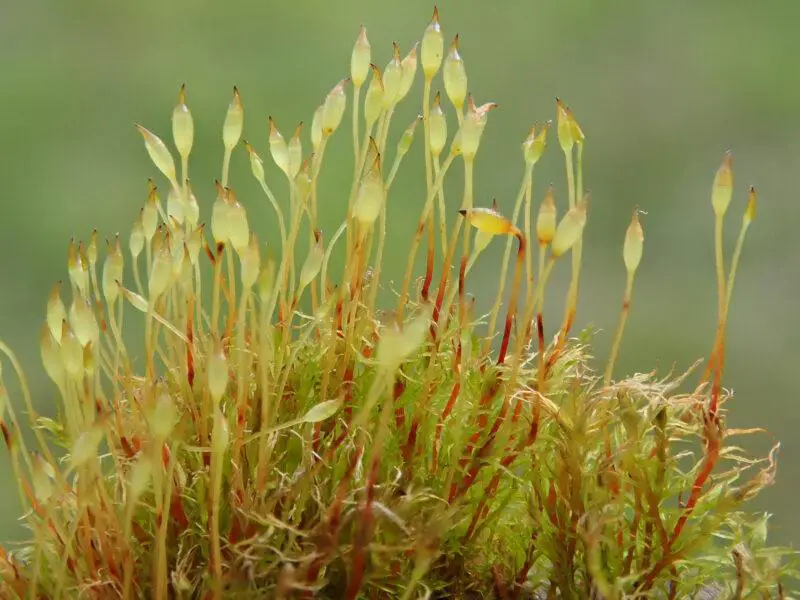

2019-10-06-13-51-55-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranella-rufescens/
Discovering the Delightful Dicranella amplexans Moss
Mosses are fascinating little plants that often go unnoticed, but they play important ecological roles. Today we’ll take a closer look at one particular species:
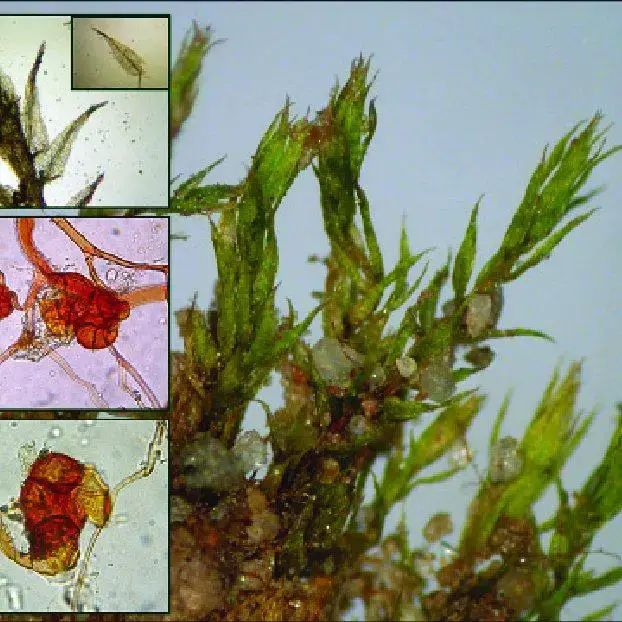

