
8051031913_7ba0a69d3f_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/rockerboo/8051031913
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Calyptothecium australinum (Mitt.) Paris moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Pterobryaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is commonly referred to as Calyptothecium. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this intriguing plant.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Calyptothecium australinum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
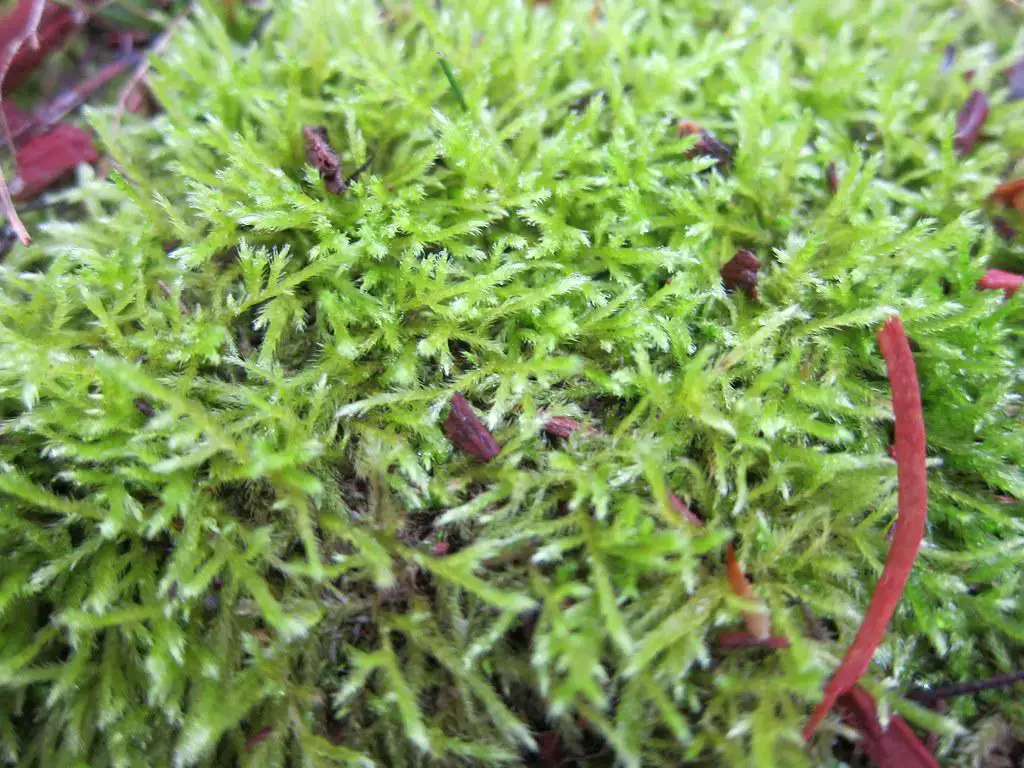
Calyptothecium australinum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, ovate-lanceolate leaves that are typically 1-2 mm long. These leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern, creating a feathery appearance. The moss’s distinctive feature is its calyptra, a cap-like structure that covers the developing sporophyte (spore-bearing structure).
