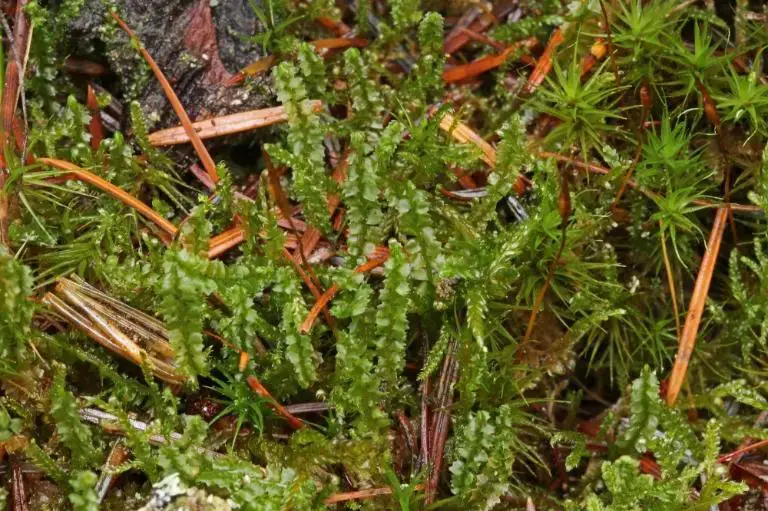

edcd447f-0fe4-46d1-9bac-afb3012e35fa_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/07939358-7572-4dc4-9725-afb3012e366e
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. moss stands out as a fascinating representative of the Anastrophyllaceae family. Often referred to simply as Lophozia, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn.
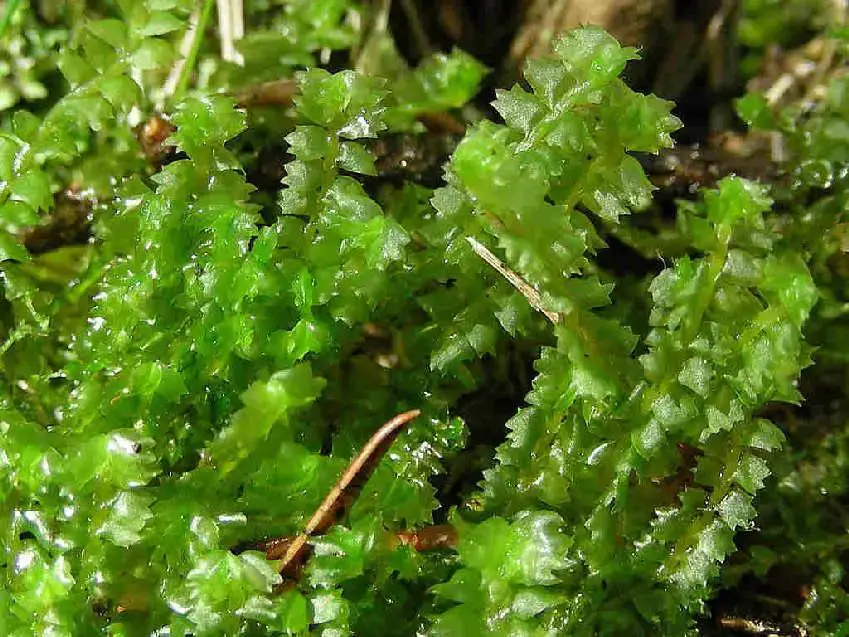

Barbilophozia_barbata_2.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Barbilophozia_barbata.html
, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest lineages of land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or patches on the ground or on decaying wood. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with leaves arranged in two rows along the stem. The leaves are deeply bilobed, giving the plant a distinctive appearance. This characteristic feature is what sets it apart from other varieties within the
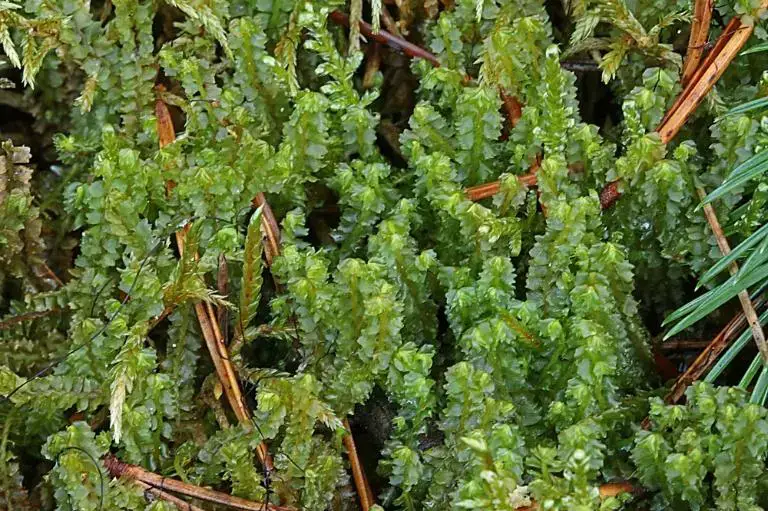

