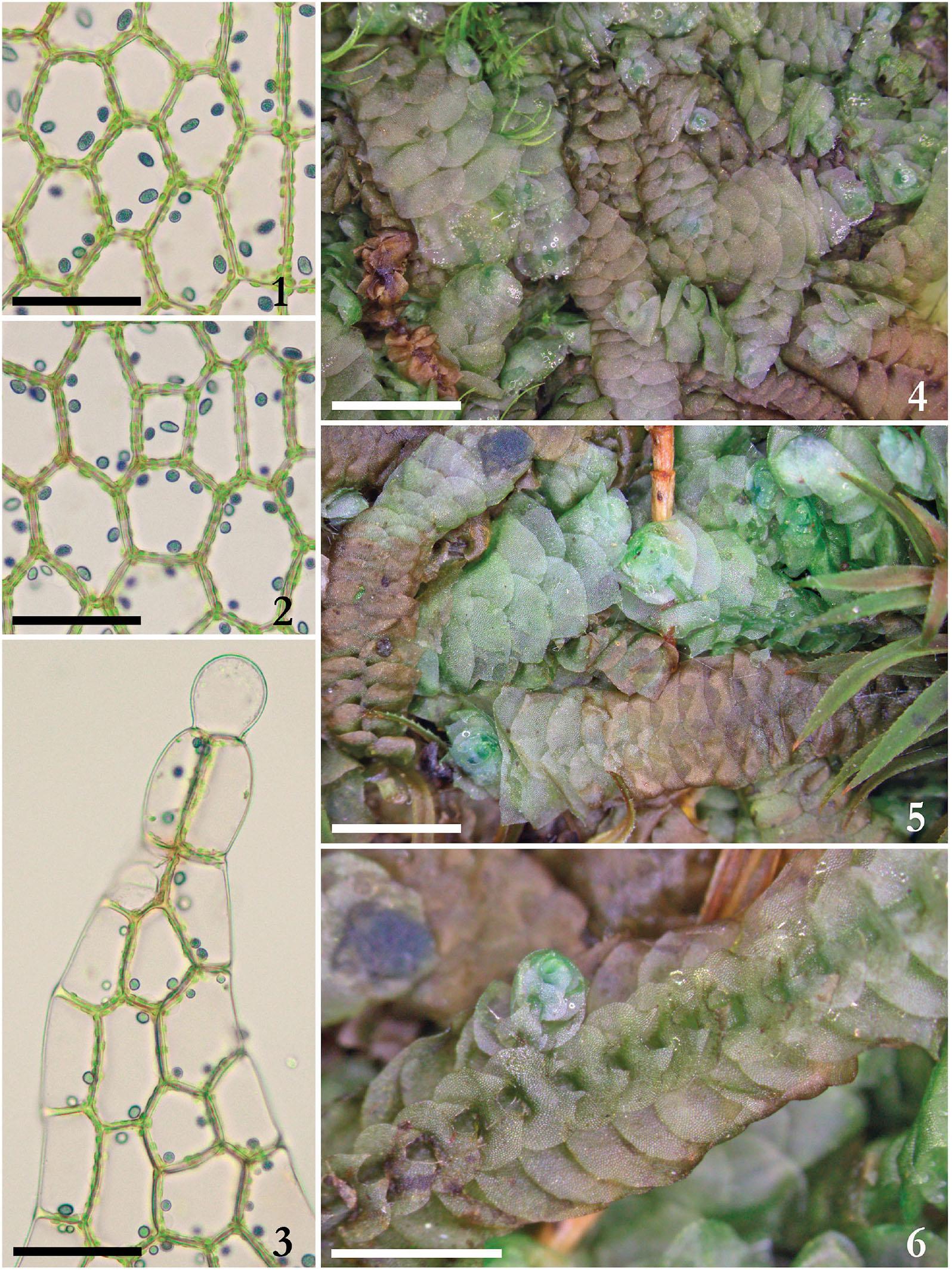
f04_219.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Herzogia/volume-32/issue-1/heia.32.1.2019.219/Calypogeia-vietnamica-sp-nov-Calypogeiaceae-Hepaticae-from-North-Vietnam-and/10.13158/heia.32.1.2019.219.full
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Calypogeia cellulosa (Spreng.) Steph. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Calypogeiaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s wonders.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Calypogeia cellulosa, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, belong to the Marchantiophyta division, collectively known as bryophytes. These ancient and resilient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.
