image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/kochibii/28720036863/
Introduction
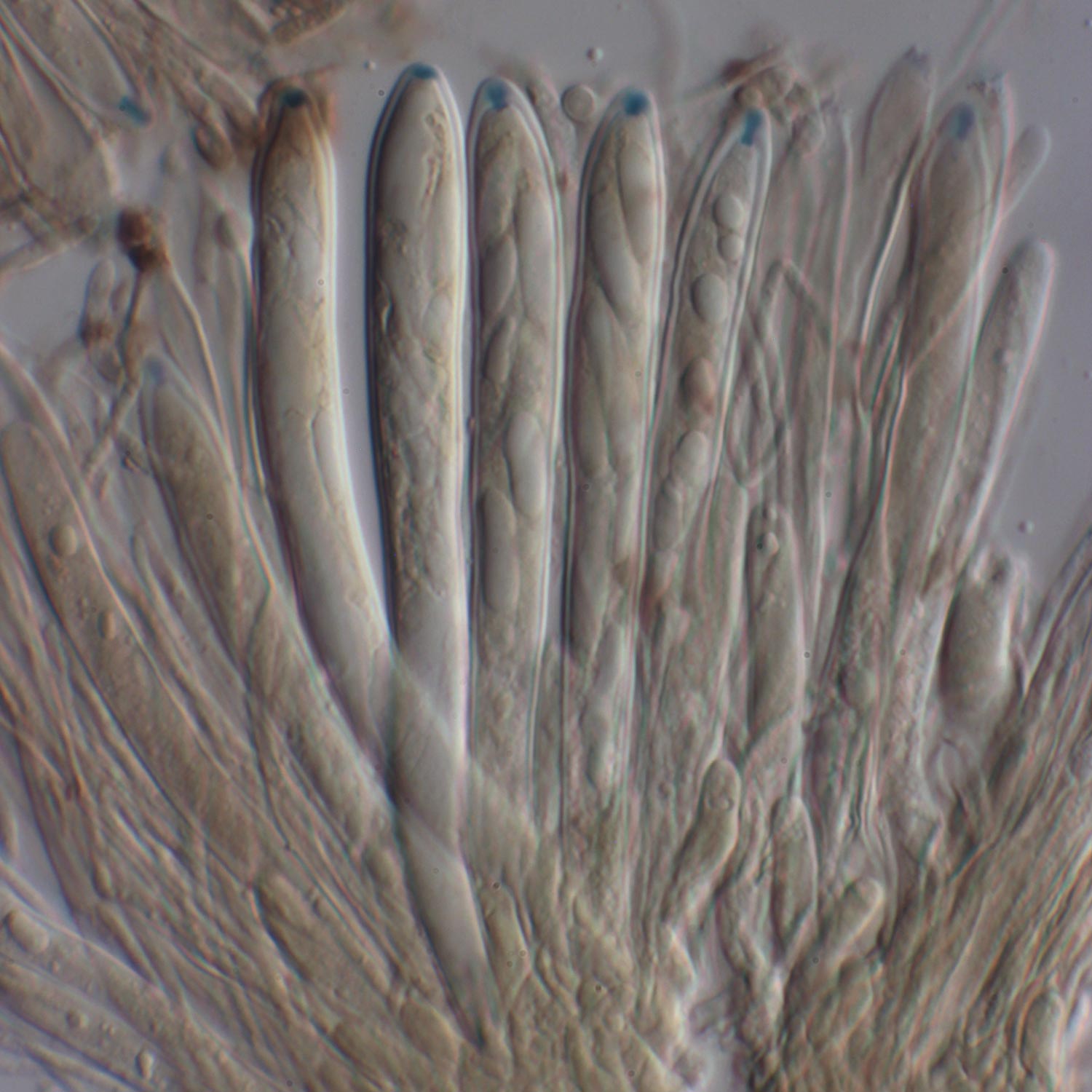

image from: https://fungi.myspecies.info/file-colorboxed/7550
Deep within the lush tapestry of nature lies a tiny, unassuming marvel – the

image from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/Sematophyllaceae/6536687
Acroporium megasporum moss. This diminutive plant, belonging to the Sematophyllaceae family, has captured the hearts of bryophyte enthusiasts worldwide with its intricate beauty and fascinating ecological roles.
Background
Bryophytes, often referred to as the “ancient lineage of land plants,” have been around for over 400 million years. Among this diverse group, mosses like