bd8ddcf7-8901-4f6e-96fc-afba0151e5da_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/b1730d06-b8b6-487b-8311-afba0151e652
Lophozia genus.
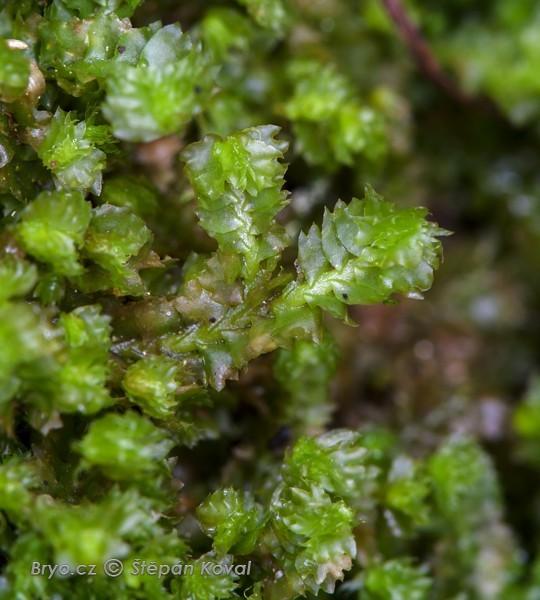

2046_Barbilophozia_barbata_2009_07_09_7304.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=en&gallery=barbilophozia_barbata&id=2046
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, including regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as coniferous and mixed forests, bogs, and damp rock crevices. Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. is often found growing in association with other bryophytes, forming intricate and diverse moss carpets.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.
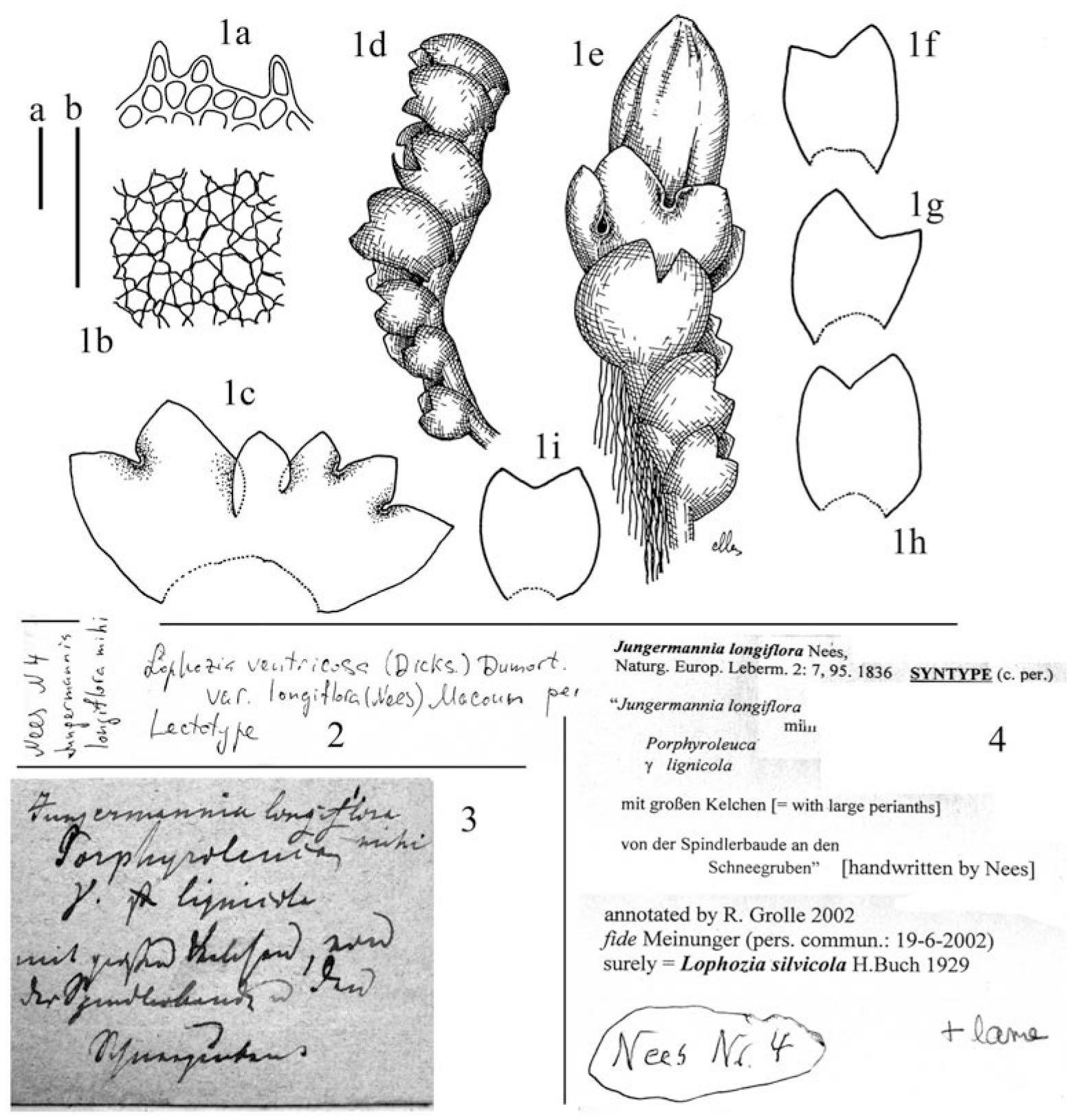
f01_635.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/Herzogia/volume-29/issue-2/heia.29.2.2016.635/Notes-on-iLophozia-i-VIII-The-Lectotypification-of-iLophozia-longiflora/10.13158/heia.29.2.2016.635.full
