497083_b5dff9f6.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/497083.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Chaetomitrium spinosum E.B.Bartram. Belonging to the Symphyodontaceae family, this moss is commonly referred to as Chaetomitrium. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Chaetomitrium spinosum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but their importance cannot be overstated.

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sxEeti2dw10
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Chaetomitrium spinosum is a striking moss species characterized by its spinose (spiny) leaves and distinctive growth patterns. Its gametophyte (the haploid phase) consists of slender, branched stems adorned with spirally arranged leaves. These leaves are

merah2.JPG from: https://pak.pandani.web.id/2018/05/ganggang-yang-dapat-dimanfaatkan.html
lanceolate (lance-shaped) and acuminate (tapering to a slender point), with a spinose (spiny) appearance due to the presence of

7.CalPhotos_0000_0000_0708_2095.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/635271
papillae (small protuberances) on their surfaces.
Global Distribution and Habitat
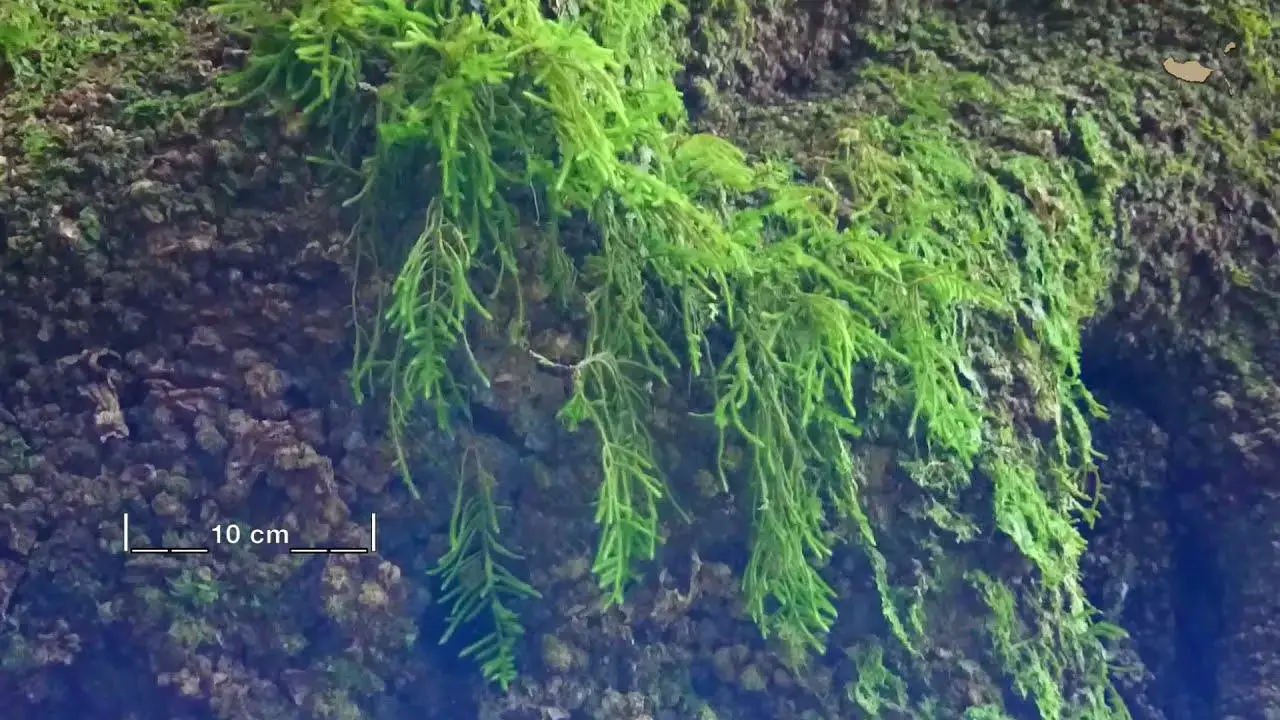
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded rock surfaces to decaying logs and tree bark. Chaetomitrium spinosum is particularly well-adapted to humid and temperate environments, where it can form dense mats or cushions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Chaetomitrium spinosum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation, water retention, and nutrient cycling. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Chaetomitrium spinosum is its ability to tolerate desiccation (drying out) and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available. This trait allows the moss to survive in environments with fluctuating water availability.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Chaetomitrium spinosum played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat contributed to the successful regeneration of the ecosystem.
Technical Table
Conclusion
Chaetomitrium spinosum E.B.Bartram, a remarkable moss species, exemplifies the intricate beauty and ecological significance of bryophytes. From its unique morphology to its vital roles in various ecosystems, this moss deserves our appreciation and continued study. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the incredible diversity and resilience of these often-overlooked organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush, verdant carpet of moss, you’ll pause and ponder the wonders of Chaetomitrium spinosum.