Growth-habit-detail-of-leaves-and-gemmae-of-Dicranella-staphylina-photo-V-Plasek_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Growth-habit-detail-of-leaves-and-gemmae-of-Dicranella-staphylina-photo-V-Plasek_fig1_237256802
Dicranella amplexans (Mitt.) A.Jaeger, a charming moss in the Dicranellaceae family. Get ready to learn all about this marvelous miniature marvel!
Background on Bryophytes
Before we dive into the details on D. amplexans specifically, let’s review some background on mosses in general. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other land plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have root-like rhizoids, a stem-like structure called a seta, and leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and flowers.
Morphology and Identification
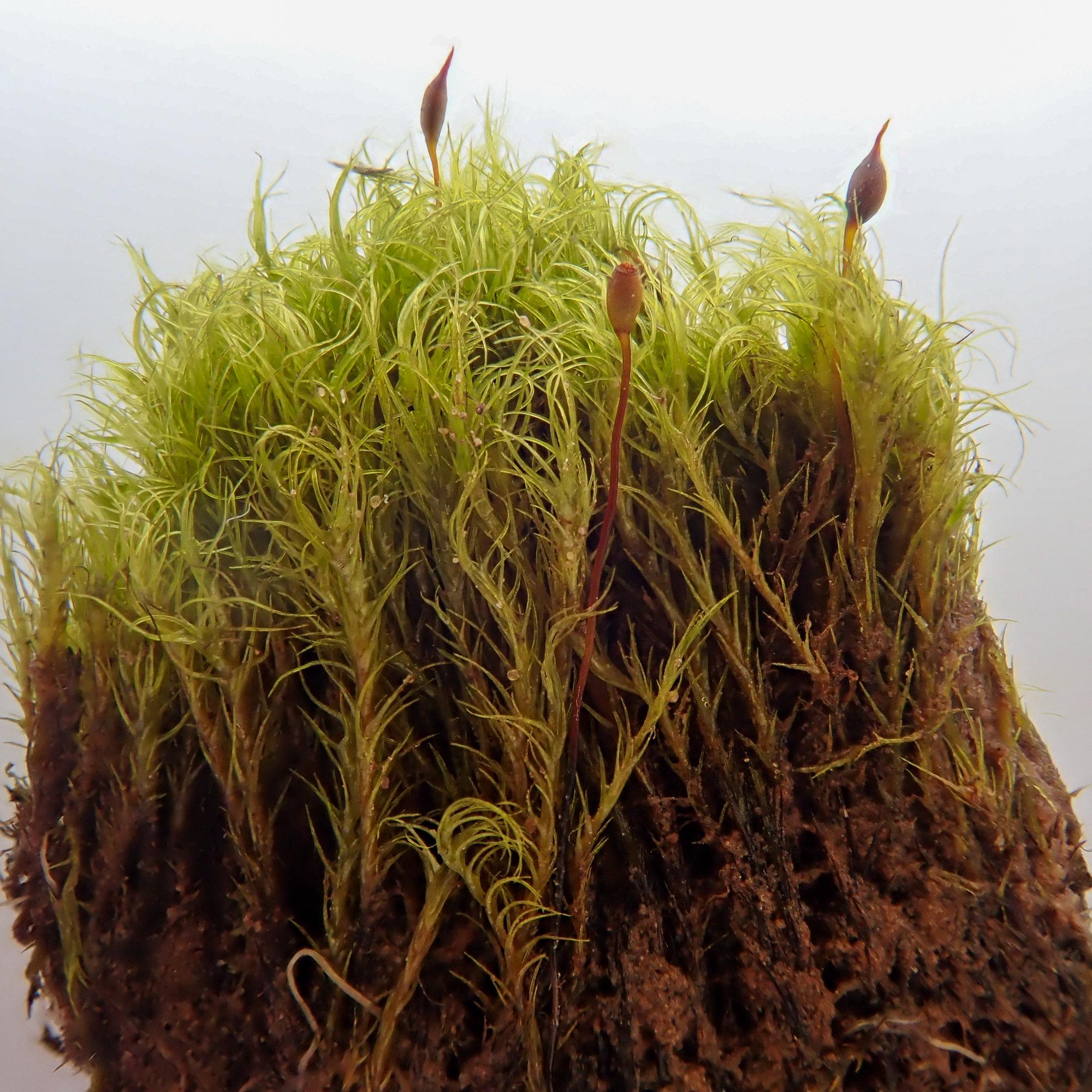
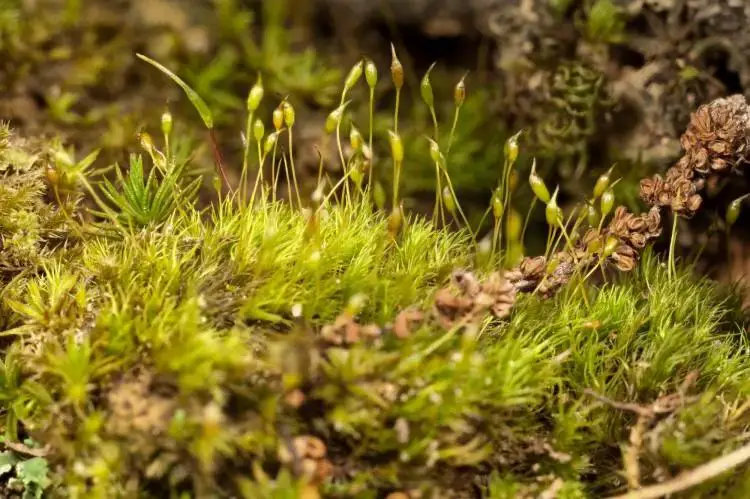
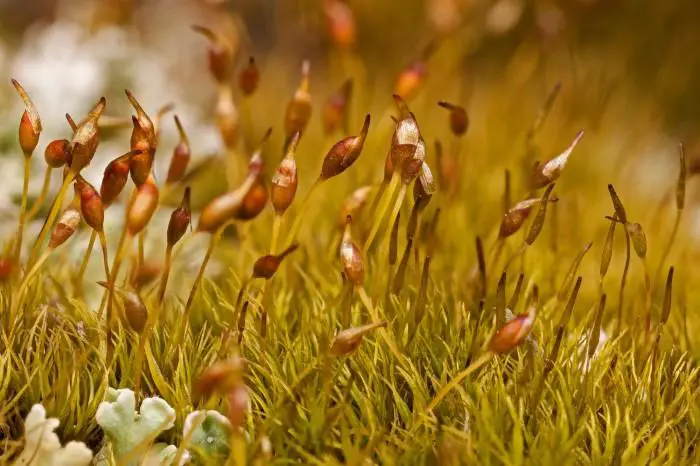
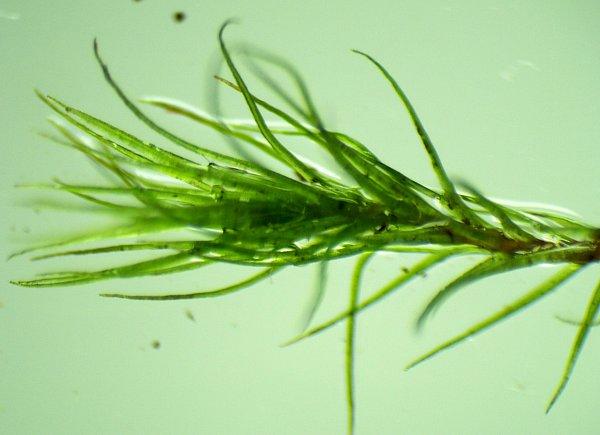
Dicranella amplexans is a small, delicate moss that forms loose tufts or mats. Its phyllids are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and have a clasping base that wraps around the stem, which is a key identifying feature and the inspiration for its species name “amplexans” meaning embracing or clasping. The phyllid margins are entire (smooth-edged) and the costa (midrib) extends to the tip.
Sporophytes (spore-producing structures) are common. The seta is reddish and the capsule is inclined to horizontal and slightly curved. Peristome teeth are divided about halfway to the base.
Global Distribution and Habitat
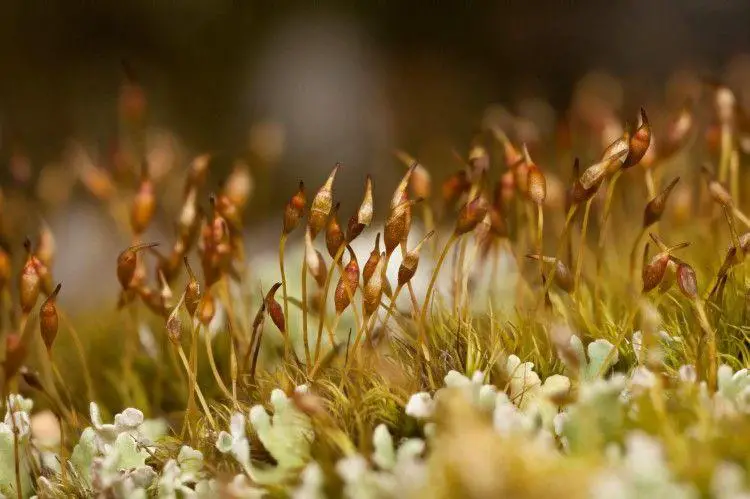