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth once moisture returns. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest in North America, researchers discovered that Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. played a crucial role in maintaining soil moisture and facilitating the establishment of seedlings. The moss’s dense mats created a microclimate that protected the delicate seedlings from desiccation, ensuring their survival and contributing to the overall biodiversity of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table

closeup-usnea-barbata-moss-growing-tree-branch-closeup-usnea-barbata-moss-growing-tree-branch-270348503.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/closeup-usnea-barbata-moss-growing-tree-branch-closeup-usnea-barbata-moss-growing-tree-branch-image270348503

barbilophozia_quadriloba.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/lophoziaceae/index.html
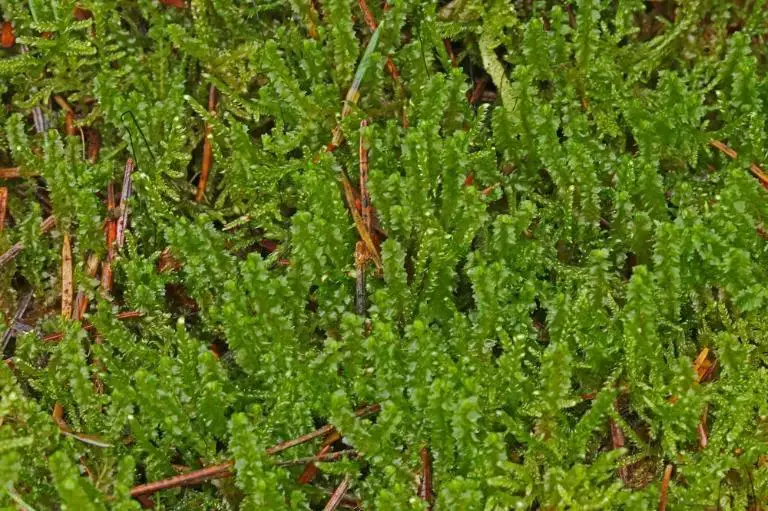

