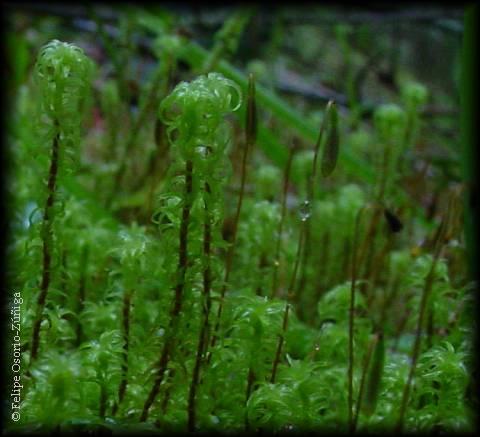

leptodontium_sp02.jpg from: https://www.chilebosque.cl/moss/leptodontium_sp.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Leptodontium, this unassuming yet fascinating moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

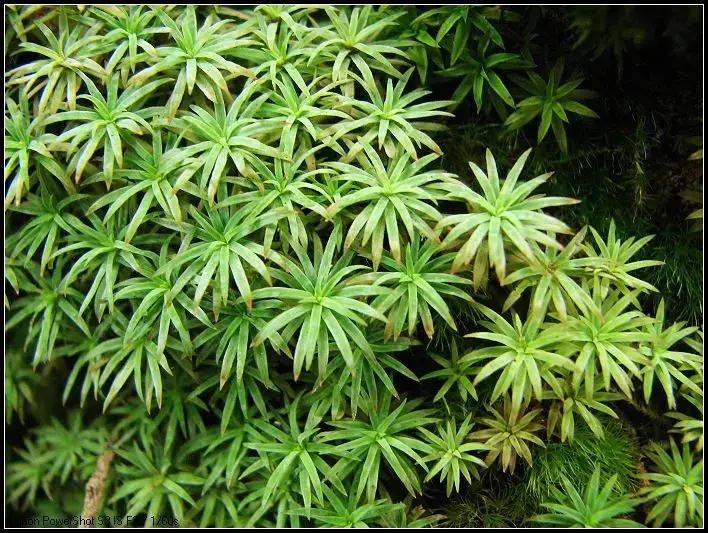
medium.jpg from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/136928-leptodontium
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive recurved or revolute leaf margin. The leaf cells are

t010e787b7efcd5e97e.png from: https://baike.so.com/gallery/list?ghid=first&pic_idx=1&eid=5596454&sid=5809055
elongated and smooth, contributing to the moss’s delicate appearance. When mature, Leptodontium produces capsules on short setae, which aid in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species is widely distributed across various regions, including South America, Central America, North America, Europe