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Brotherella-henonii-Duby-MFleisch-A-Habit-B-A-portion-of-branch-C-G-Branch_fig4_331050368
Acroporium megasporum have carved out a unique niche, thriving in moist and shaded environments. These resilient organisms have adapted to survive in some of the harshest conditions on Earth, making them true champions of the plant kingdom.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
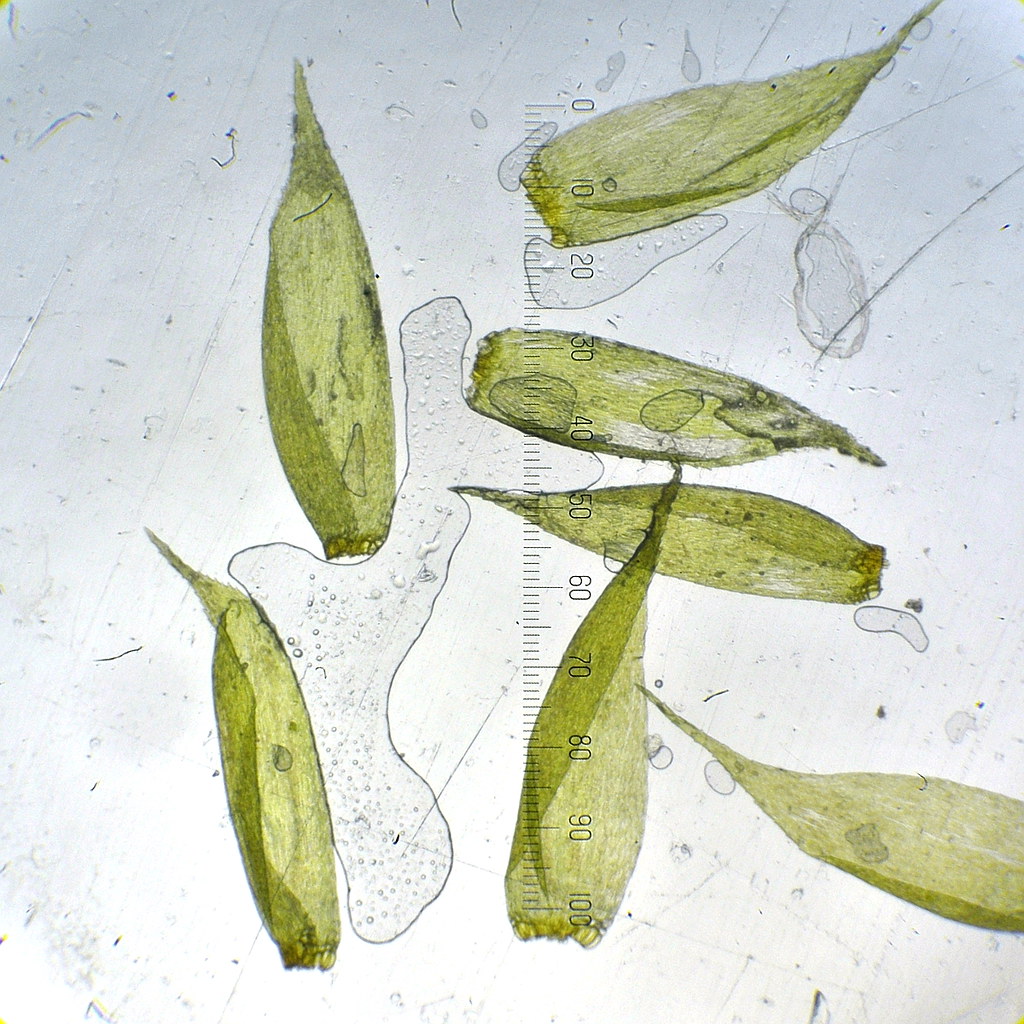
Acroporium megasporum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate fronds form dense, velvety mats, adorned with tiny, intricate leaves that spiral around the stem. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib running along their length. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a mesmerizing pattern of hexagonal shapes, each one a testament to nature’s intricate design.