that often extends beyond the leaf tip. Tortula is dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a wide global distribution, found in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It grows on a variety of substrates including soil, rock, concrete, and tree bark. T. cochlearifolia is able to tolerate disturbance and some pollution, so it’s often found in urban areas as well as more natural habitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Tortula plays an important role in its ecosystem:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and small invertebrates
- Pioneers the colonization of bare ground, paving the way for other plants
T. cochlearifolia has several adaptations that allow it to thrive:
- Leaves contort when dry to reduce moisture loss
- Rhizoids anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients
- Spore dispersal enables colonization of new areas

Tortula_subulata_008.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Tortula_subulata.html
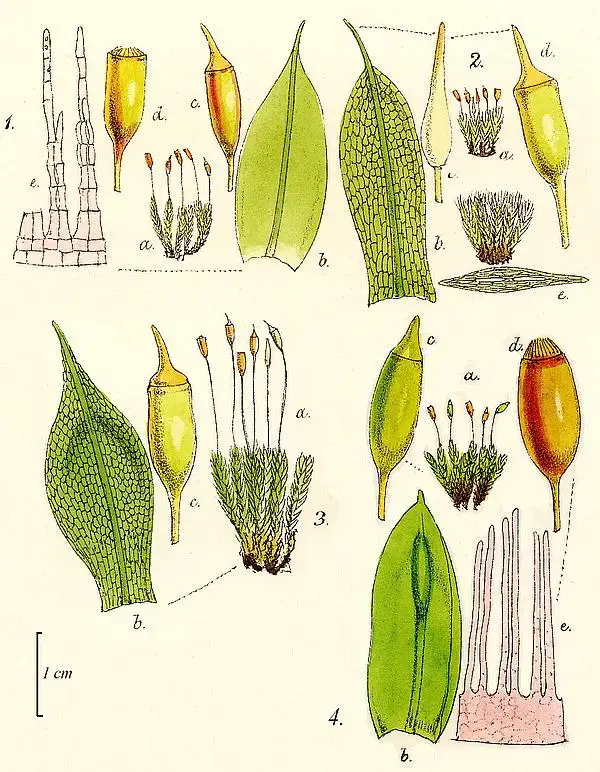
berke232.jpg from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/britms/www/pottiace.htm
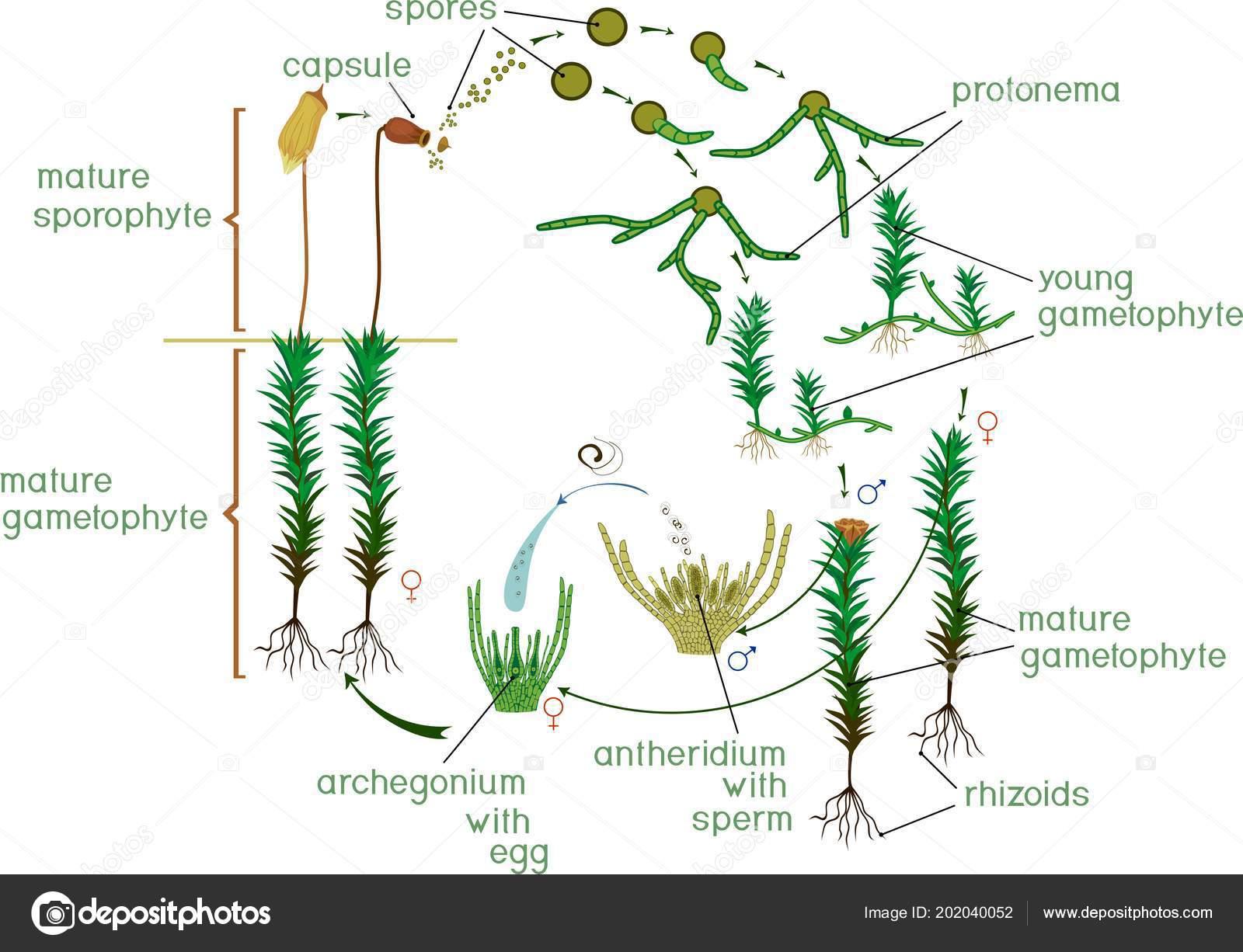
