
lepidozia-163.jpg from: https://www.cpbr.gov.au/bryophyte/photos-captions/lepidozia-163.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the

Rock-Fingerwort-Lepidozia-cupressina-from-Shaftoe-Crags-2048×1536.jpg from: https://www.nhsn.org.uk/the-hidden-world-of-bryophytes-in-the-north-east/
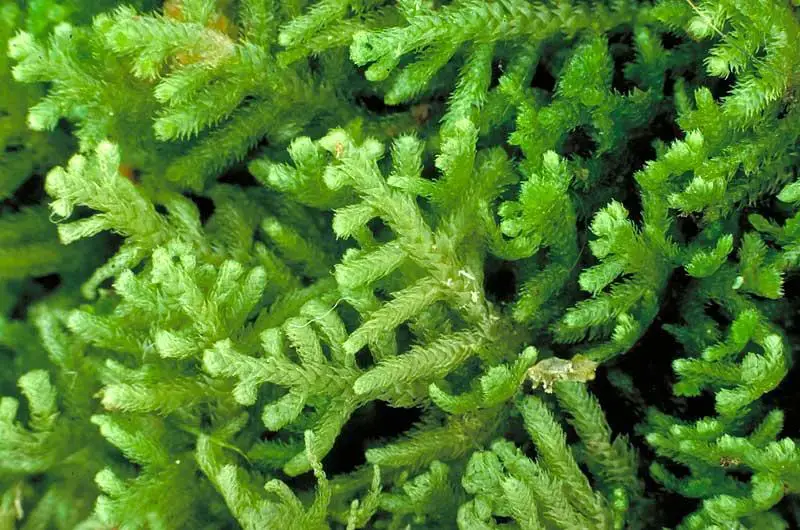
Lepidozia bidens J.J.Engel moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lepidoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lepidozia, this unassuming yet intriguing moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
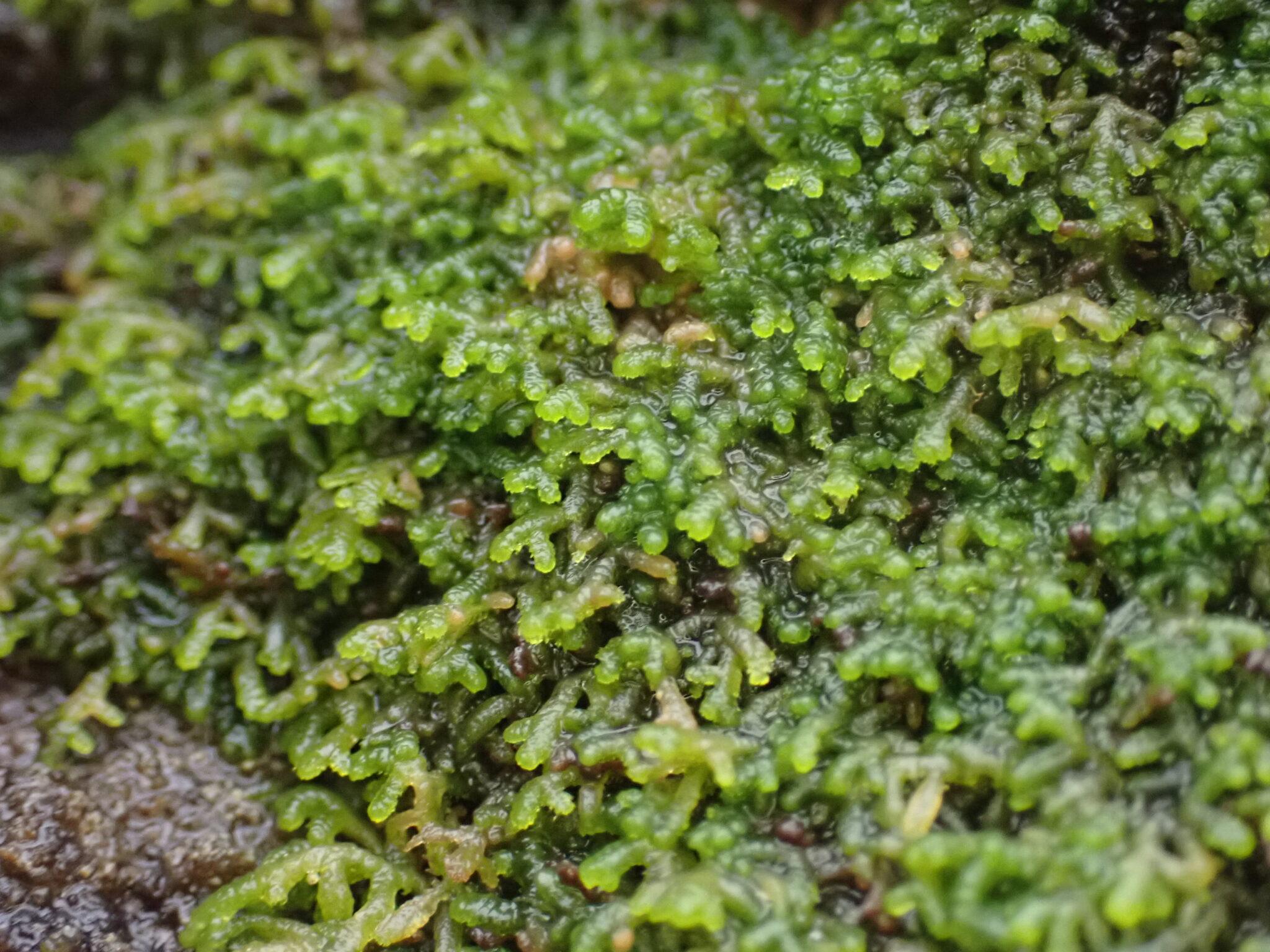
Before we explore the wonders of Lepidozia bidens, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the Marchantiophyta division and the
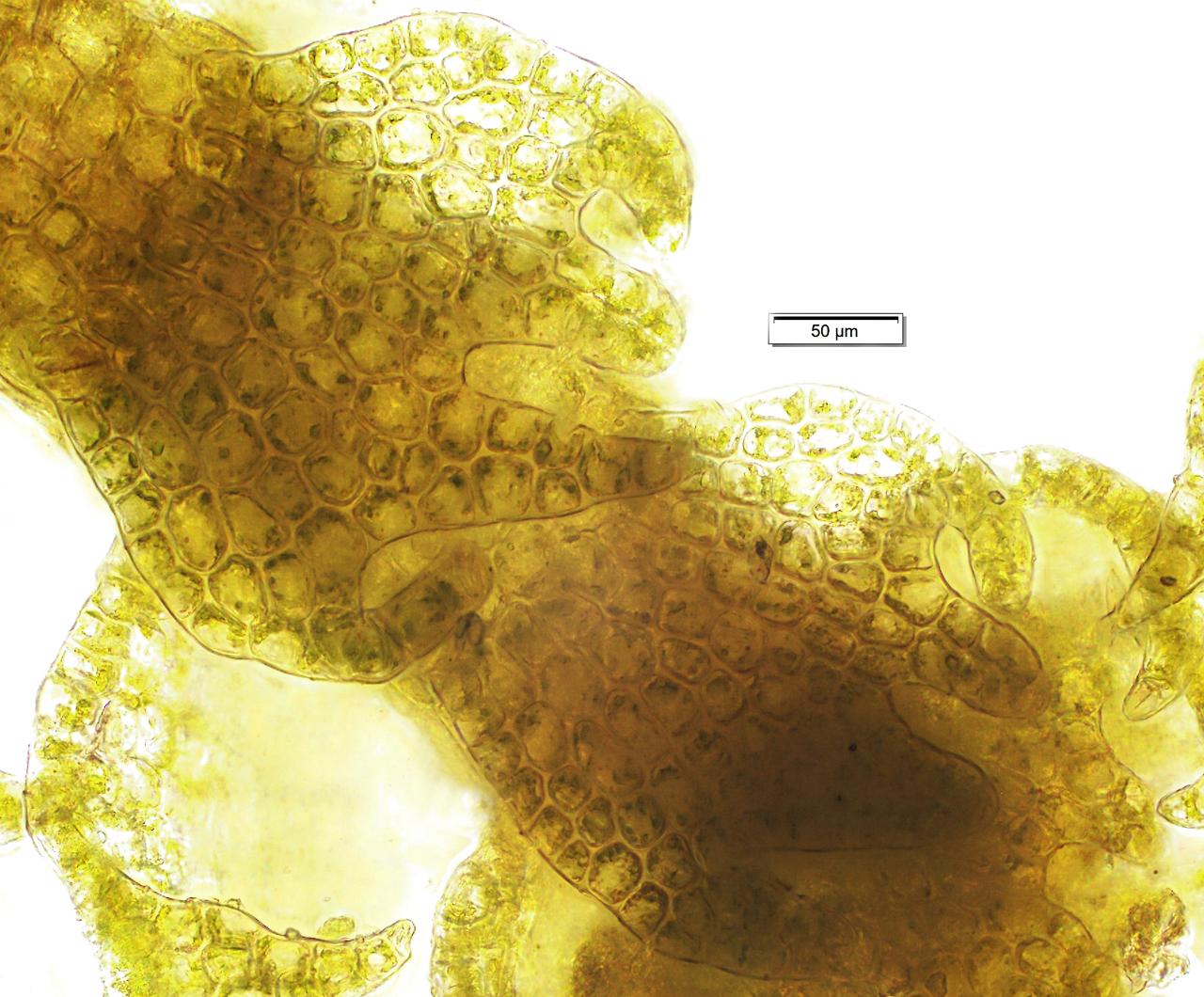
lepidozia_reptans.jpg from: https://www.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/lepidozia_reptans.html
