Unveiling the Secrets of Dolichomitra cymbifolia: A Captivating Moss with Ecological Significance
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!

Dolichomitra-cymbifolia04L.jpg from: https://digital-museum.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~museum/habit/moss_habit/Dolichomitra cymbifolia/Dolichomitra_cymbifolia.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Dolichomitra cymbifolia (Lindb.) Broth. moss. Belonging to the Lembophyllaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating
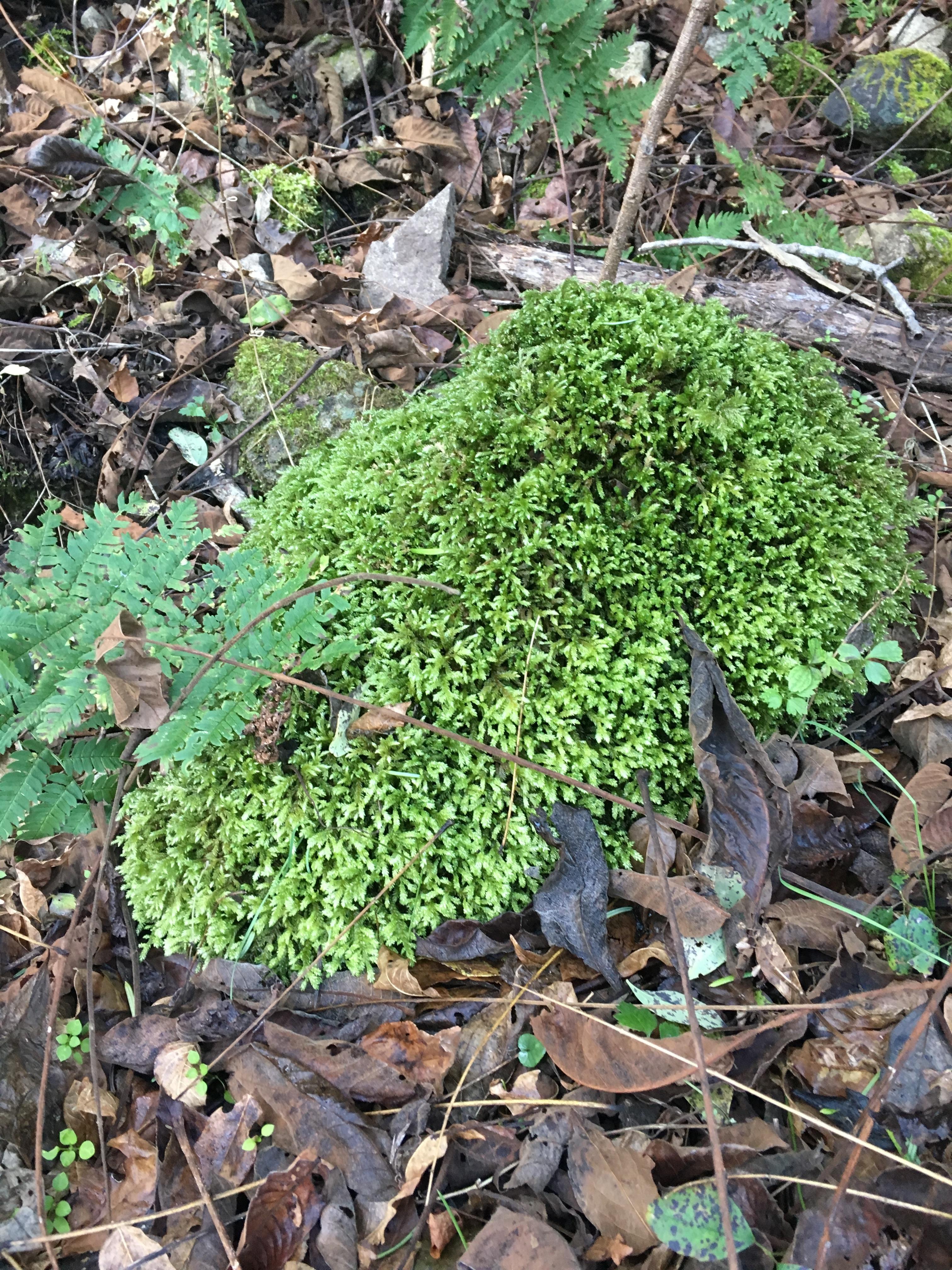

