2256b89bd9397bb240fb77d5873773c3982db012 from: https://identify.plantnet.org/the-plant-list/species/Primula capitata Hook./data
Introduction
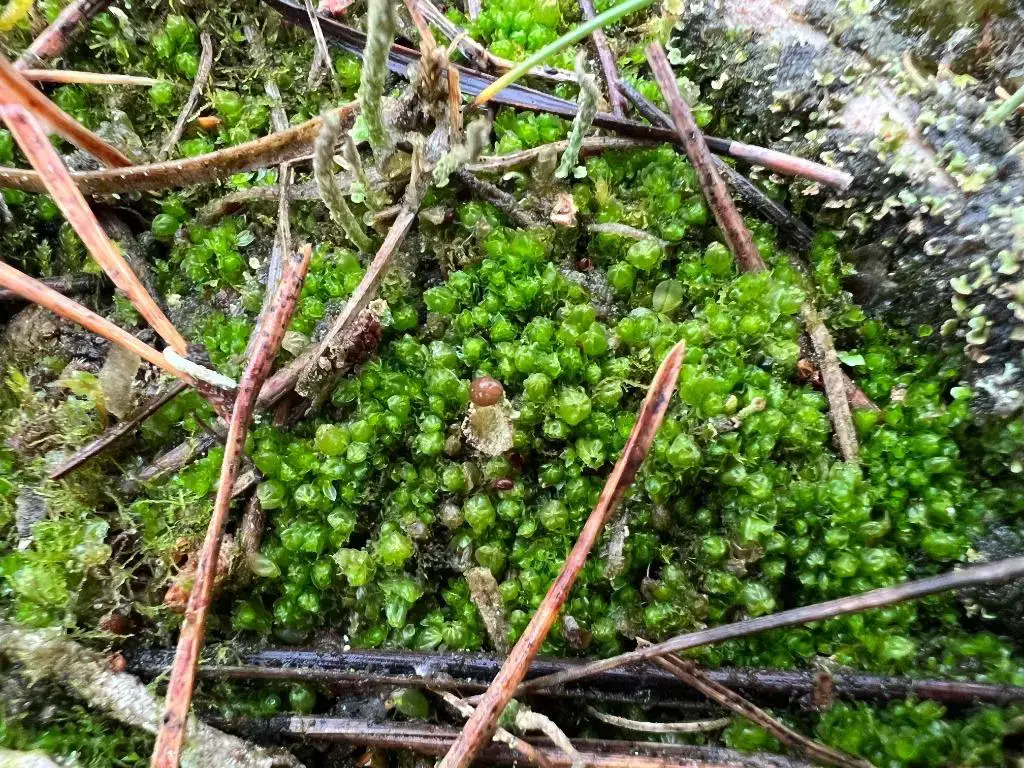
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia capitata (Hook.) Macoun moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Lophoziaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this

obsfoto_2e0d0693-ab1b-4076-9e8f-0f8aed044e3f.jpg from: https://www.naturbasen.dk/art/16943/roed-foldbaeger
Marchantiophyta species, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Lophozia capitata, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Mosses, along with liverworts and hornworts, belong to the Bryophyte phylum, a group of non-vascular plants that play a crucial role in various ecosystems. These diminutive yet resilient organisms have adapted to survive in some of the harshest environments on Earth, making them true champions of the plant kingdom.