Jungermanniopsida class, liverworts like Lepidozia are fascinating organisms that have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lepidozia bidens is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate, feathery appearance belies its resilience and ability to withstand harsh conditions. One of the defining characteristics of this moss is its bidens (meaning “two-toothed”) leaves, which are deeply divided into two lobes, giving it a distinctive appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
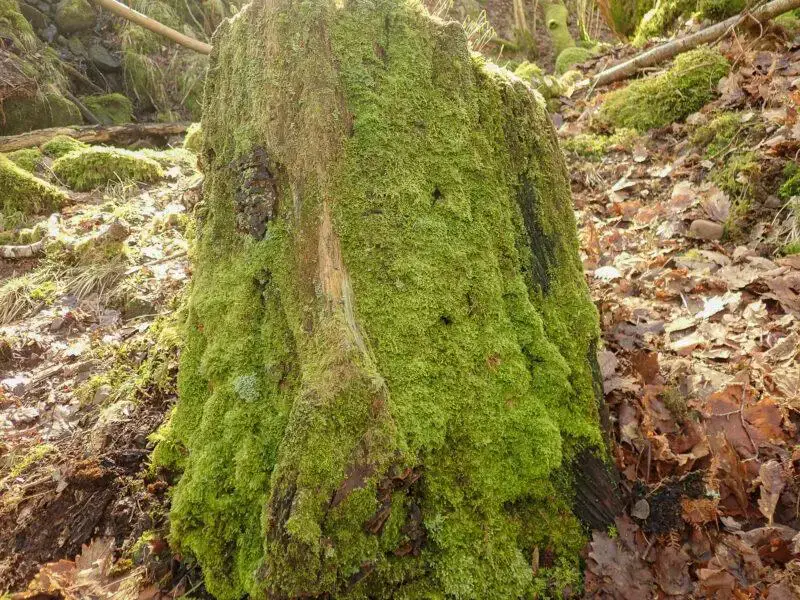
While Lepidozia bidens can be found in various regions around the world, it is particularly prevalent in temperate and tropical areas. This moss thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on decaying logs, tree bark, or rocky surfaces. Its ability to colonize these habitats is a testament to its adaptability and resilience.