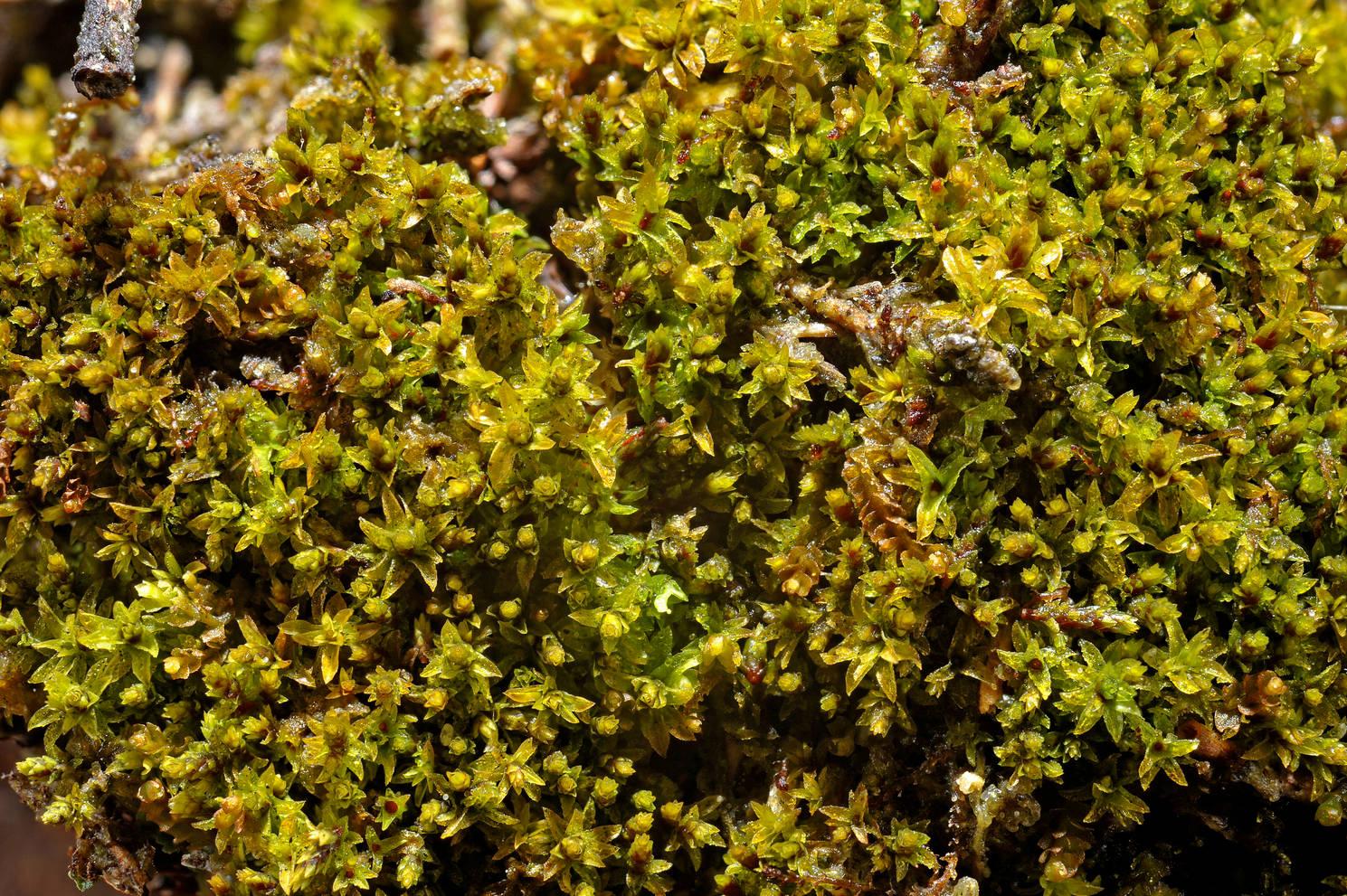
_49547925_thatchmoss(leptodontiumgemmascens)growingonoldthatchontheshopatselworthy,ontheholnicoteestate,somerset2cntpl-rosshoddinott.jpg from: https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-11565593
, Asia, and Australasia. It thrives in a range of habitats, from exposed rock surfaces and soil banks to tree bark and decaying wood. Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor environments, making it a resilient pioneer species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Leptodontium plays vital roles in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This trait allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Andes Mountains of South America