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species can be found across various regions of the world, from the temperate forests of North America to the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia. Acroporium megasporum thrives in moist, shaded environments, often carpeting the forest floor, tree trunks, and rotting logs. Its ability to absorb and retain moisture makes it a vital component of these ecosystems, creating a microhabitat for countless other organisms.
image from: https://www.baike.com/wikiid/4355543150966325721
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Acroporium megasporum plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of its environment. Its dense mats act as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, preventing soil erosion, and providing a nurturing environment for seedlings and other plants to take root. Additionally, these mosses serve as a vital food source and shelter for a myriad of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
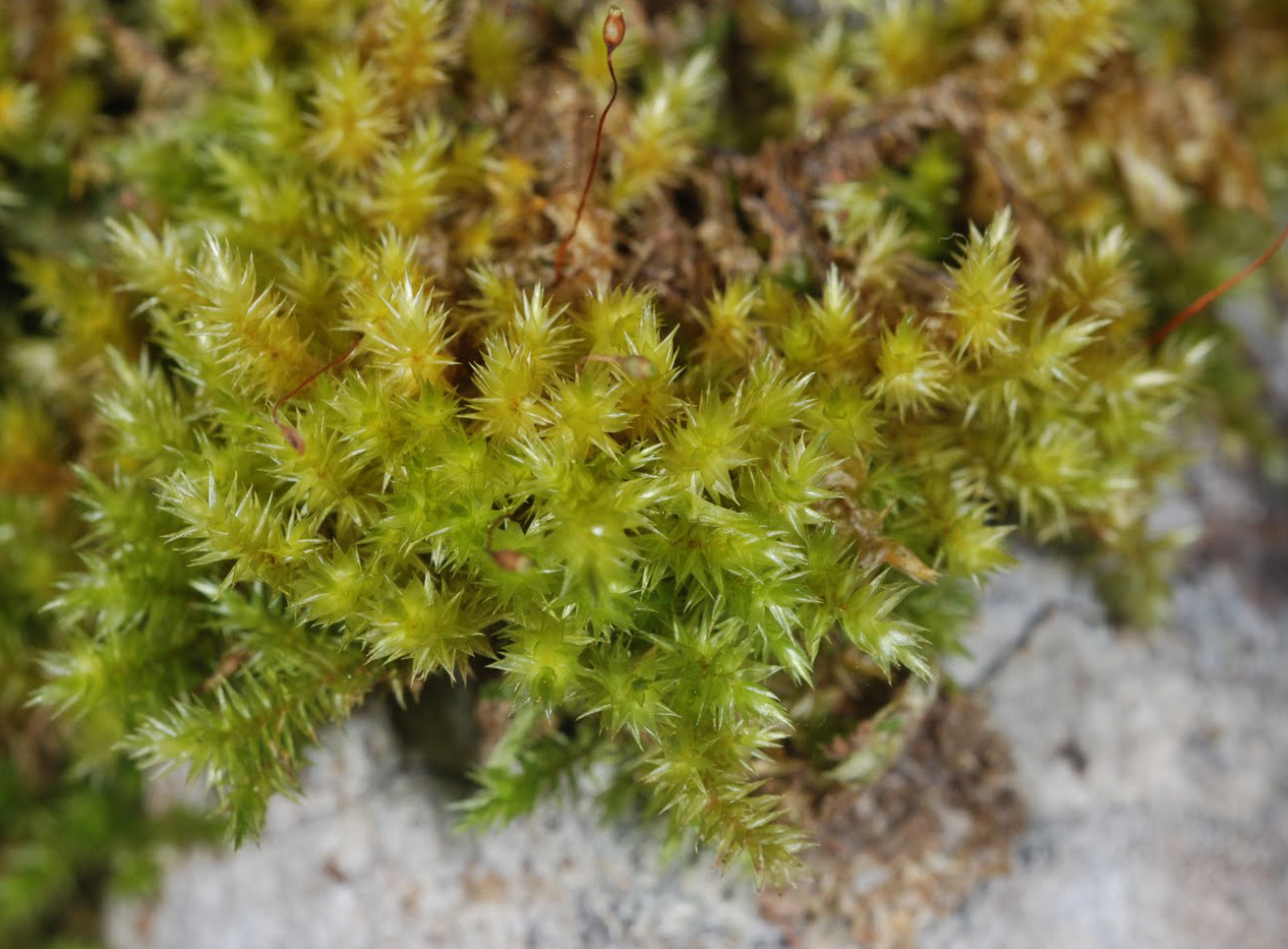