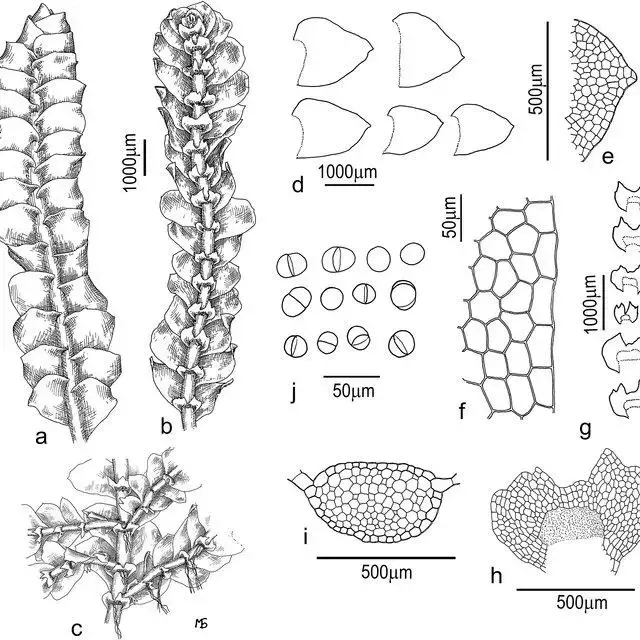
Calypogeia-sinensis-Bakalin-Buczkowska-a-plant-segment-dorsal-view-b-c-plant_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Cells-of-the-Calypogeia-azurea-complex-and-the-related-taxa-with-oil-bodies-a-C_fig1_328208028
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Calypogeia cellulosa is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form. Its delicate fronds are typically green to yellowish-green in color, with a translucent appearance that allows light to filter through. The plant’s leaves are deeply divided, giving it a feathery, lace-like appearance.
One of the most distinctive features of Calypogeia cellulosa is its oil bodies, which are small, spherical structures found within the cells. These oil bodies contain unique chemical compounds that contribute to the plant’s aroma and potentially play a role in its ecological interactions.
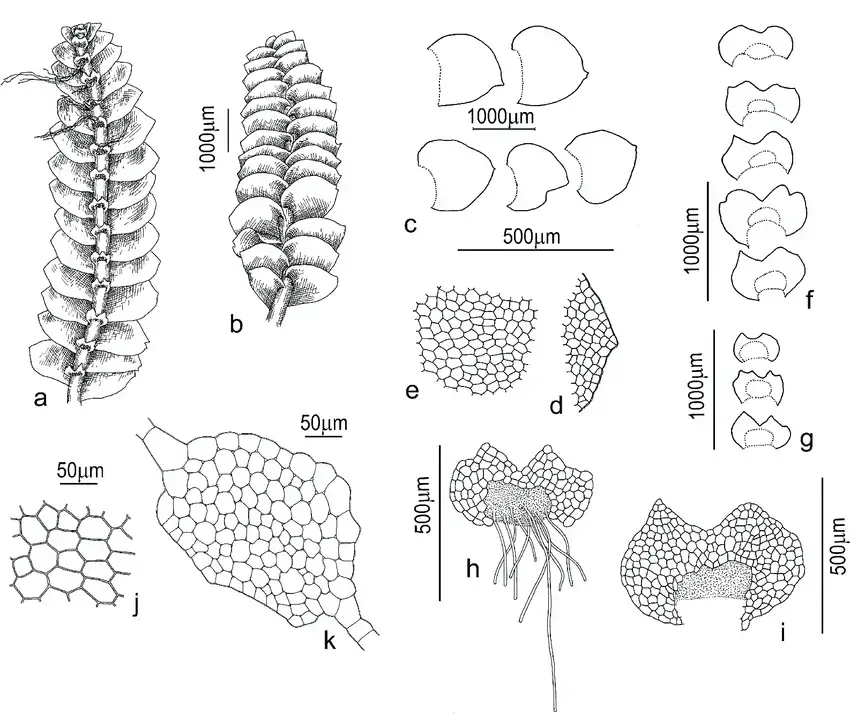
Calypogeia-orientalis-Buczkowska-Bakalin-a-plant-segment-dorsal-view-b-plant.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Calypogeia-orientalis-Buczkowska-Bakalin-a-plant-segment-dorsal-view-b-plant_fig6_328208028
Global Distribution and Habitat
Calypogeia cellulosa is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and New Zealand. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, rocks, or soil in forests and woodlands.