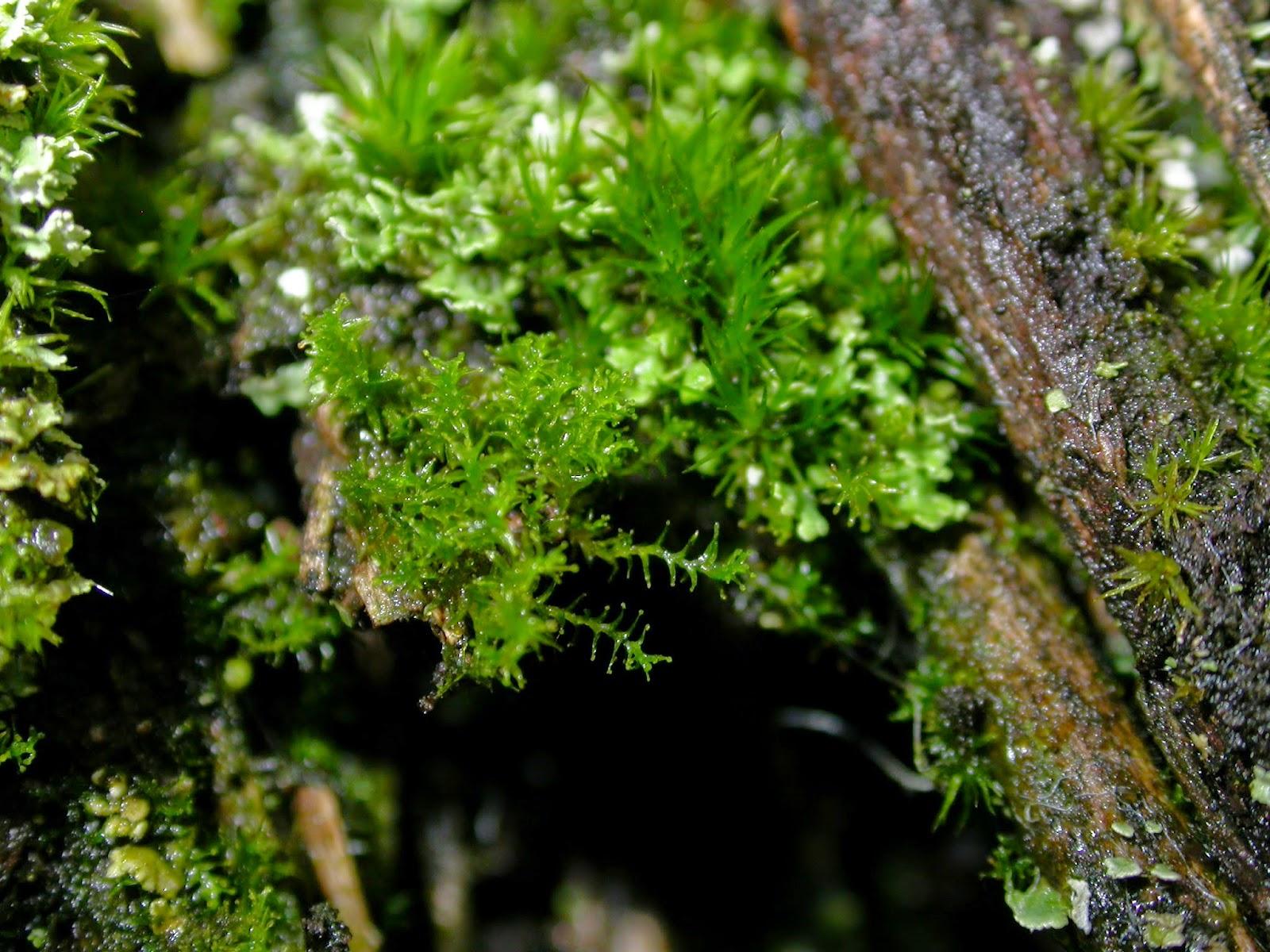
leptodontium_flexifolium.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Pottiaceae/leptodontium-flexifolium/en/
, researchers found Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén to be a dominant species in high-altitude rock outcrops. Its ability to colonize these harsh environments highlights its resilience and adaptability.

Leptodontium_gemmascens%2C_Cosmeston_(2).JPG from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2014/11/thatch-moss-and-first-for-glamorgan.html
Another notable example comes from New Zealand, where Leptodontium is a common sight on the bark of native trees in temperate rainforests. Its presence contributes to the overall biodiversity and ecological balance of these unique ecosystems.
Technical Table
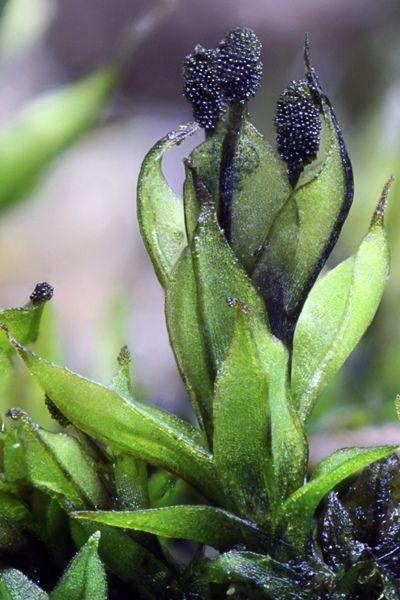