Global Distribution and Habitat
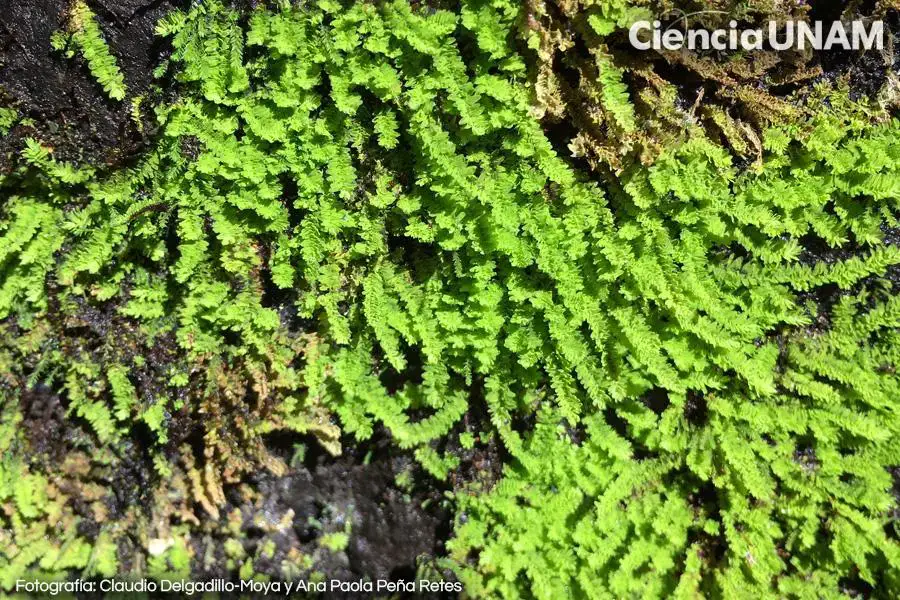
This moss species is widely distributed across various regions, including Australia, New Zealand, South America, and Southeast Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on tree trunks, rotting logs, and damp soil in forests and woodlands.

gl_musgos_03_30102017.jpg from: https://ciencia.unam.mx/contenido/galeria/161/galeria-diversidad-de-musgos-de-mexico-mas-alla-de-la-navidad
Calyptothecium australinum is well-adapted to these habitats, where it forms dense mats or cushions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
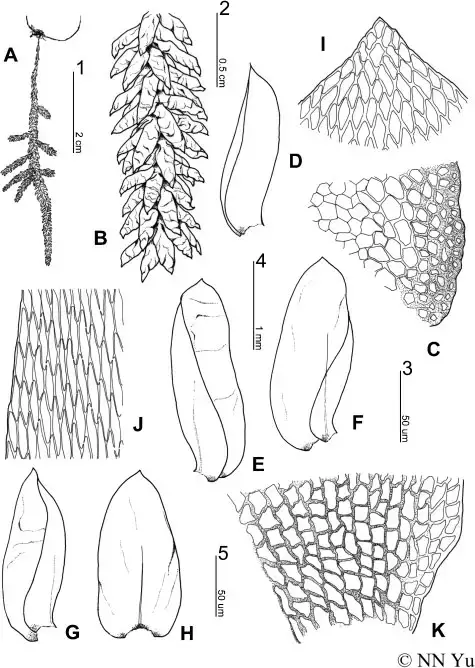
Pterobryopsis-australinum-Mitt-N-NYu-YJia-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-branch-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pterobryopsis-australinum-Mitt-N-NYu-YJia-A-Habit-B-Portion-of-branch-C_fig1_274865942
Despite its diminutive size, Calyptothecium australinum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers

02847c0a0d56c52a6a6ae2af8865cce6.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/520306563169466965/
, colonizing bare surfaces and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. They also contribute to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for various organisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Calyptothecium australinum

mosses-clumps-deep-green-tree-barks-like-rhythms-patterns-87799511.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/stock-photo-mosses-clumps-deep-green-tree-barks-like-rhythms-patterns-image87799511