2021-02-27-13-25-53-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/lepidozia-reptans/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lepidozia bidens plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to the overall biodiversity of the area and serves as a microhabitat for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi. Additionally, this moss possesses remarkable adaptations that allow it to survive in challenging conditions, such as desiccation tolerance and the ability to rapidly rehydrate after periods of drought.

lepidozia-fugax-01.240×240-u1i1s1q90f1.jpg from: https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/lepidozia-fugax/
Case Studies/Examples
One fascinating example of Lepidozia bidens‘s ecological significance can be found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Here, this moss plays a crucial role in the intricate web of life within old-growth forests, providing shelter and sustenance for a myriad of organisms, from tiny invertebrates to larger mammals.

81bXJEygXqL._SL1500_.jpg from: https://www.amazon.com/Very-Best-J-Moss/dp/B00GYVPGVW
Technical Table

1200x1200bf-60.jpg from: https://music.apple.com/us/album/the-j-moss-project/309679087
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lepidozia bidens J.J.Engel |
| Family | Lepidoziaceae |
Division
 74141_orig.jpg from: https://idfg.idaho.gov/species/taxa/4837 |
Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Leaf Structure | Deeply divided into two lobes (bidens) |
Habitat
 81iIQSzeEWL.jpg from: https://www.amazon.de/J.-Moss/e/B00197GMBO |
Moist, shaded environments (decaying logs, tree bark, rocky surfaces) |
| Distribution | Temperate and tropical regions worldwide |
Conclusion

csm_JuttaEngel_01_4544d16c61.jpeg from: https://www.uniklinikum-saarland.de/de/einrichtungen/fachrichtungen/biophysik/biophysik2/
The Lepidozia bidens J.J.Engel moss, a member of the Lepidoziaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s intricate design and resilience. From its distinctive morphology to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other secrets might this tiny moss hold, waiting to be uncovered by curious minds?