29fc5a3bf7eec09b7a1a2d3b31d65408.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/494692340290372782/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Phylum
 leptodontium_longicaule01.jpg from: https://www.musgosdechile.cl/leptodontium.html |
Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
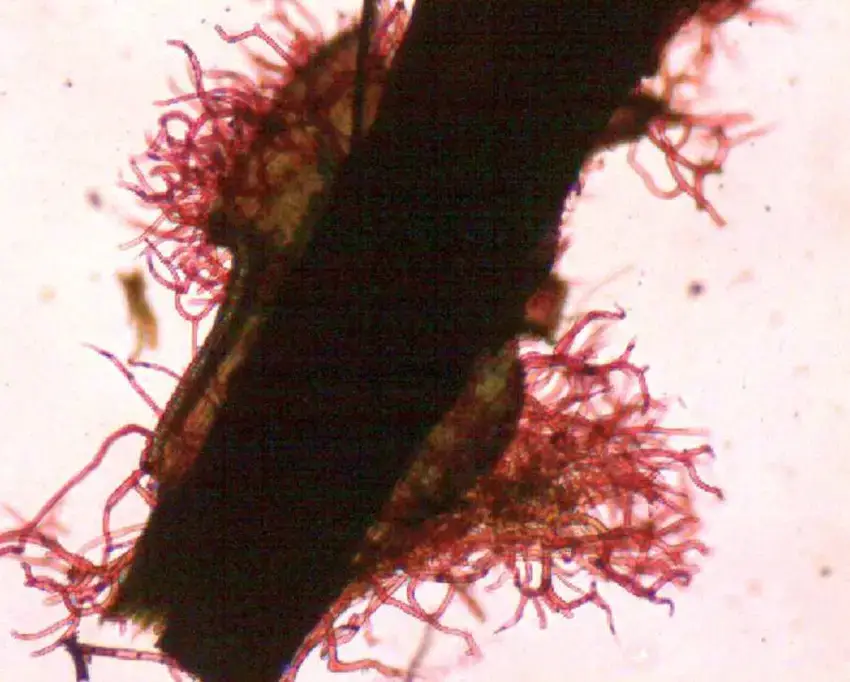 Tomentum-of-Leptodontium-tricolor-The-pink-stain-implies-the-present-of-pectic-mucilage.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Tomentum-of-Leptodontium-tricolor-The-pink-stain-implies-the-present-of-pectic-mucilage_fig8_289991659 |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Leptodontium |
| Species | microruncinatum Dusén |
Growth Form
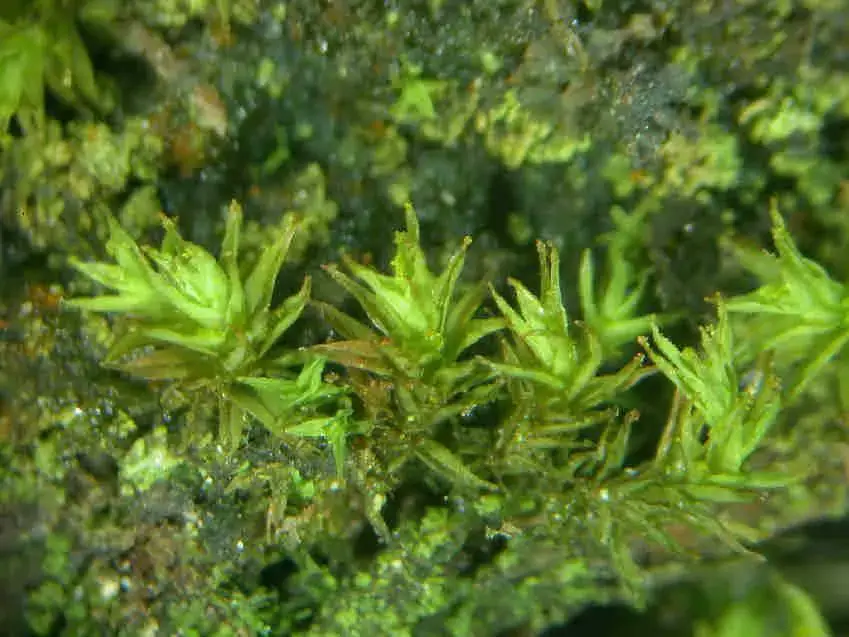 Leptodontium_gemmascens_005C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Leptodontium_gemmascens.html |
Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Recurved or revolute |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, smooth |
| Capsules | Present, on short setae |
Conclusion
The Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén moss, a member of the Pottiaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments, from exposed rock surfaces to tree bark, showcases its versatility. Despite its small stature, this moss plays crucial roles in ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, water retention, and providing microhabitats for other organisms.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, the Leptodontium microruncinatum Dusén serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and complexity found in even the smallest of life forms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of moss, you’ll pause and wonder about the fascinating stories it has to tell.