trees-covered-with-spanish-moss-and-tillandsia-capitata-plants-in-the-cloud-forest-along-the-trail-to-the-hill-of-the-jaguar-an-important-zapotec-rel-2K7RXT1.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/trees-covered-with-spanish-moss-and-tillandsia-capitata-plants-in-the-cloud-forest-along-the-trail-to-the-hill-of-the-jaguar-an-important-zapotec-rel-image486718849.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lophozia capitata is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green mats or tufts. Its stems are creeping and irregularly branched, with leaves that are deeply bilobed and arranged in two rows along the stem. The leaves are often concave and have a distinctive shape, with the lobes being unequal in size and shape. This unique leaf morphology is one of the key identifying features of
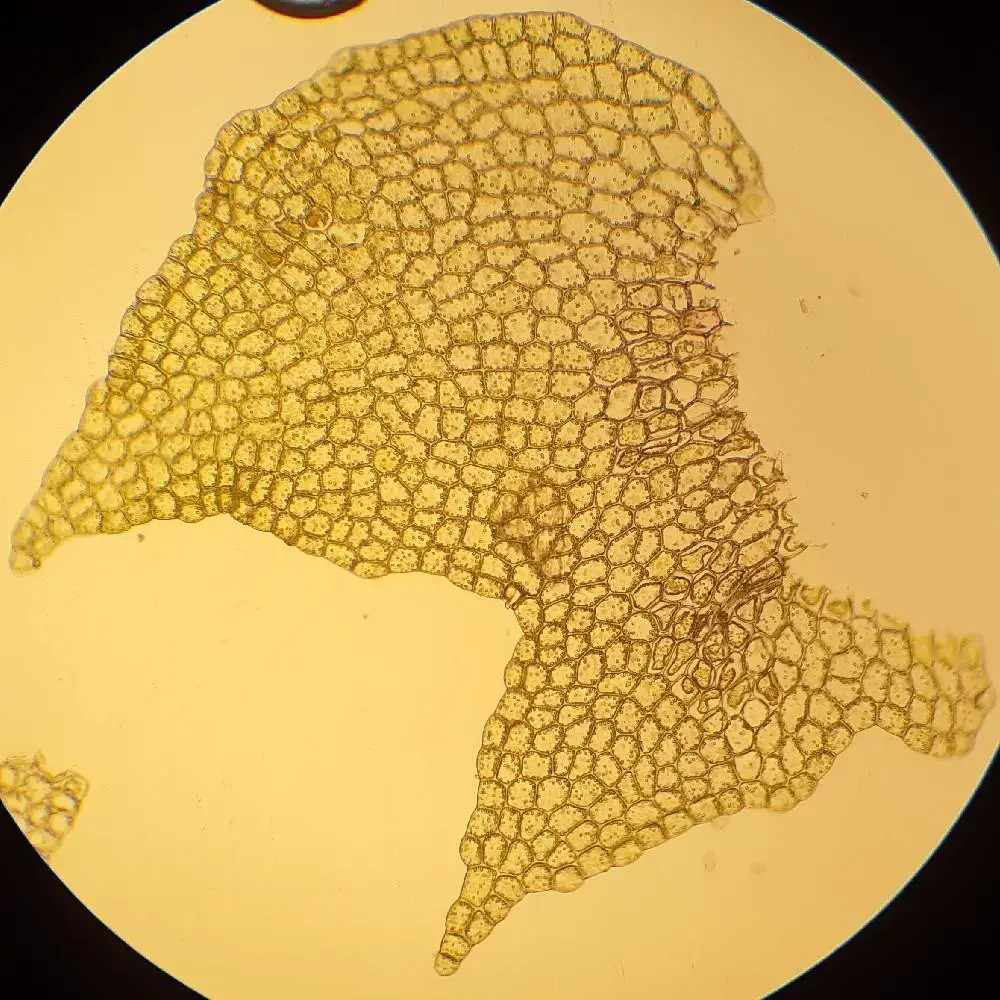
42673142.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/225300543?_popup=1

trees-covered-with-spanish-moss-and-tillandsia-capitata-plants-in-the-cloud-forest-along-the-trail-to-the-hill-of-the-jaguar-an-important-zapotec-rel-2K7RXRY.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/trees-covered-with-spanish-moss-and-tillandsia-capitata-plants-in-the-cloud-forest-along-the-trail-to-the-hill-of-the-jaguar-an-important-zapotec-rel-image486718847.html
Lophozia capitata.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests and woodlands to rocky outcrops and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and gravel pits.

250.jpg from: https://biodiversity.bt/observation/show/2127
Lophozia capitata is known for its ability to colonize and thrive in acidic environments, making it a valuable indicator species for assessing environmental conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,
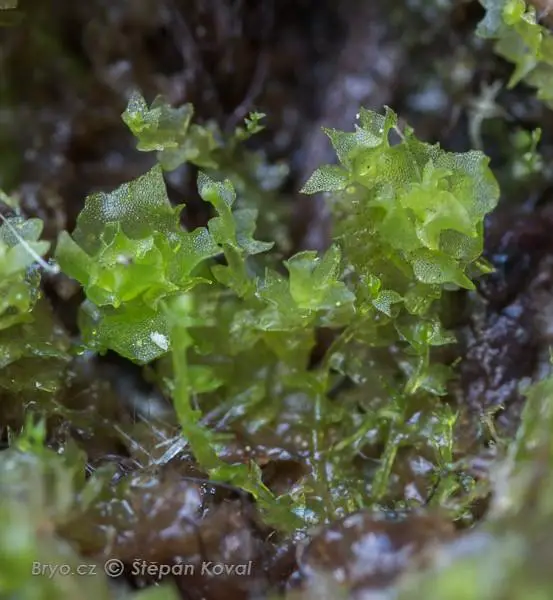