This moss prefers acidic and nutrient-poor substrates, making it well-adapted to thrive in environments where other plants may struggle. Its ability to colonize and flourish in such conditions is a testament to its remarkable resilience and adaptability.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Calypogeia cellulosa plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich the soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, it serves as a vital microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of
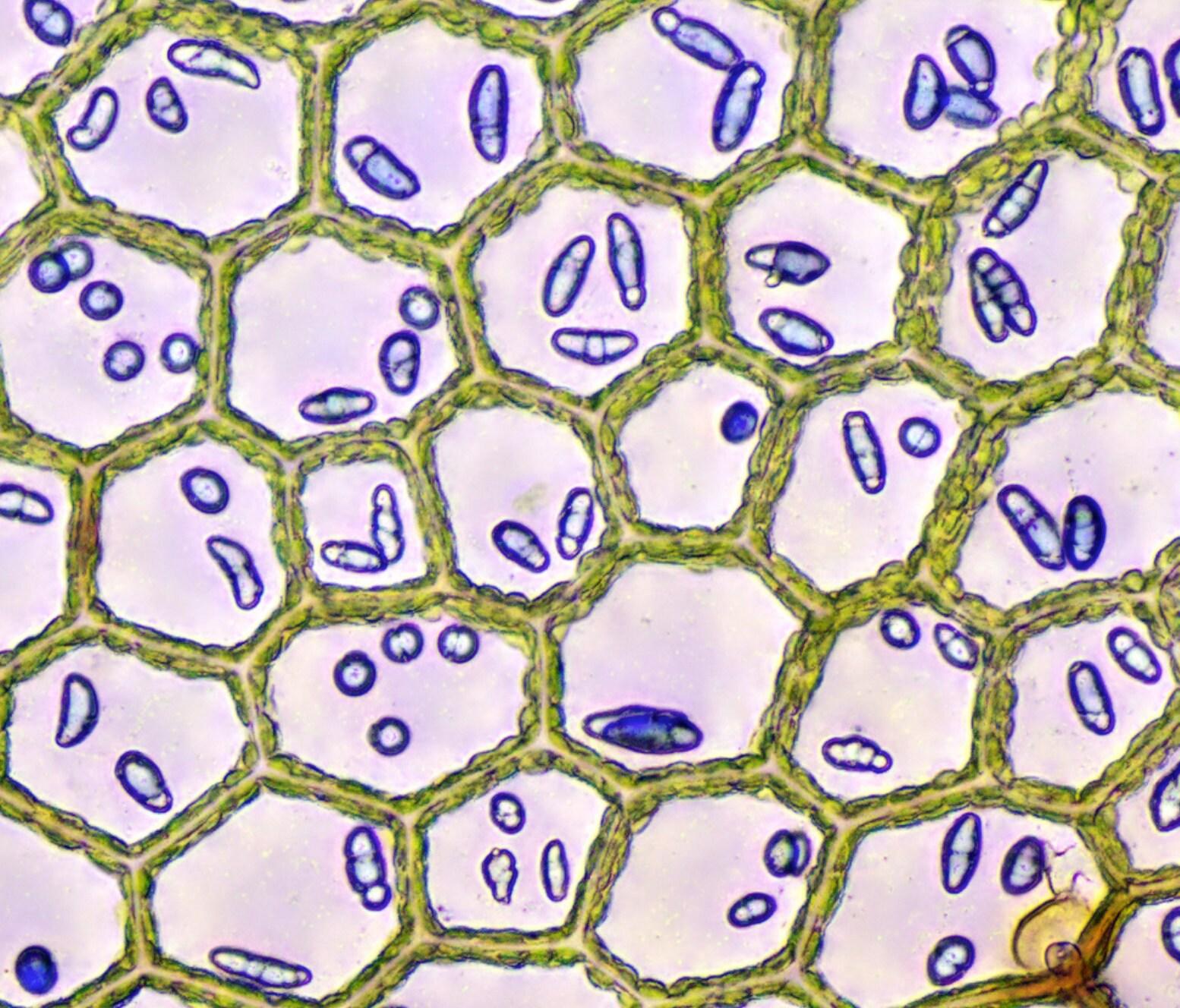

