
c2e97e01084e06754598b4b219cd8d1e.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.it/pin/453878468693779580/
Introduction
The world of mosses is a fascinating and often overlooked realm, home to a diverse array of species that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. Among these unsung heroes is the Herbertus angustevittatus (Steph.) Fulford, a moss belonging to the Herbertaceae family, commonly known as Herbertus. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of life that thrives in even the most unexpected places.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Herbertus angustevittatus, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it exists. Mosses are non-vascular plants that belong to the phylum Marchantiophyta and the class Jungermanniopsida. These diminutive yet resilient organisms have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. They play vital roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
HEBERTUS%2BJUNIPERIOIDES0001.jpg from: https://popmicrosoftnueva.blogspot.com/2020/01/hepaticas-herberttaceae-hebertus.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
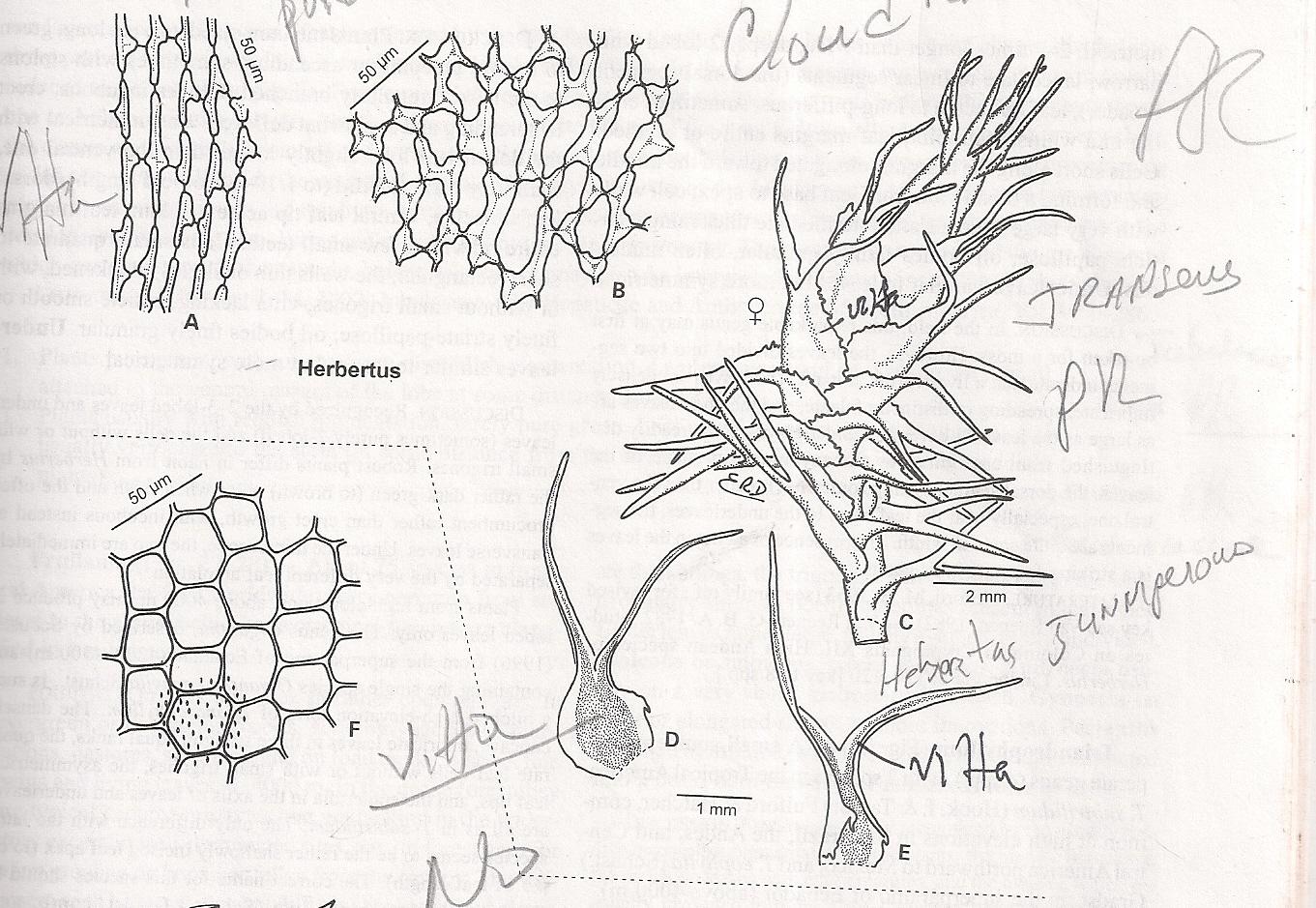
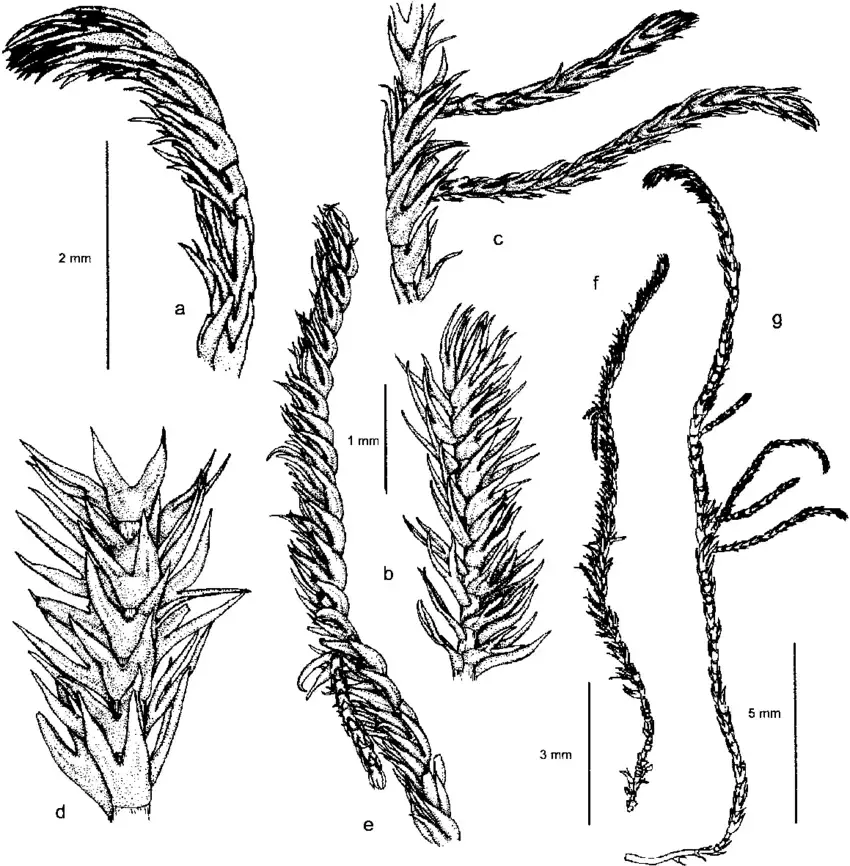
Herbertus angustevittatus is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with closely overlapping leaves that are deeply divided into two lobes. The leaves are typically yellowish-green to dark green in color, with a distinctive narrow, elongated shape that gives the species its name – “angustevittatus” means “narrow-banded” in Latin.
One of the key identifying features of Herbertus angustevittatus

Morphological-variations-of-the-leaves-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-a-B-Germany-Arnold_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sporophytic-characters-of-Herbertus-sendtneri-a-an-incomplete-sporophyte-packed-with_fig1_320243669
is the presence of underleaves, which are small, scale-like structures found on the underside of the stem. These underleaves are deeply bifid (divided into two parts) and help distinguish this species from other members of the Herbertaceae family.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Herbertus angustevittatus is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist, shaded forests and rock crevices to the bark of trees and decaying logs. This moss is particularly well-adapted to cool, humid environments, where it can take advantage of the moisture and shade provided by its surroundings.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Localities-of-Herbertus-aduncus-subsp-aduncus-in-Hunan-Grey-line-border-of-warm.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Localities-of-Herbertus-aduncus-subsp-aduncus-in-Hunan-Grey-line-border-of-warm_fig5_46668763
Despite its diminutive size, Herbertus angustevittatus plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps to stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture for a wide range of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Herbertus angustevittatus is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating an impressive resilience that has allowed it to thrive in a variety of environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Herbertus angustevittatus played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as logging or wildfires. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas and create a stable substrate for other plants to establish themselves made it a key player in the process of ecological succession.