2980_Heterogemma_capitata_2016_05_10_9949.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=heterogemma_capitata&id=2980
Lophozia capitata plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, these mosses act as efficient water reservoirs, helping to regulate moisture levels and prevent soil erosion.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia capitata is its ability to survive desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once favorable conditions return. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
Lophozia capitata has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological significance and potential applications. For instance, researchers have investigated the moss’s ability to accumulate heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution. Additionally, its role in facilitating the establishment of other plant species in disturbed areas has been explored, highlighting its importance in ecosystem restoration efforts.
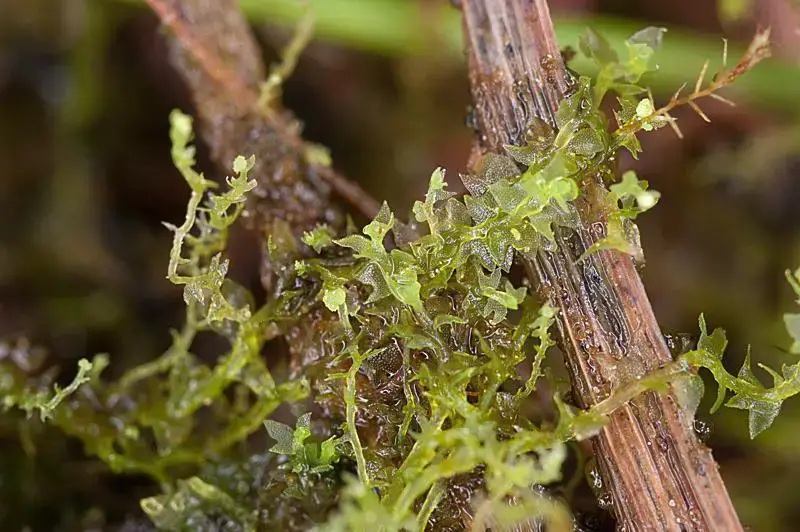

881022.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/881020.html
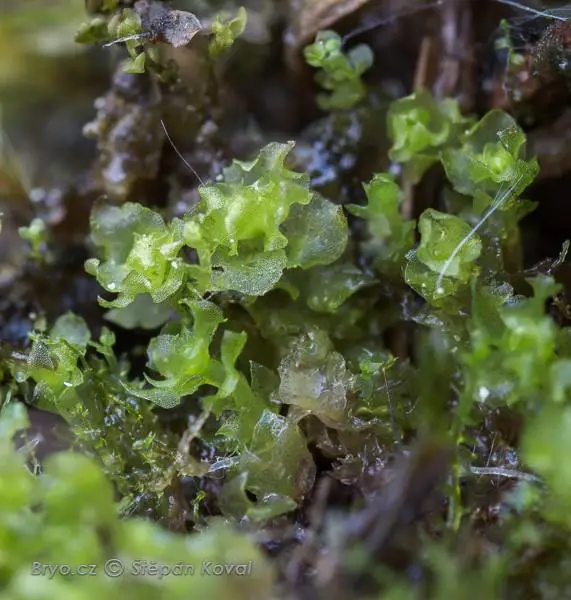

2979_Heterogemma_capitata_2016_05_10_9939.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=heterogemma_capitata&id=2979
Technical Table

75dcc57fa1ee7c459ec9b1e0aac2d566.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/especie/primula-capitata
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Jungermanniales |
| Family | Lophoziaceae |
| Genus | Lophozia |
| Species | capitata |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Bilobed, arranged in two rows |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, rocky outcrops, disturbed sites |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe, Asia) |
Conclusion
The Lophozia capitata (Hook.) Macoun moss, a member of the Lophoziaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its unique morphology, widespread distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, the Lophozia moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and importance of these often overlooked organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where every organism plays a vital role, how can we better appreciate and protect the unsung heroes like Lophozia capitata, ensuring their continued existence and contribution to the delicate balance of our ecosystems?