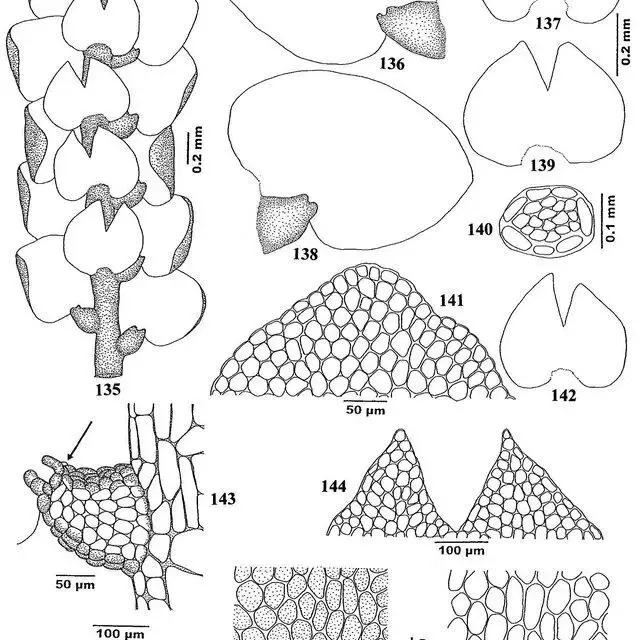
147-Lejeunea-contracta-Mizut-135-Part-of-plant-in-ventral-view-136-138-Leaves_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/51-Lejeunea-alata-Gottsche-37-Part-of-plant-in-ventral-view-38-39-Leaves-40_fig1_281129131
Introduction

Nepenthes-alata-upper-pitchers.jpg from: https://www.thescienceblog.net/the-rarest-plants-on-the-planet-part-1/
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Hygrolejeunea alata (Gottsche) Steph. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Lejeuneaceae family. This diminutive yet resilient plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its intricate beauty and fascinating adaptations. Join us as we delve into the intriguing realm of this moss, exploring its morphology, global distribution, ecological roles, and the remarkable ways it has evolved to thrive in diverse environments.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Hygrolejeunea alata, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it exists. Mosses belong to the division Marchantiophyta, which encompasses a diverse array of non-vascular plants known as

004b2b8d309ef6ab3cc15c828b0149c3.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/dioscorea-alata–489133209540631774/
bryophytes. These ancient organisms have been around for millions of years, playing crucial roles in various ecosystems and serving as indicators of environmental health.
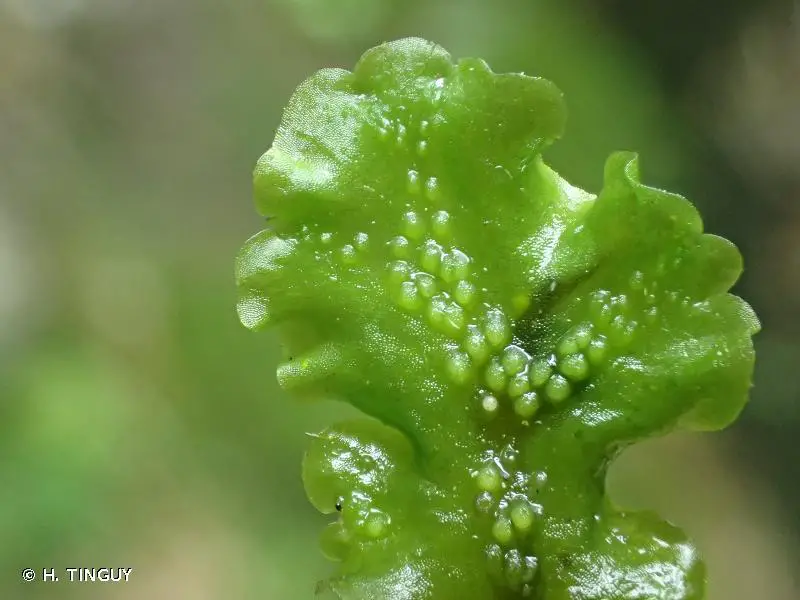