il_fullxfull.4784965803_cunk.jpg from: https://www.thebryophytanursery.com/listing/1442424297/terrarium-plant-calypogeia-azurea-blue
Calypogeia cellulosa is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the plant can enter a state of dormancy, curling up and protecting its delicate structures. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its remarkable resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Calypogeia cellulosa played a crucial role in facilitating the growth and establishment of certain tree species. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and create a favorable microclimate contributed to the successful germination and survival of tree seedlings.
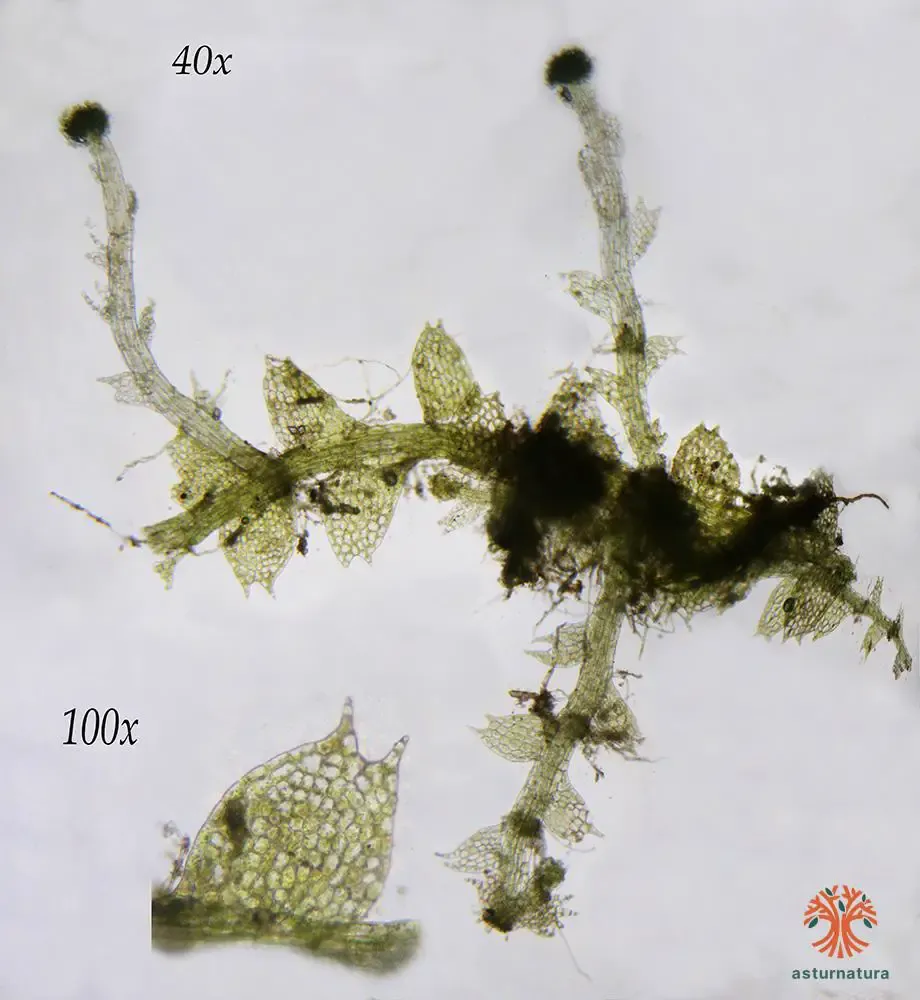

535b086ddb31c0766f9c81fa1692cc8c.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/fotografia/flora/calypogeia-arguta-2/32501.html
Technical Table
Calypogeia-granulata-Inoue-A-plant-habit-fragment-ventral-view-B-F-underleaves-C-leaf.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Calypogeia-granulata-Inoue-A-plant-habit-fragment-ventral-view-B-F-underleaves-C-leaf_fig5_342998310
