
original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one tiny moss stands out as a true marvel – the Astomum mollifolium (Müll.Hal.) Broth., a member of the
Fissidens-minutipes-MuellHal-Broth-A-Gametophyte-with-sporophyte-B-C_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-minutipes-MuellHal-Broth-A-Gametophyte-with-sporophyte-B-C_fig1_323270006
Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Astomum, this diminutive plant has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this fascinating moss, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to the world of
Weisiopsis-bahiensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Dry-gametophytes-b-Leaves-c-Apical-cells_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-1-Weisiopsis-bahiensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Gametofitos-secos-b-Filidios-c_fig1_262710312
bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back over 400 million years.
Linbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-1-Habit-of-plant-Wet-2-A-portion-of-plant.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Linbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-1-Habit-of-plant-Wet-2-A-portion-of-plant_fig1_341098152
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Figura-11-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Pseudoparafilos-filamentosos.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-11-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Pseudoparafilos-filamentosos_fig11_309232610
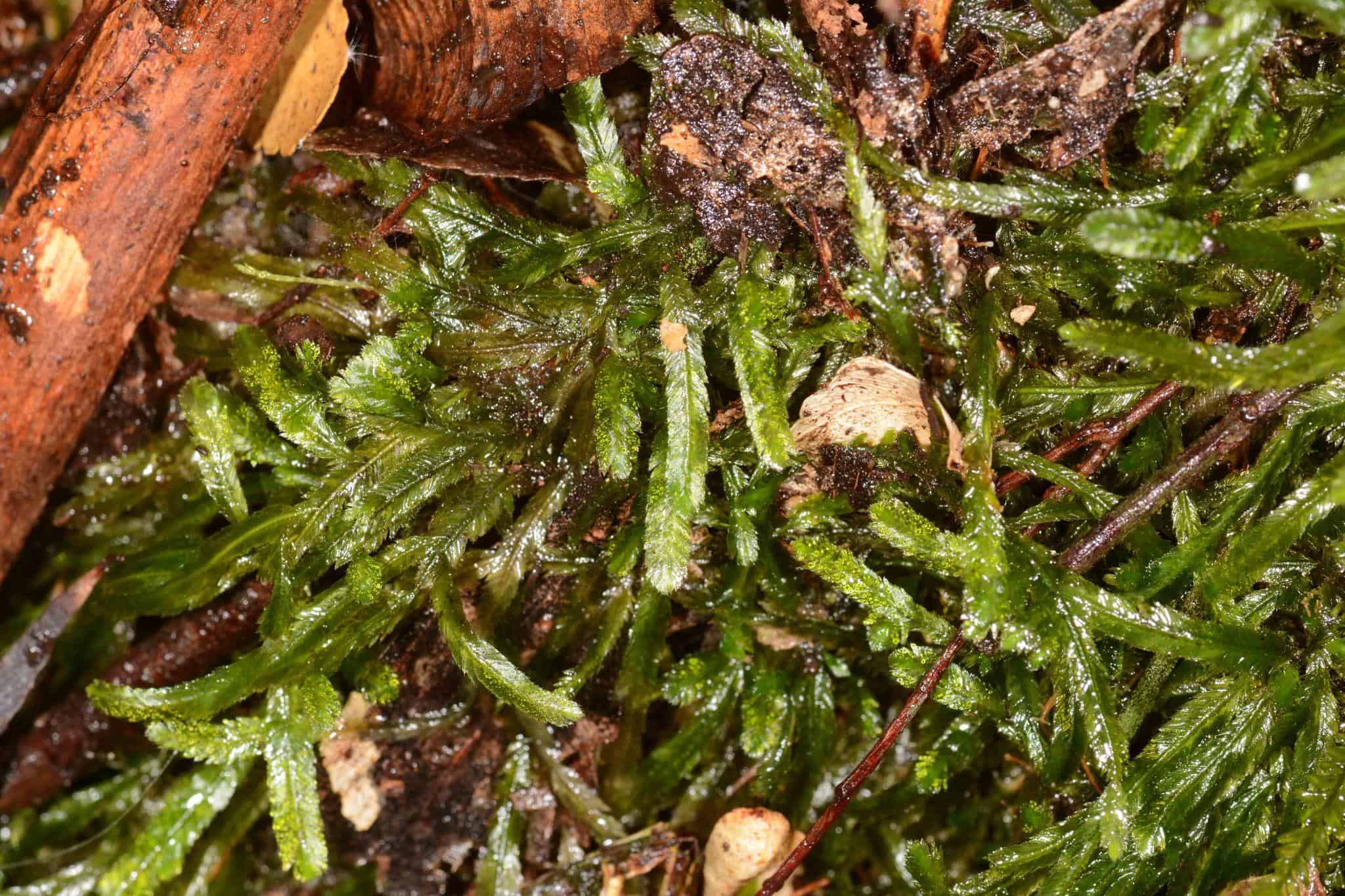
Astomum mollifolium is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive mucronate or hair-pointed apex. The leaf margins are entire, and the costa (midrib) is strong and excurrent, extending beyond the leaf apex as a short, hyaline awn.
One of the most striking features of Astomum mollifolium is its lack of a peristome, which is a specialized structure found in many mosses that aids in spore dispersal. This absence of a peristome is reflected in the genus name Astomum, derived from the Greek words “a” (without) and “stoma” (mouth).
Global Distribution and Habitat
Astomum mollifolium is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents. It has been reported from various regions, including Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, and South America. This widespread distribution is a testament to the moss’s adaptability and resilience.
In terms of habitat preferences, Astomum mollifolium thrives in a variety of environments, ranging from dry and exposed areas to more moist and shaded locations. It can be found growing on soil, rocks, tree bases, and even man-made substrates like concrete and bricks.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,
Figura-9-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-do-caulidio.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-9-Orthostichopsis-tijucae-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-Habito-b-Filidios-do-caulidio_fig9_309232610
Astomum mollifolium plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it is often one of the first plants to colonize disturbed or newly exposed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and pave the way for other plant species to establish themselves.
This moss is well-adapted to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as drought and extreme temperatures. Its dense cushion-like growth form helps to retain moisture, while its small size and ability to enter a dormant state during unfavorable conditions contribute to its resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of Astomum mollifolium‘s ecological significance can be found in urban environments. This moss has been observed growing on concrete surfaces, such as sidewalks and building foundations, where it helps to break down and weather the concrete over time, contributing to the natural recycling of materials.
Technical Table
Figura-13-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-pseudoparafilos-b-d.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-13-Orthostichopsis-tortipilis-Muell-Hal-Broth-a-pseudoparafilos-b-d_fig13_309232610

Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-10-1-Rhacocarpus-inermis-Hedw-2-Itatiella-ulei-Broth-ex-Muell-Hal-GL_fig2_350438700

DSCN8258.JPG from: https://briofitedelmatese.blogspot.com/2018/03/entosthodon-fascicularis-hedw-mull-hal.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Astomum |
| Species | mollifolium |
| Growth Form | Dense cushions or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Mucronate or hair-pointed |
| Costa | Strong, excurrent |
| Peristome | Absent |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, tree bases, concrete |
Lindbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-from-Primorsky-Territory-Lazo-Distr-Kamenka.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lindbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-from-Primorsky-Territory-Lazo-Distr-Kamenka_fig3_276195527
Conclusion
Astomum mollifolium, a humble yet remarkable moss, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its unique morphological features, widespread distribution, and ecological adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, perhaps we can find inspiration in the tenacity and perseverance of this tiny plant, thriving in even the harshest of environments. Who knows what other wonders await discovery in the realm of bryophytes?