230158.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6271
Main Content
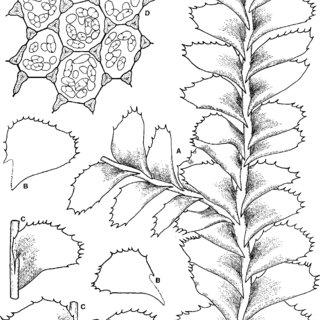
Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal_fig2_29813448
Morphology and Identification
Hygrolejeunea alata is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate leaves are arranged in a distinctive spiral pattern, each leaf adorned with a unique wing-like structure along its midrib – a trait that gives this species its name, “alata” (meaning “winged”). These intricate leaf formations not only add to the moss’s visual appeal but also play a vital role in water retention and protection against desiccation.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss
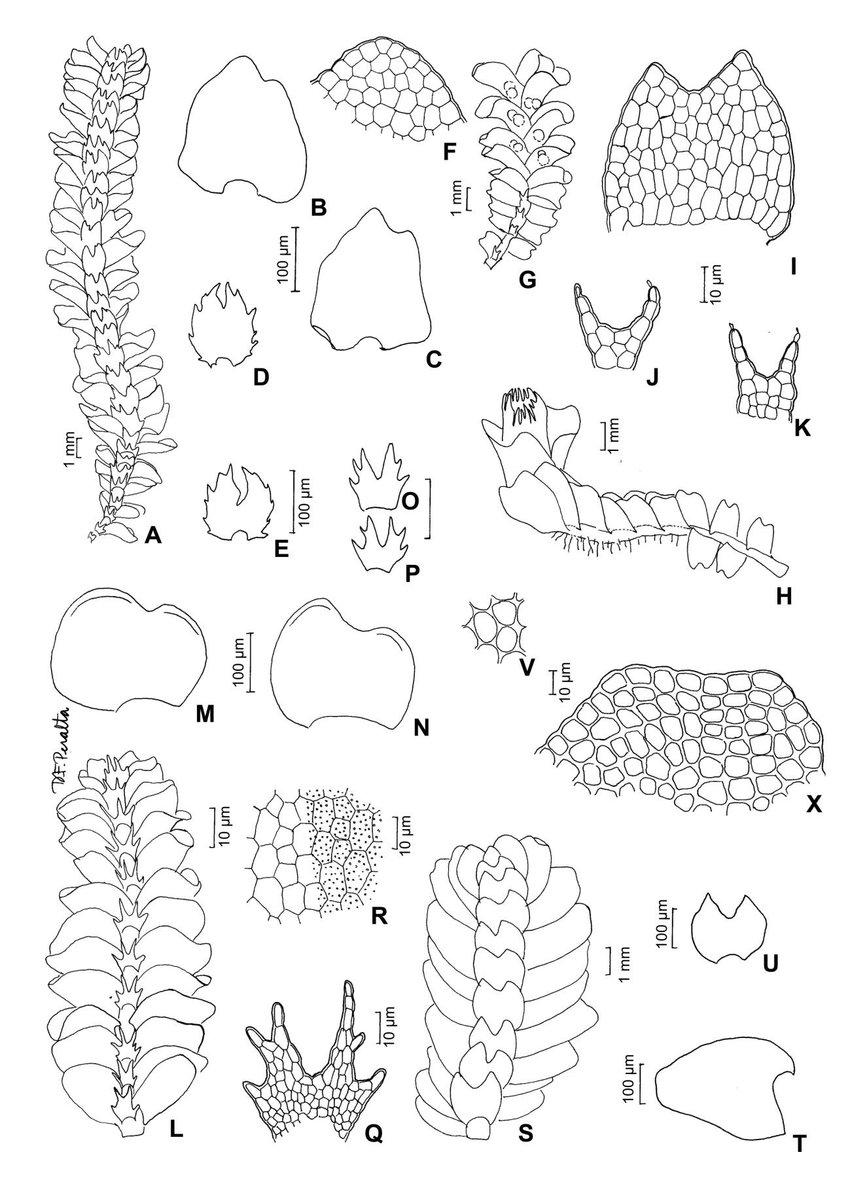
Isotachis-multiceps-Lindenb-Gottsche-Gottsche-A-aspecto-do-gametofito-B-C.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Isotachis-multiceps-Lindenb-Gottsche-Gottsche-A-aspecto-do-gametofito-B-C_fig5_270550843
has a widespread distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from temperate forests to tropical rainforests, often growing on tree bark, rocks, or soil. Hygrolejeunea alata is particularly well-adapted to moist, shaded environments, where it can take advantage of the humidity and filtered sunlight.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Hygrolejeunea alata plays a crucial role in its ecosystems. It serves as a vital component of the understory, providing shelter and moisture for countless microorganisms and invertebrates. Additionally, this moss contributes to nutrient cycling and soil formation, breaking down organic matter and facilitating the growth of other plants.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Hygrolejeunea alata is its remarkable ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its incredible resilience and adaptability.