b9c5cb4a54c812d075c95111f06ea0d5_0eb4733ecd9d65c675ffeb5a7803f9bb.jpg from: https://kokeakari.amebaownd.com/posts/2084498
Bryopsida member.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Dolichomitra cymbifolia, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but their importance cannot be overstated. Bryophytes are among the oldest land plants, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Dolichomitra cymbifolia is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are typically unbranched, and the leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern. The leaves themselves are cymbiform (boat-shaped) and have a distinctive, curved appearance. This unique leaf shape is a key identifying feature of the species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
8c1001e93901213fb80e8a9c27b721d12f2eb9383f68-bkimg-process,v_1,rw_1,rh_1,pad_1,color_ffffff from: https://baike.baidu.com/item/船叶藓
Dolichomitra cymbifolia is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist, shaded rock crevices, cliffs, and even on tree bark or rotting logs. This moss prefers cool, humid environments and is often found in mountainous regions or near streams and waterfalls.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Dolichomitra cymbifolia plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It acts as a pioneer species, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, this moss contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other organisms to thrive.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dolichomitra cymbifolia is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. Once moisture becomes available, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to survive in challenging environments.
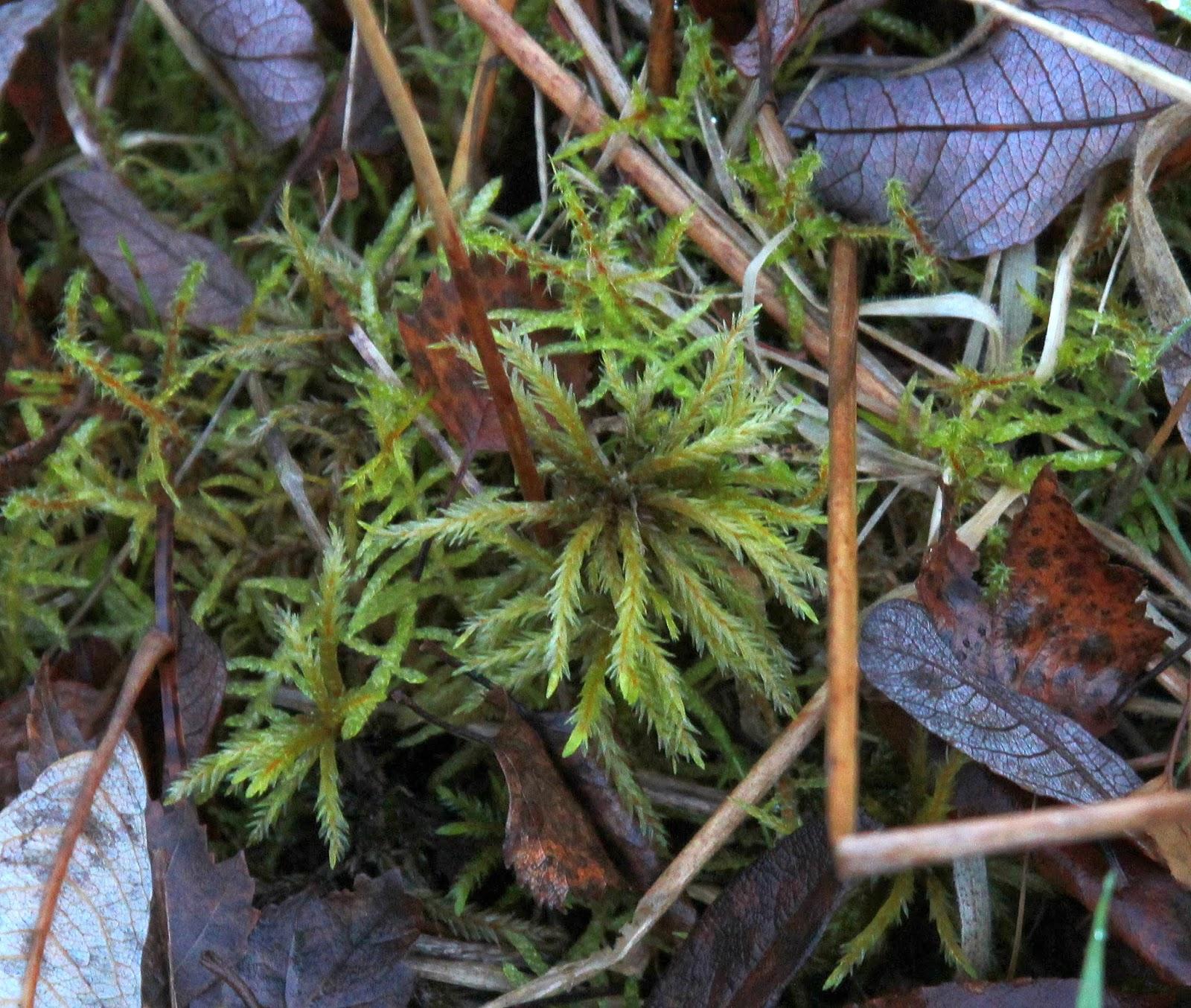

IMG_1253.JPG from: https://bryobits.blogspot.com/2014/01/a-collection-of-bryo-pics-from-cullaloe.html
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Dolichomitra cymbifolia played a crucial role in the recovery of forest ecosystems after disturbances such as wildfires or logging. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize disturbed areas and create a suitable microhabitat facilitated the establishment of other plant species, contributing to the overall restoration of the ecosystem.
Technical Table