e7262ce40dcee1b899d04535ead33b98.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/mossdicranella-heteromalla–394416879843089766/
This species has a widespread distribution, found in many regions around the world including:
- Europe
- Asia
- Africa
- North America
- Central America
- South America
It grows on damp soil, rocks, and rotten wood in forests and along streams from lowlands to mountains. It prefers shaded sites but can tolerate some sun exposure.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, D. amplexans plays several important roles in its ecosystems:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion

dscn9948.jpg from: https://diversionsinnaturalhistory.wordpress.com/bryophytes/dicranella-schreberiana/

2020-09-10-14-49-38.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/dicranella-subulata/
- Provides shelter and habitat for micro-organisms and tiny invertebrates
- Pioneers disturbed sites and enriches soil as it breaks down
- Serves as a bioindicator of air and water quality
Its small size and ability to dry out and rehydrate allow it to exploit microhabitats and withstand periods of drought. The clasping leaf bases may help conduct water internally.

Dicranella-heteromalla-71-750×499.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-dicranella-heteromalla/dicranella-heteromalla-7-2/

770c76355b2451a63a77417d809eb72c.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/dicranella-palustris–494692340290372744/
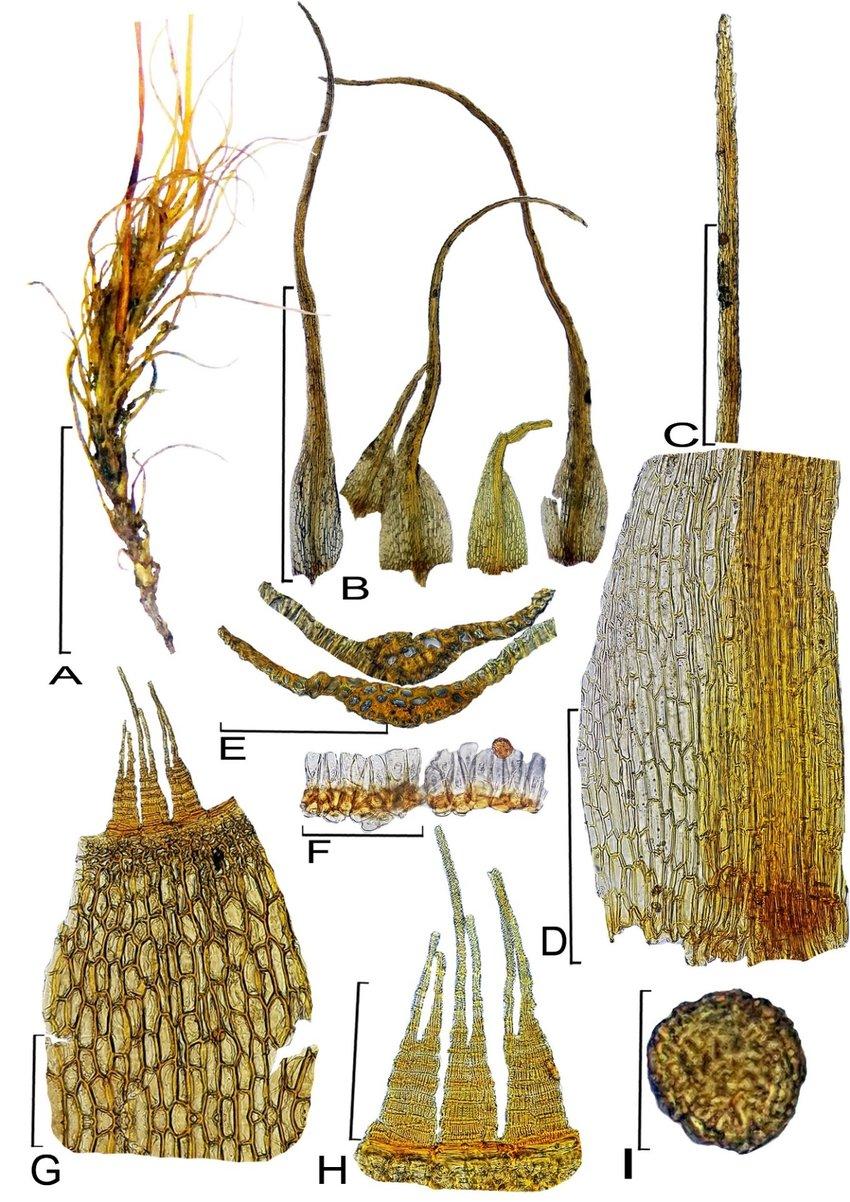
Figura-3-Dicranella-angustifolia-Mitt-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apice-do-filidio-D.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-3-Dicranella-angustifolia-Mitt-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apice-do-filidio-D_fig3_343400267

Dicranella-heteromalla-5-700×466.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-dicranella-heteromalla/dicranella-heteromalla-5/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phyllids | Lanceolate with clasping base |
| Phyllid margins | Entire |
| Costa | Extends to tip |
| Seta | Reddish |
| Capsule | Inclined to horizontal, slightly curved |
| Peristome teeth | Divided about halfway |
Conclusion
Dicranella amplexans may be small, but it’s certainly not insignificant! This plucky little moss has successfully colonized many parts of the globe and serves admirably in the ecosystems it inhabits. Next time you’re out in nature, take a moment to appreciate the mighty miniature mosses all around you. What other marvelous secrets might they hold?

fh_moss2.jpg from: https://illinoiswildflowers.info/mosses/plants/fh_moss.html