is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate rainforest in New Zealand, researchers discovered that Calyptothecium australinum

0f4836145801cfa62535fa6aa82d7b7a.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/35051/articles
played a crucial role in the regeneration of tree seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microhabitat for seedling establishment, protecting them from desiccation and offering a stable substrate for root development.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Phylum
 cfa00dea49582263589fa4d9c248269f.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8962 |
Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Pterobryaceae |
Genus
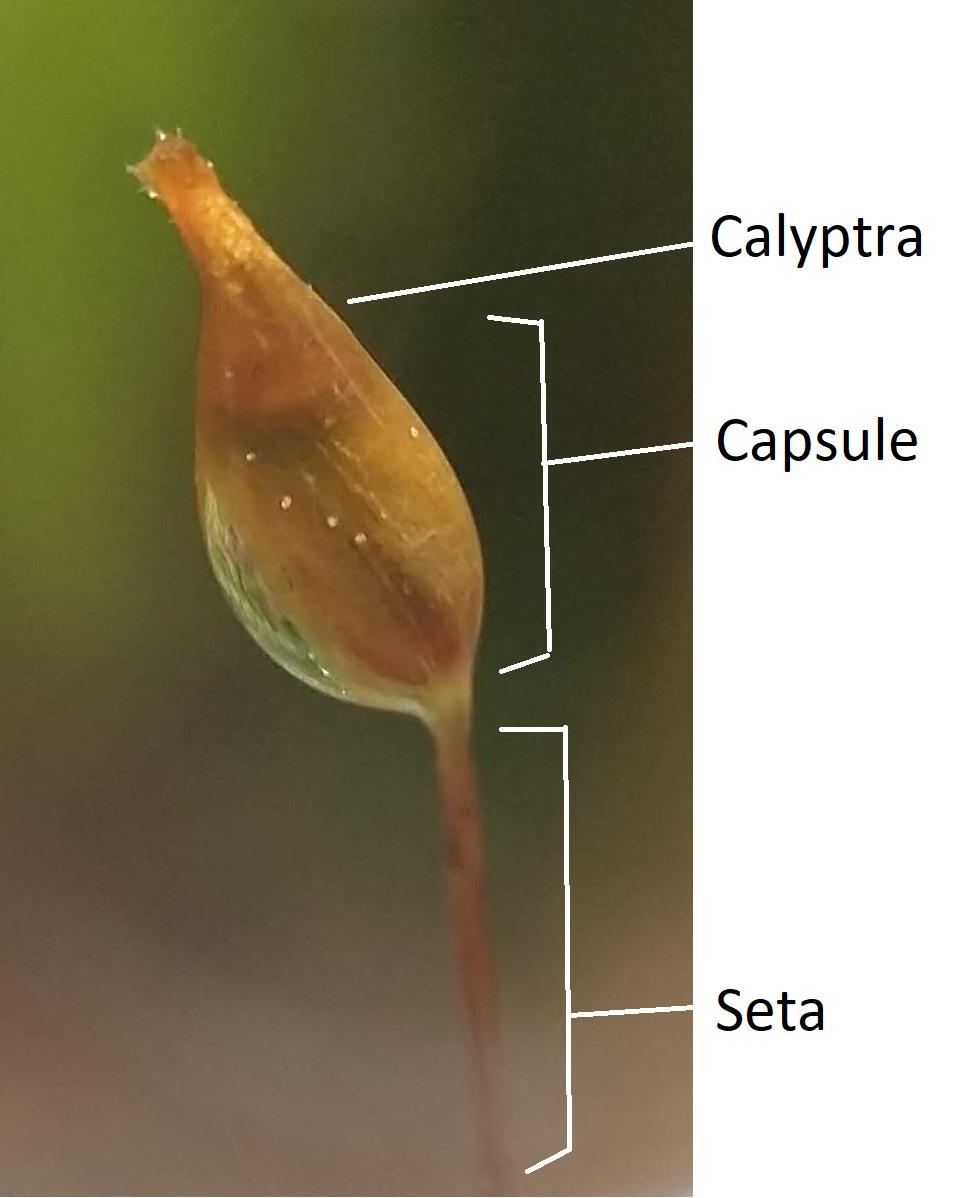 Moss_sporangium_calyptra.jpg from: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Botany/A_Photographic_Atlas_for_Botany_(Morrow)/05:_Bryophytes/5.03:_Mosses |
Calyptothecium |
| Species | Calyptothecium australinum (Mitt.) Paris |
Conclusion
The Calyptothecium australinum (Mitt.) Paris moss, a member of the Pterobryaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s diversity and resilience. Despite its unassuming appearance, this species plays crucial roles in various ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, moisture retention, and facilitating the growth of other plants. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate web of life, let us ponder: What other hidden wonders await discovery in the world of bryophytes?