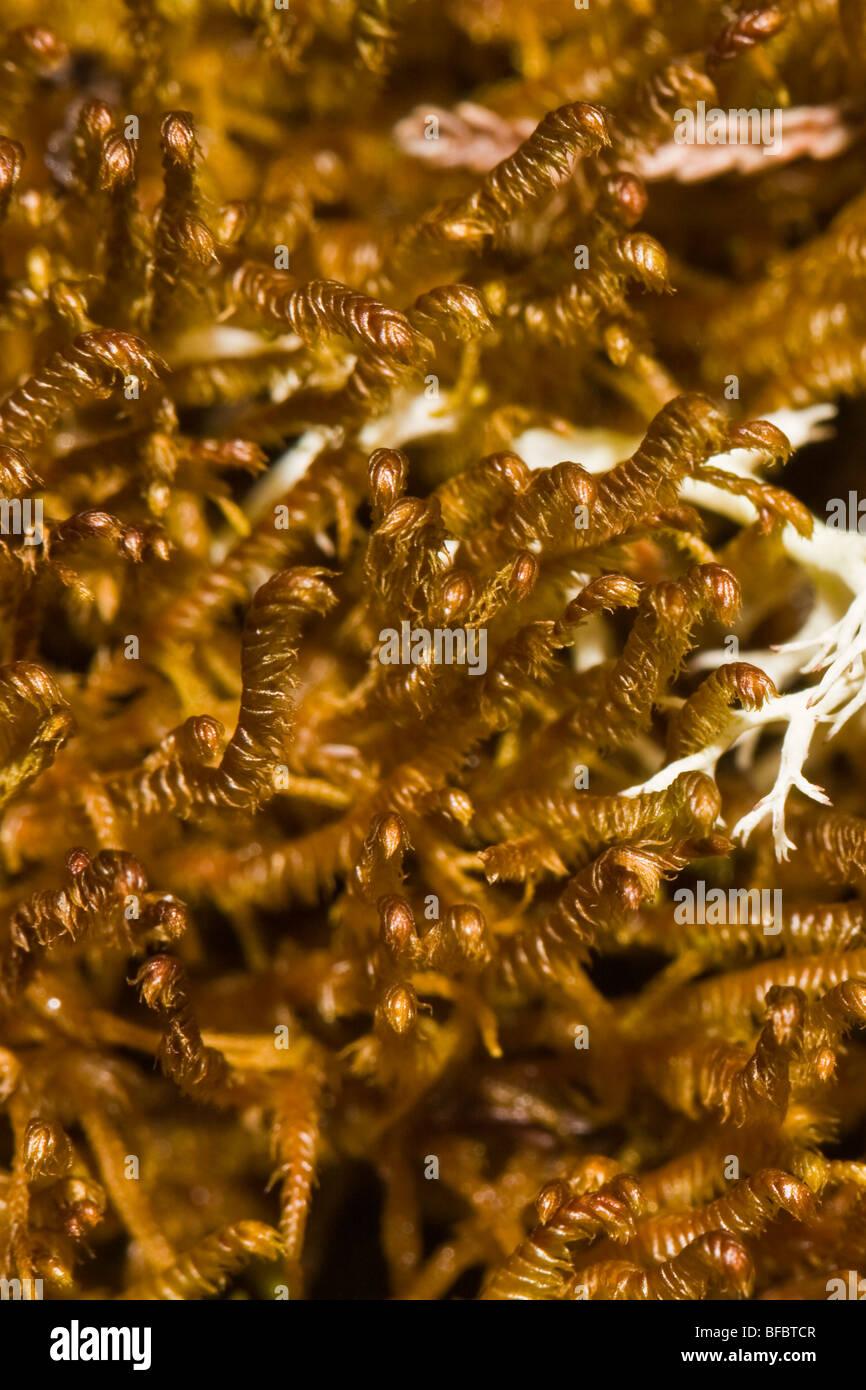

northern-prongwort-herbertus-borealis-BFBTCR.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/northern-prongwort.html
Another interesting example comes from the United Kingdom, where Herbertus angustevittatus has been found growing on the walls of historic buildings and structures. Its presence in these environments not only adds a touch of natural beauty but also serves as an indicator of the air quality and moisture levels in the area.

21365d2e1bd9d749fa8c4d84473cb768.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/46139
Technical Table

mini_magick20190214-14152-fby1k9.png from: https://www.academia.edu/14168061/Phylogenetic_biogeography_of_the_leafy_liverwort_Herbertus_Jungermanniales_Herbertaceae_based_on_nuclear_and_chloroplast_DNA_sequence_data_correlation_between_genetic_variation_and_geographical_distribution
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Herbertaceae |
| Genus | Herbertus |
| Species | Herbertus angustevittatus (Steph.) Fulford |
| Common Name | Herbertus |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply divided into two lobes, narrow and elongated |
| Underleaves | Present, deeply bifid |
| Color | Yellowish-green to dark green |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded forests, rock crevices, bark of trees, decaying logs |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, parts of South America |
| Ecological Role | Soil stabilization, moisture retention, pioneer species, habitat for invertebrates |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy during dry periods |
Conclusion
The Herbertus angustevittatus (Steph.) Fulford moss, or simply Herbertus, is a remarkable example of the incredible diversity and resilience found in the world of bryophytes. Despite its unassuming appearance, this moss plays vital roles in various ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, moisture retention, and providing habitat for a wide range of invertebrates. Its ability to survive periods of desiccation and rapidly colonize disturbed areas makes it a true pioneer species, paving the way for the establishment of more complex plant communities.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, species like Herbertus angustevittatus serve as a reminder of the importance of preserving and protecting even the smallest and most overlooked organisms. Who knows what other wonders and secrets the world of mosses holds, waiting to be discovered by the curious and observant among us?