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Calypogeia cellulosa (Spreng.) Steph. |
| Family | Calypogeiaceae |
| Division | Marchantiophyta |
Class
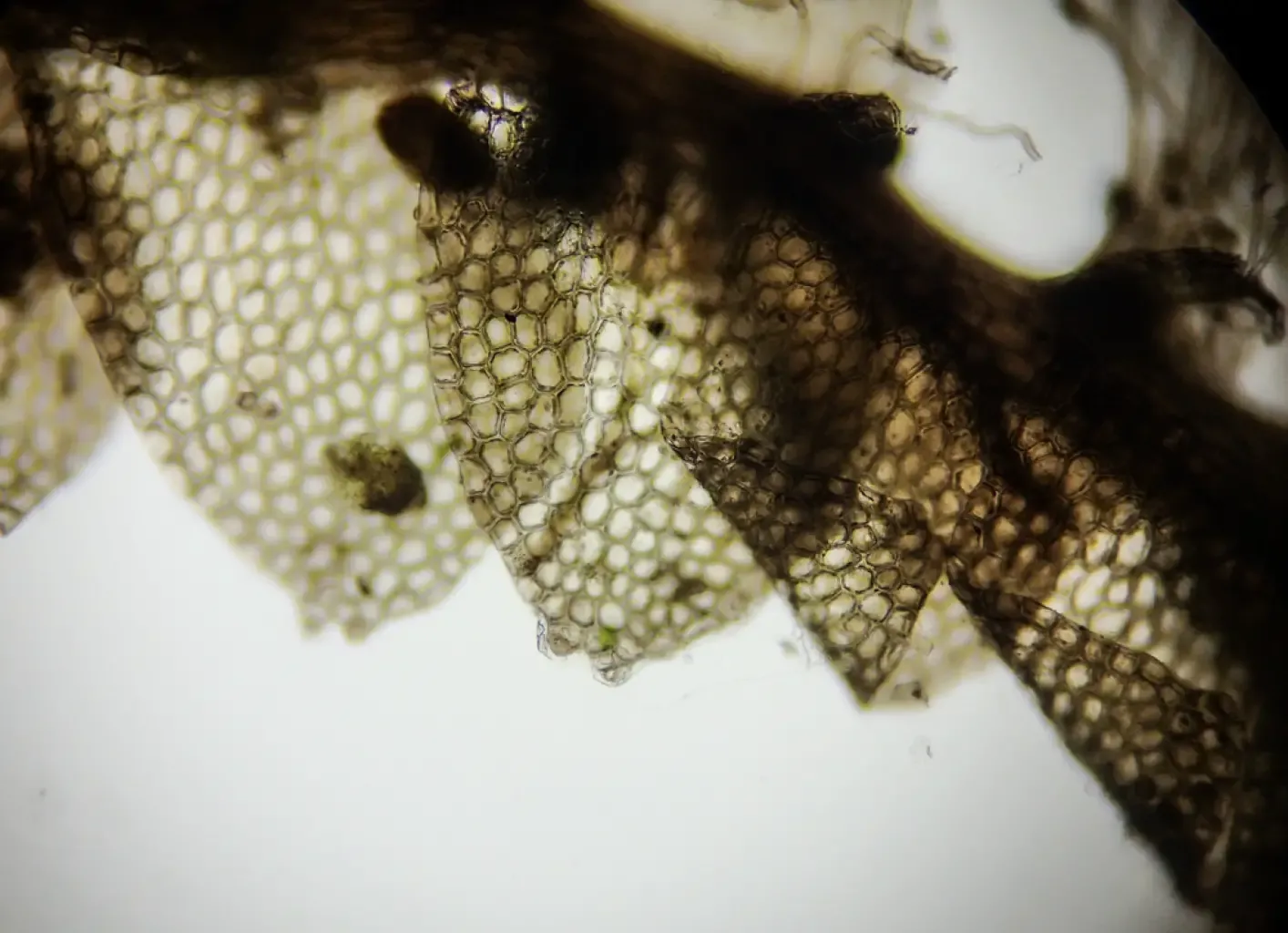 0d1f399b73c70924690f1829494ada65.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/fotografia/flora/calypogeia-muelleriana-2-de-4/41859.html |
Jungermanniopsida |
Growth Form
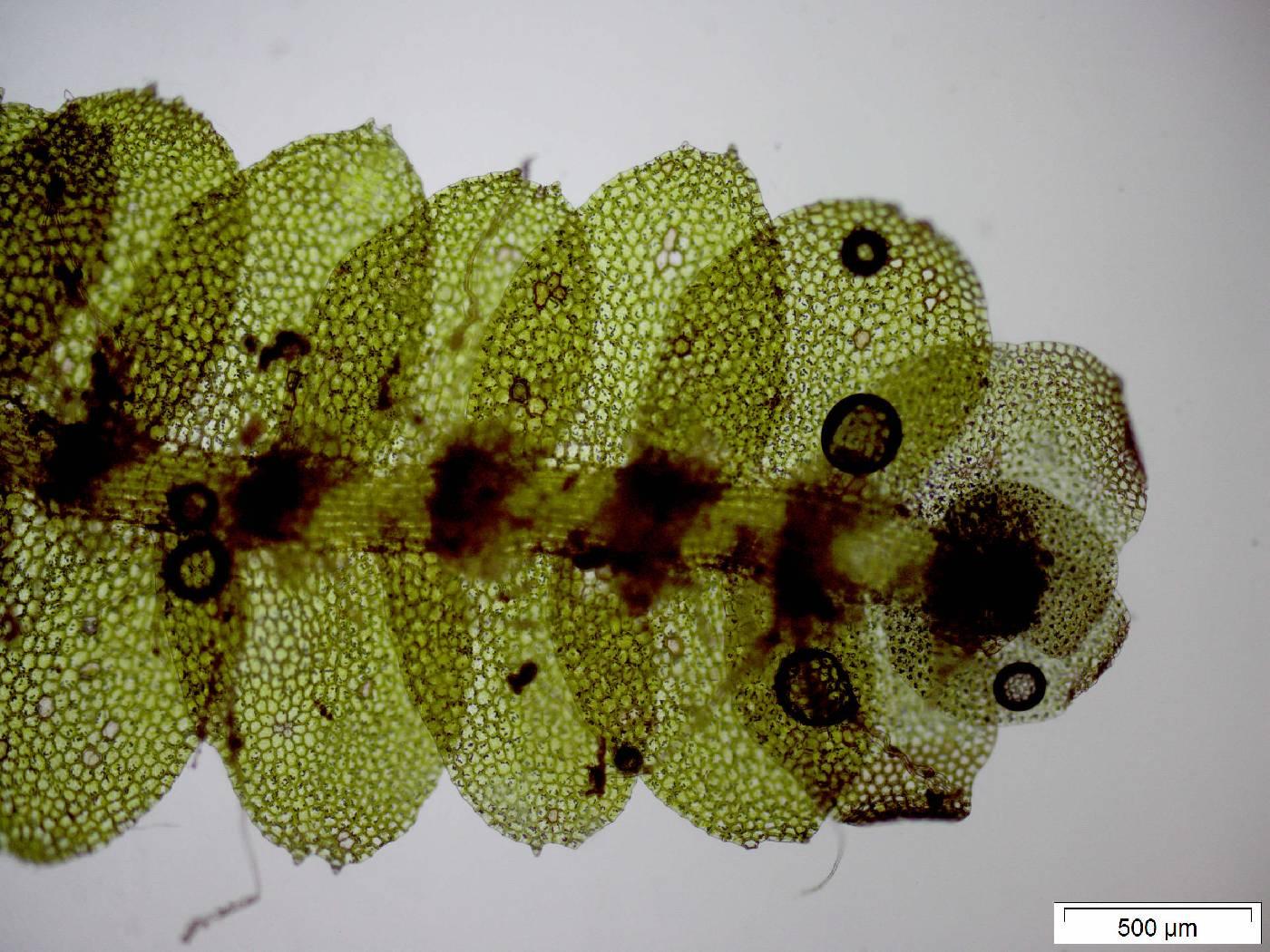 Calypogeia_20100320-9_plant_1527025975.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?tid=16896&clid=0&pid=0&taxauthid=1 |
Thallose liverwort |
Color