cad6cee4-311a-4a74-8554-afa1013e821a_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/dc8d866f-1b1e-4413-b6ed-afa1013e82c8
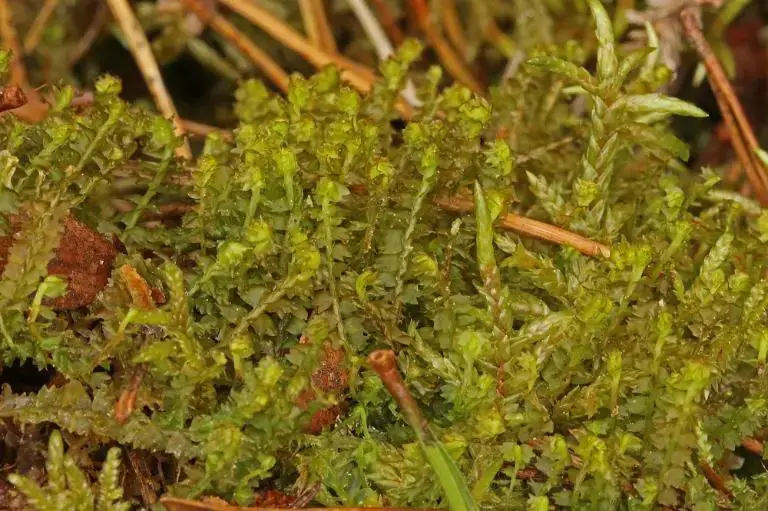

27a55615-6847-4b0d-be82-afff015c0d3b_medium.jpg from: https://arter.dk/observation/record-details/f5a318e9-a029-404a-a825-afff015c0dc9
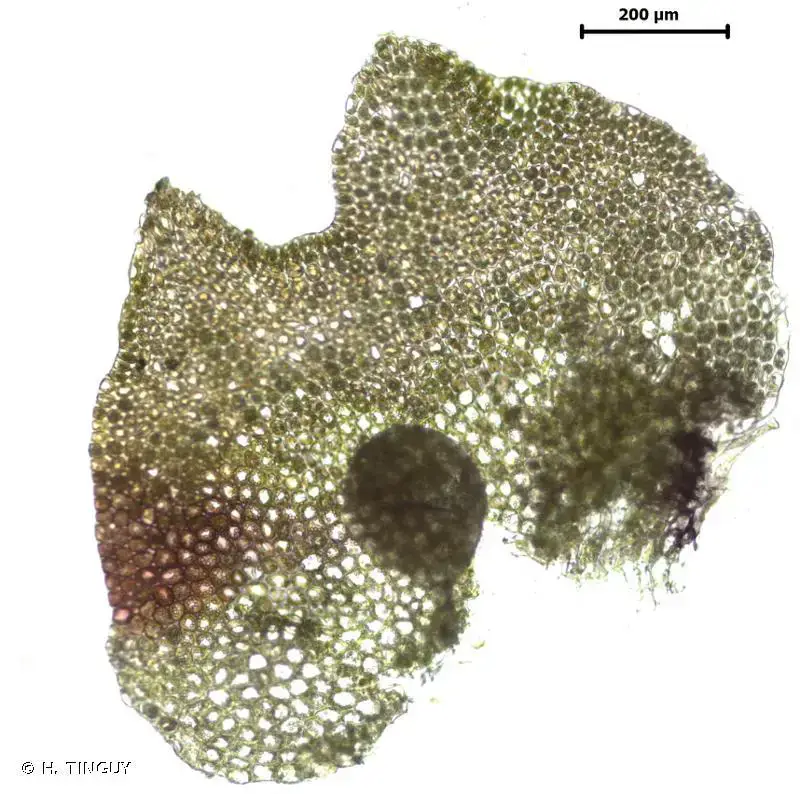
431864.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6352
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. |
| Family | Anastrophyllaceae |
| Common Name | Lophozia |
| Growth Form | Creeping moss, forming dense mats or patches |
| Leaf Arrangement | Leaves arranged in two rows along the stem |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply bilobed |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, bogs, rock crevices) |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
The Lophozia barbata var. biloba Schiffn. moss, a member of the Anastrophyllaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the ecosystems it inhabits is profound. From its unique morphology to its remarkable adaptations and ecological roles, this unassuming plant deserves our appreciation and continued study. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us, woven together by the contributions of even the smallest organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the seemingly insignificant, what other wonders might we uncover if we take the time to observe and appreciate the marvels of nature that lie at our feet?