i0007-2745-107-3-377-f01.gif from: https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-107/issue-3/0007-2745(2004)107[0377:CCBGAN]2.0.CO;2/Codriophorus-corrugatus-Bryopsida-Grimmiaceae-A-New-Species-from-East-Asia/10.1639/0007-2745(2004)107[0377:CCBGAN]2.0.CO;2.full
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Codriophorus corrugatus Bedn.-Ochyra. Belonging to the Grimmiaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable moss is commonly referred to as Codriophorus. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Codriophorus corrugatus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.

0279635_5.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/frullania/taxa/index.php?taxon=160615
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
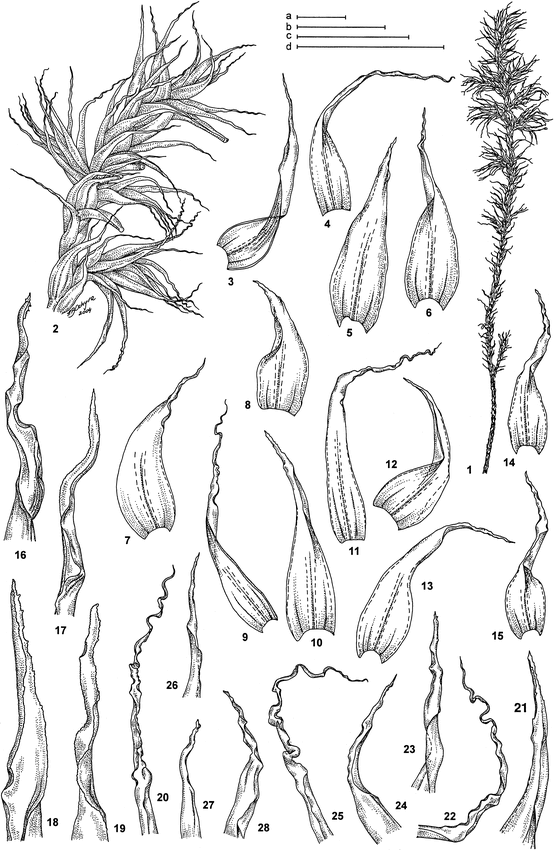
Codriophorus corrugatus is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive corrugated or wrinkled appearance, hence the specific epithet “corrugatus.” The leaf margins are often recurved, and the costa (midrib) is prominent, extending to the leaf apex or slightly beyond. The sporophytes (reproductive structures) are relatively short, with a
b219ebc4b74543a982261fa30b409d82b9014a90be1f-bkimg-process,v_1,rw_1,rh_1,pad_1,color_ffffff from: https://baike.baidu.com/item/短无尖藓/62722974
reddish-brown seta (stalk) and a cylindrical capsule.
Global Distribution and Habitat

379935.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434090
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from rock outcrops and boulders to tree bark and soil. Codriophorus corrugatus is often found in

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/487592-Codriophorus-acicularis
dry, exposed

894583.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/894577.html
, and

DSCN9431.JPG from: https://enkistroy.ru/raznoe/nazvanie-mxi-kakie-byvayut-nazvanie-mxov-yandeks-kyu.html
nutrient-poor environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability to harsh conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Codriophorus corrugatus plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a pioneer species, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant communities.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Codriophorus corrugatus is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is limited or unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers found that Codriophorus corrugatus played a crucial role in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion on steep slopes. Its dense mats helped retain moisture and provided a suitable environment for other plant species to establish themselves, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Genus | Codriophorus |
| Species | corrugatus Bedn.-Ochyra |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, corrugated |
| Leaf Margin | Often recurved |
| Costa | Prominent, extending to leaf apex or slightly beyond |
| Sporophyte | Reddish-brown seta, cylindrical capsule |
Conclusion
The Codriophorus corrugatus Bedn.-Ochyra moss, a member of the Grimmiaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?