depositphotos_202040052-stock-illustration-moss-life-cycle-diagram-life.jpg from: https://depositphotos.com/vector/moss-life-cycle-diagram-life-cycle-common-haircap-moss-polytrichum-202040052.html
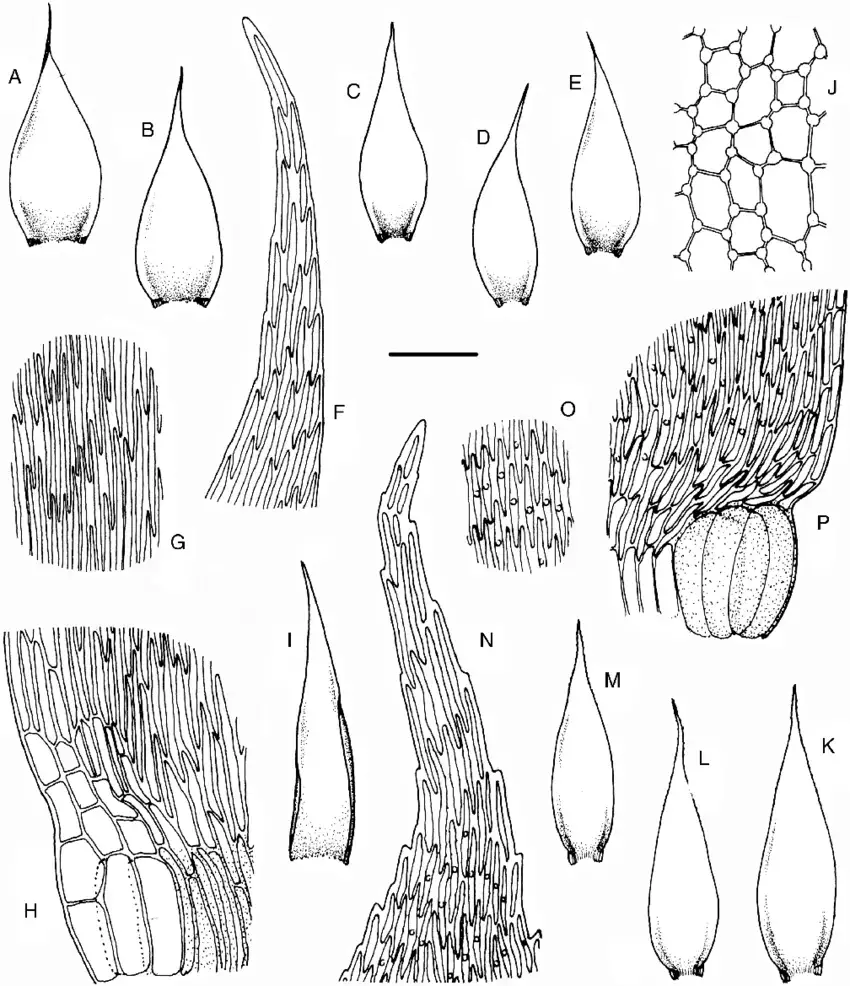
AJ-Wijkia-albescens-Ther-Pde-la-Varde-Crum-KP-W-jacobsonii-Dixon-Crum.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/AJ-Wijkia-albescens-Ther-Pde-la-Varde-Crum-KP-W-jacobsonii-Dixon-Crum_fig1_309898287
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Division
 esporofito%2Bcompleto.jpg from: https://revistarimega.blogspot.com/2021/12/anthocerotophyta.html |
Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tortula |
| Species | T. cochlearifolia |
| Leaf shape | oblong to spoon-shaped |
| Midrib | strong, often extending beyond leaf tip |
Conclusion
Tortula cochlearifolia may be small, but it is mighty! This globally-distributed moss plays a vital ecological role and has fascinating adaptations. Next time you see some moss growing on a tree or rock, take a closer look – it just might be

Tortula-truncata-2-700×466.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-tortula-truncata/
Tortula! What other secrets are hiding in the world of mosses?