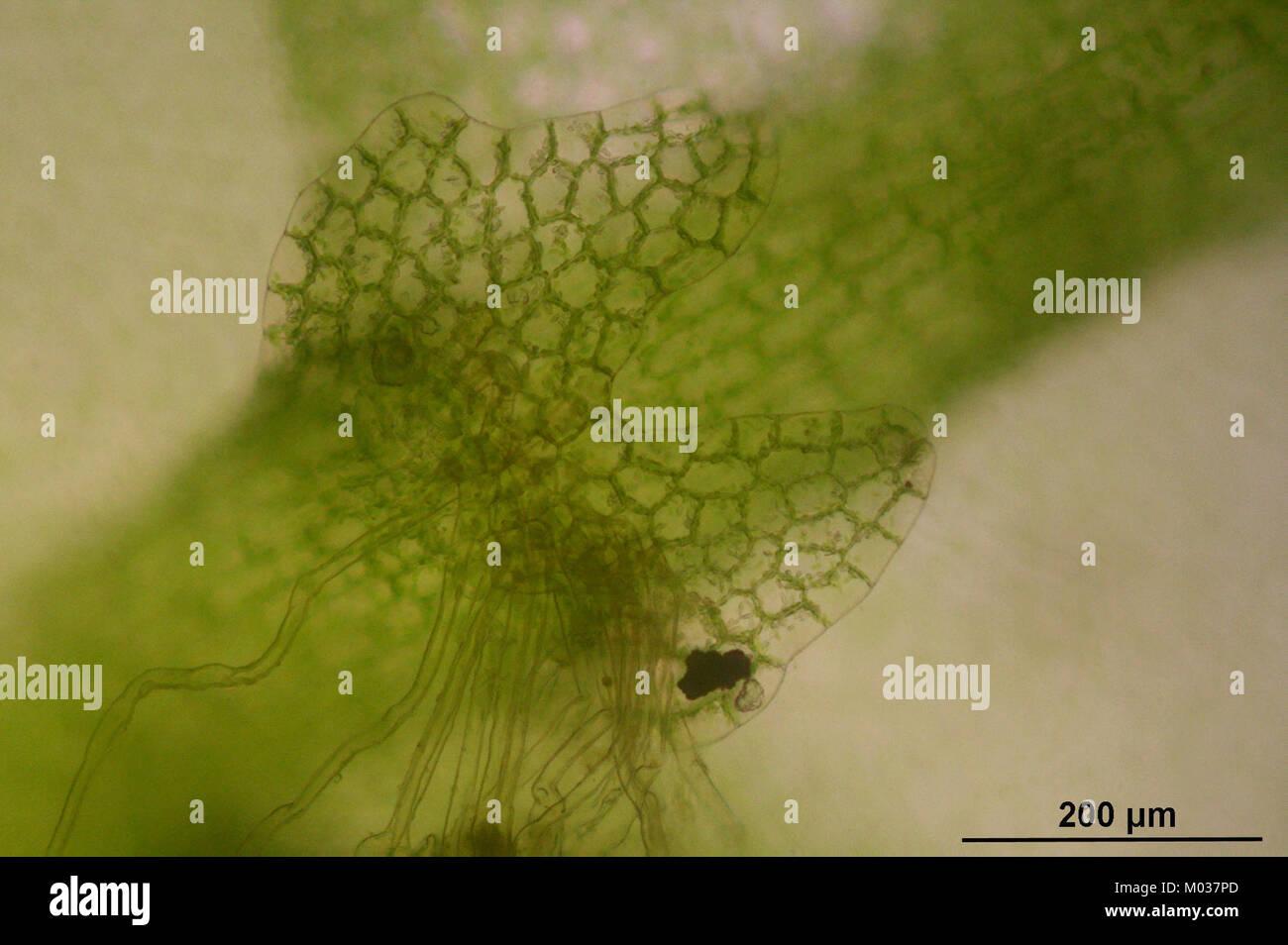 calypogeia-fissa-c-145141-481243-3969-M037PD.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/calypogeia.html |
Green to yellowish-green |
| Leaf Structure | Deeply divided, feathery |
Oil Bodies
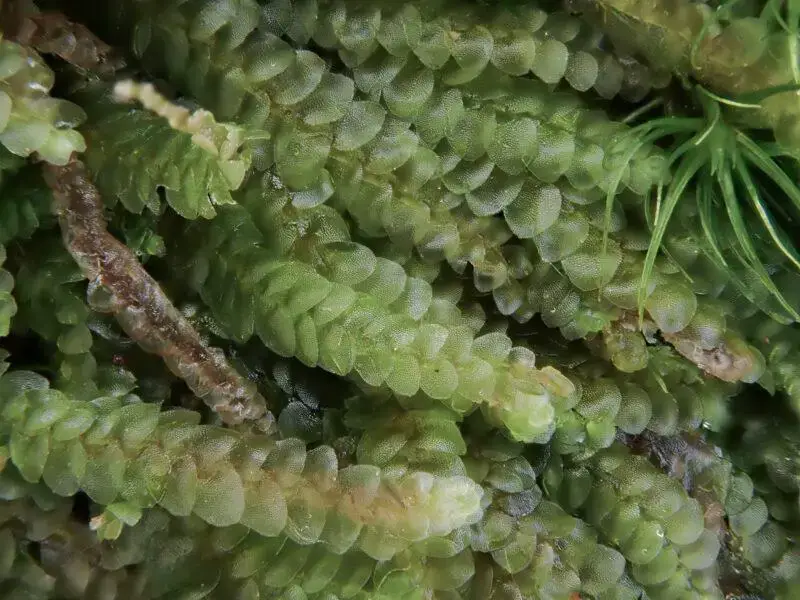 2021-02-27-15-55-47-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/calypogeia-azurea/ |
Present, spherical |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Substrate Preference | Acidic, nutrient-poor |
| Global Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, New Zealand |
Conclusion
The Calypogeia cellulosa (Spreng.) Steph. moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its delicate yet intricate morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has much to teach us about the intricate web of life that surrounds us. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, perhaps we can find inspiration in the resilience and adaptability of this remarkable moss.
Thought-provoking question: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, how can we ensure the preservation of these often overlooked yet crucial components of our ecosystems?