9ba13f0e2f7c85270bd4a461f07e9870.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/066f8adbf1dc27f5f7041c6008ed3bb8

209957.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/listeEspeces/Rhynchium
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
 fig6.png from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/biodiversity-in-ecosystems-linking-structure-and-function/the-importance-of-large-trees-in-shrine-forests-for-the-conservation-of-epiphytic-bryophytes-in-urba |
| Family | Lembophyllaceae |
| Genus | Dolichomitra |
| Species | cymbifolia
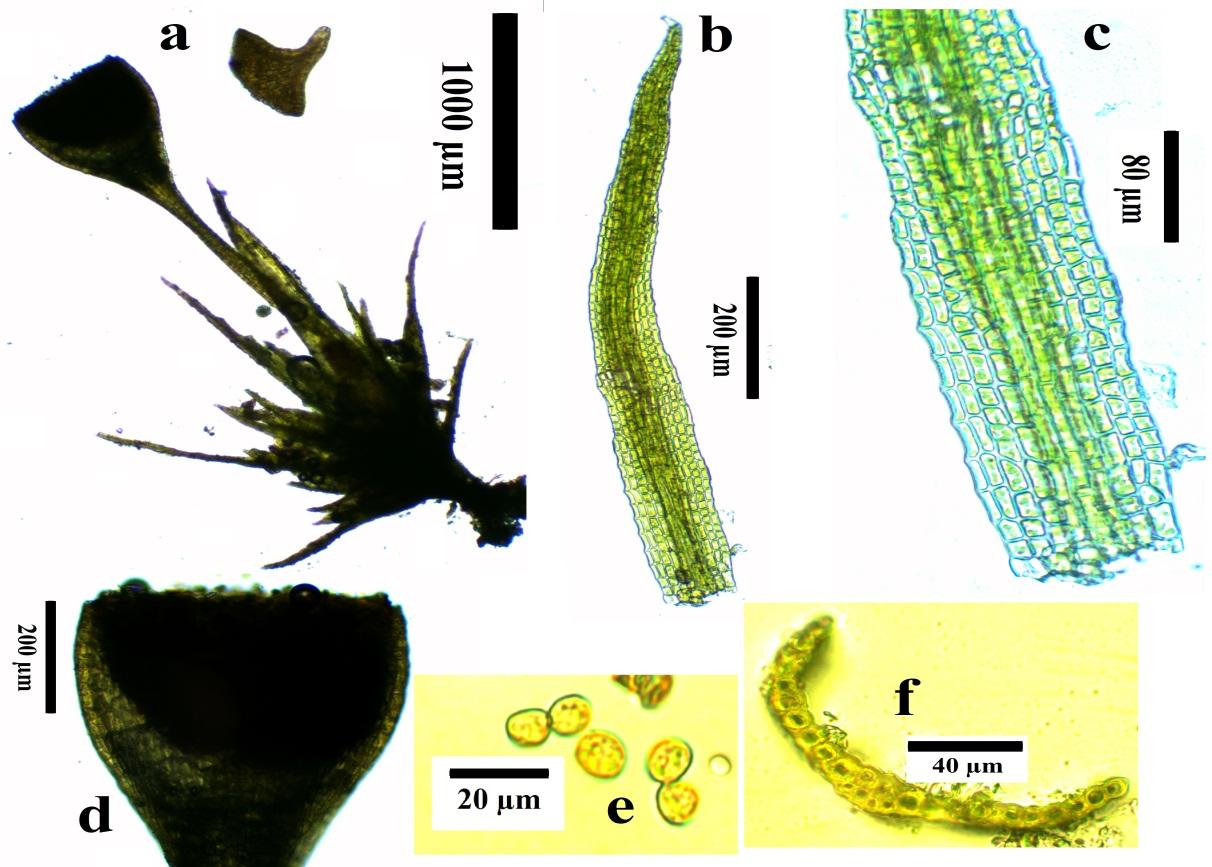 image6.jpeg from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/current-progress-in-biological-research/contribution-to-the-moss-flora-of-kizilda-isparta-national-park-in-turkey |
| Common Name | Dolichomitra moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Cymbiform (boat-shaped), curved |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded rock crevices, cliffs, tree bark, rotting logs |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, parts of South America |
Conclusion
The Dolichomitra cymbifolia (Lindb.) Broth. moss, with its unique morphology and ecological significance, is a true gem in the world of bryophytes. From its ability to withstand desiccation to its role as a pioneer species, this unassuming plant continues to captivate moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we delve deeper into the intricate web of life, the importance of seemingly small organisms like

cd1e546462a33769ba40d5df80199b49–freshwater-plants-aquarium.jpg from: https://sites.google.com/site/prolainstyle/akvariumnye-rastenia/mohripariaklimaciumaponskijclimaciumjaponicum
Dolichomitra cymbifolia becomes increasingly apparent. Perhaps the next time you encounter a moss-covered rock or log, you’ll pause to appreciate the resilience and beauty of these ancient and remarkable plants.