Case Studies/Examples
In the temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest, Hygrolejeunea alata is a common sight, forming vibrant green carpets on the trunks of towering conifers. Its presence is often an indicator of a healthy, undisturbed ecosystem, as it thrives in areas with minimal disturbance and high humidity levels.
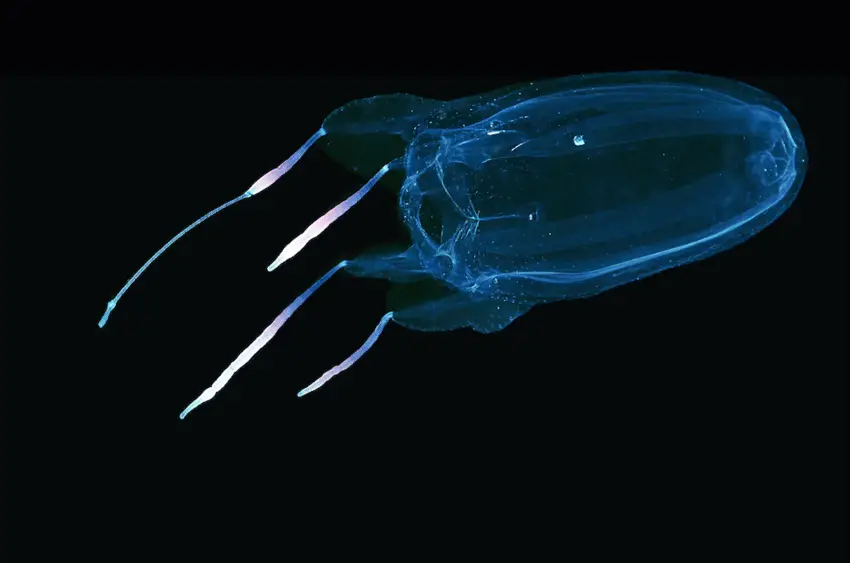
Female-Alatina-alata-in-the-waters-off-Bonaire-The-Netherlands-Alatina-alata-is-a.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Female-Alatina-alata-in-the-waters-off-Bonaire-The-Netherlands-Alatina-alata-is-a_fig1_309748790
Technical Table

Nepenthes-alata-Pitcher-Plant-March-scaled.jpg from: https://littleprinceplants.com/our-plants/terrarium-plants/closed-terrariums/nepenthes-alata-pitcher-plant/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hygrolejeunea alata (Gottsche) Steph. |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral, with wing-like structures along the midrib |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (e.g., tree bark, rocks, soil) |
| Distribution | Widespread, found on every continent except Antarctica |
Conclusion
The Hygrolejeunea alata (Gottsche) Steph. moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and adaptability of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other remarkable adaptations might we discover in the vast and fascinating realm of mosses?

original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/4276916

Nepenthes-alata-Pitcher-Plant-March2.jpg from: https://littleprinceplants.com/our-plants/terrarium-plants/open-terrariums/nepenthes-alata-pitcher-plant/