image from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat.html
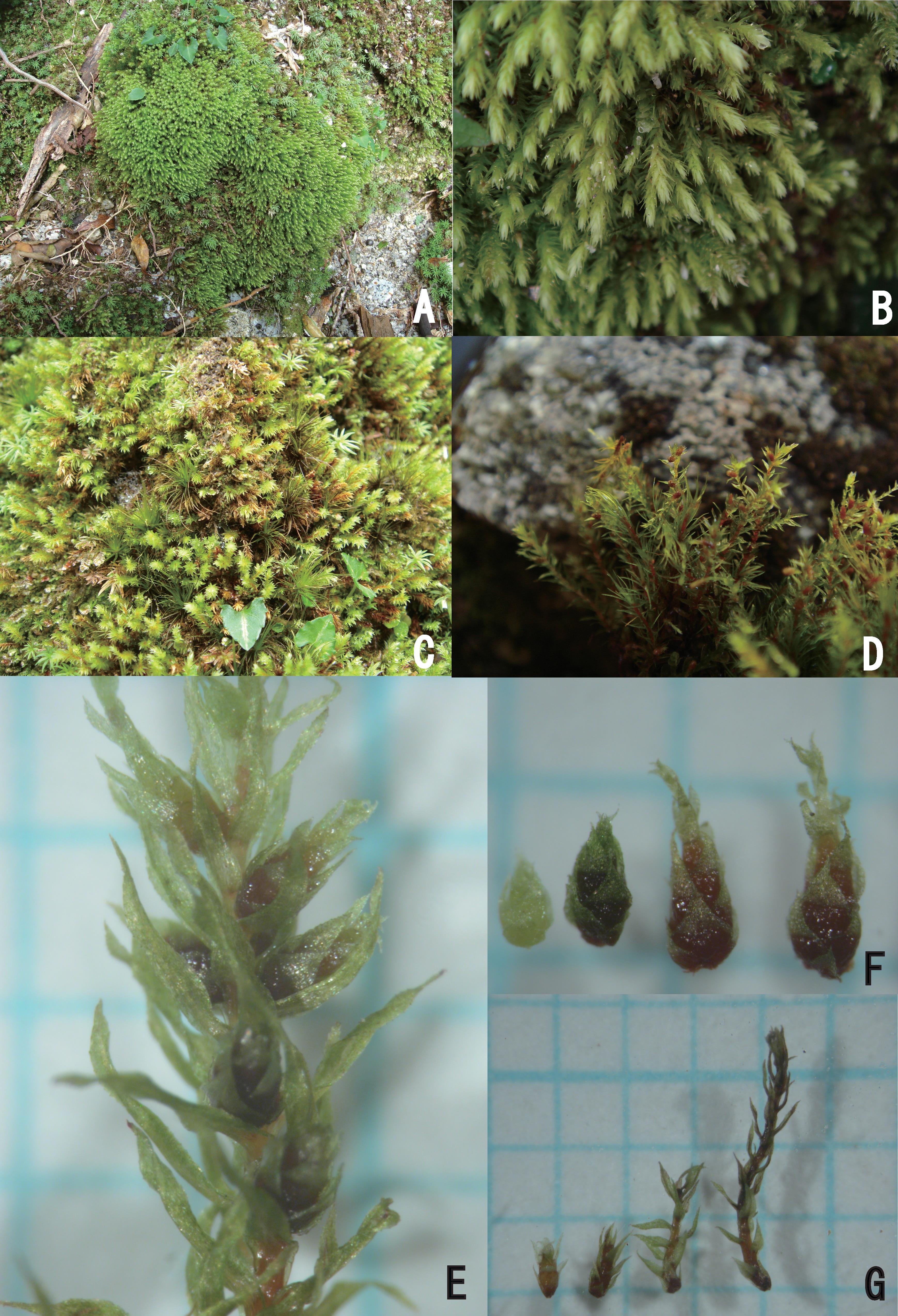
image from: https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-112/issue-4/0007-2745-112.4.749/Habitat-and-morphological-differentiation-between-span-classgenus-speciesPohlia-annotina-span/10.1639/0007-2745-112.4.749.full

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Thelotrema-megasporum-holotype-A-Habit-B-Apothecia-C-Section-through-apothecia_fig2_323968571
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Acroporium megasporum is its ability to survive periods of drought. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, unfurling its fronds and resuming its vital functions.
Case Study: The Moss Garden of Kyoto
In the heart of Japan’s ancient capital, Kyoto, lies a breathtaking moss garden known as Kokedera. Here, Acroporium megasporum and other moss species have been meticulously cultivated, creating a verdant tapestry that captivates visitors from around the world. This living work of art showcases the beauty and resilience of these humble plants, reminding us of the intricate connections that bind all life on our planet.
Technical Table

image from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/20719304532/

image from: https://plantdollar.com/plant/acroporium/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Acroporium megasporum (Duby) M.Fleisch. |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Leaf Cells | Hexagonal pattern |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Temperate and tropical regions worldwide |
| Ecological Roles | Moisture retention, soil stabilization, microhabitat creation |
| Adaptations | Drought tolerance, dormancy |